**Accurate Answer:** Voltage drop occurs when electrical current flows through a conductor, causing a loss of voltage. This can affect the performance of electrical devices.
**** Voltage drop is a common issue in electrical circuits, impacting efficiency and functionality. It happens due to resistance in wires or connections, which consumes energy and reduces voltage. Understanding voltage drop is crucial for designing effective electrical systems. Proper wire sizing and connections minimize voltage drop, ensuring devices receive adequate power.
Electricians and engineers must consider voltage drop in their calculations to avoid potential problems. Regular maintenance and inspections also help in identifying and rectifying voltage drop issues. By addressing voltage drop, you can enhance the reliability and longevity of your electrical installations.
Introduction To Voltage Drop
Understanding voltage drop is crucial in electrical systems. It impacts the performance and safety of circuits. Let’s explore what voltage drop is and why it matters.
Basics Of Voltage Drop
Voltage drop occurs when electrical current flows through a conductor. As current moves, it loses voltage due to resistance. This loss is called voltage drop.
Several factors affect voltage drop:
- Conductor length
- Conductor material
- Current load
- Temperature
Longer conductors have higher resistance. Materials like copper have lower resistance. High current loads increase voltage drop. Temperature changes can affect resistance too.
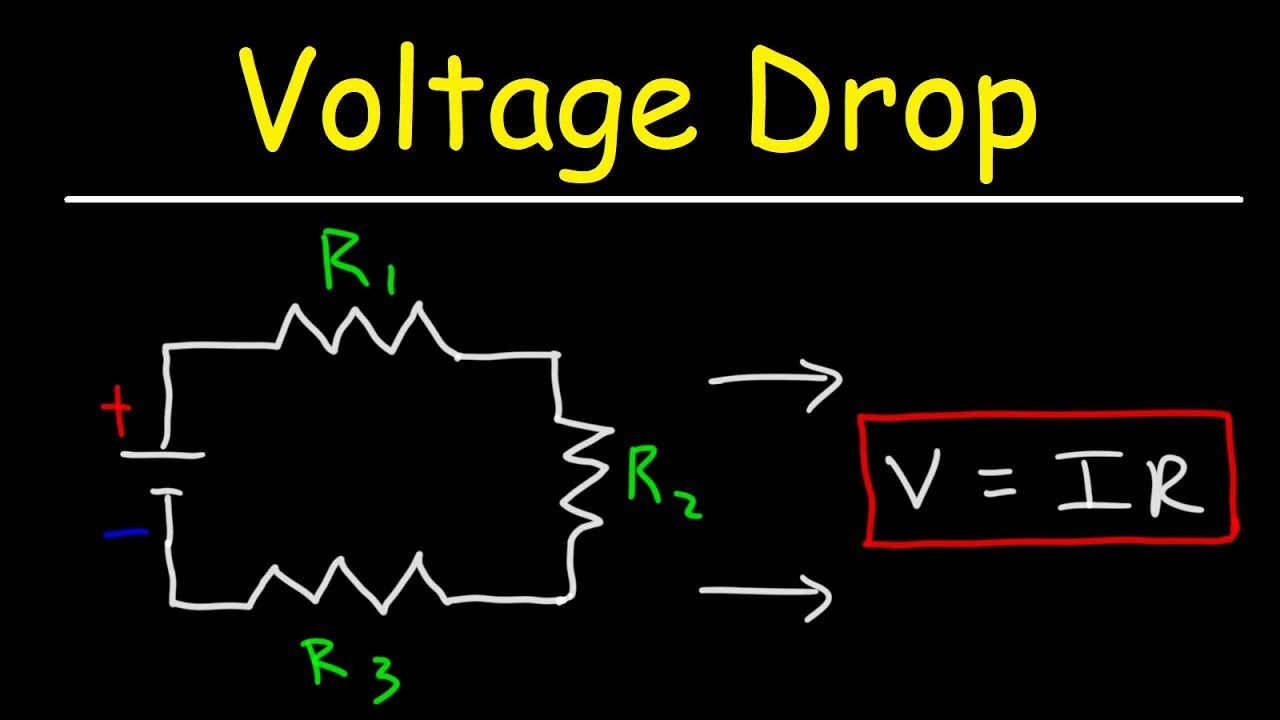
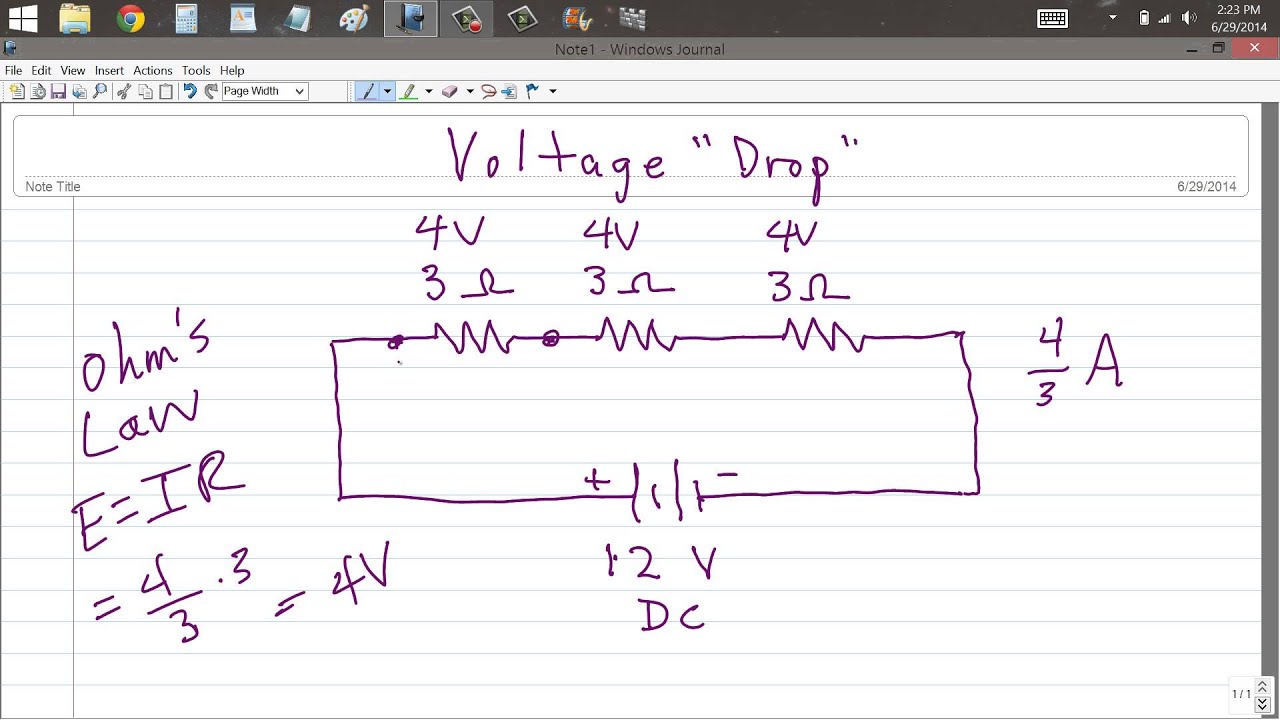
Use this simple formula to calculate voltage drop:
Voltage Drop (V) = Current (I) x Resistance (R)Importance Of Managing Voltage Drop
Managing voltage drop is essential for many reasons. It ensures the efficiency and safety of electrical systems.
Here are some key reasons to manage voltage drop:
- System Efficiency: Excessive voltage drop reduces efficiency. Devices may not receive adequate power.
- Safety: High voltage drop can cause overheating. This may lead to fires or equipment damage.
- Compliance: Electrical codes often set limits for voltage drop. Compliance is necessary for safety and legal reasons.
To manage voltage drop effectively, consider these practices:
- Use shorter conductors
- Choose low-resistance materials
- Minimize current load
- Monitor and adjust for temperature changes
Managing voltage drop ensures safe and efficient electrical systems. It helps maintain optimal performance and compliance with standards.
Causes Of Voltage Drop
Understanding the causes of voltage drop is crucial for maintaining an efficient electrical system. Voltage drop can lead to reduced performance and potential damage to your equipment. Let’s explore the main factors causing voltage drop.
Distance And Wire Length
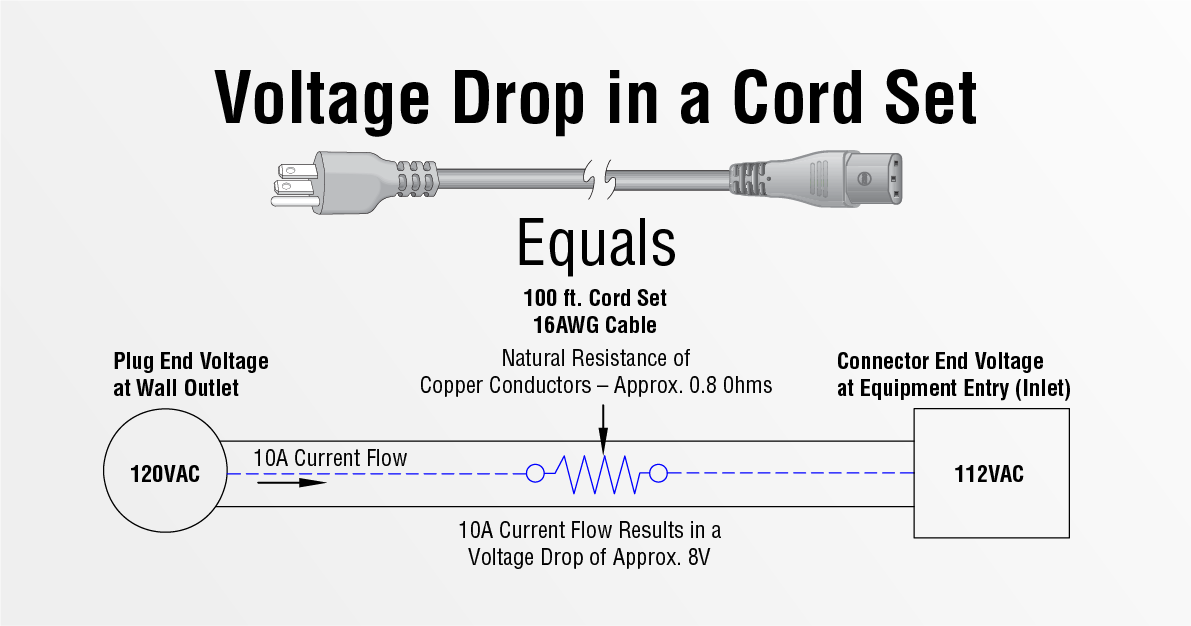
The length of the wire affects voltage drop significantly. Longer wires have higher resistance. This increased resistance reduces the voltage delivered to the load.
For example, a 100-foot wire will have more resistance than a 10-foot wire. The longer the distance, the greater the voltage drop.
| Wire Length (Feet) | Resistance (Ohms) |
|---|---|
| 10 | 0.1 |
| 100 | 1.0 |
| 1000 | 10.0 |
Wire Gauge And Resistance
The thickness or gauge of the wire also impacts voltage drop. Thinner wires have more resistance. Higher resistance leads to greater voltage drop.
Wire gauge is measured in American Wire Gauge (AWG). Lower AWG numbers indicate thicker wires. Thicker wires have less resistance.
- 12 AWG wire has less resistance than 16 AWG wire.
- Thicker wires are better for long distances.
Load And Current Draw
The amount of current drawn by the load affects voltage drop. Higher current draw leads to more voltage drop. This is due to increased resistance.
For example, a light bulb drawing 10 amps will cause more voltage drop than a bulb drawing 1 amp. Ensuring the load is within the wire’s capacity is crucial.
- Check the current rating of your wire.
- Ensure the load does not exceed this rating.
Avoid overloading circuits to prevent voltage drop and equipment damage.
Effects Of Voltage Drop
Voltage drop can cause serious problems. These problems can affect your equipment and energy efficiency. Understanding these effects helps you protect your systems.
Impact On Equipment
Voltage drop can damage your equipment. Motors, lights, and electronics may not work correctly. They may overheat or fail if voltage is too low.
Low voltage can reduce the lifespan of your devices. They have to work harder to perform the same tasks. This extra strain leads to faster wear and tear.
Here is a table summarizing the potential impacts:
| Equipment | Impact |
|---|---|
| Motors | Overheating, reduced efficiency |
| Lights | Dim lighting, flickering |
| Electronics | Malfunction, reduced lifespan |
Energy Efficiency Concerns
Voltage drop affects energy efficiency. Your system uses more power to do the same work. This increases your energy bills.
Here are some ways voltage drop impacts energy efficiency:
- Higher energy consumption due to increased load
- Reduced performance of electrical devices
- Increased operational costs
Reducing voltage drop can save energy. It helps you lower costs and improve system performance.
Credit: m.youtube.com
Calculating Voltage Drop
Understanding voltage drop is essential in electrical systems. It ensures efficient energy use and prevents equipment damage. Calculating voltage drop helps identify power loss in cables. This section will guide you through the process.
Voltage Drop Formulas
Voltage drop can be calculated using specific formulas. These formulas consider the length of the wire, current, and material type. Here are the commonly used formulas:
- Single-phase AC Circuit:
V_drop = (2 L I R) / 1000 - Three-phase AC Circuit:
V_drop = (√3 L I R) / 1000 - DC Circuit:
V_drop = (2 L I R) / 1000
Where:
- L: Length of the wire (in meters)
- I: Current (in amperes)
- R: Resistance (in ohms per meter)
Using these formulas, you can calculate the voltage drop for different circuits.
Using Online Calculators
Calculating voltage drop manually can be complex. Online calculators simplify the process. These tools require basic input like wire length, current, and material.
Here is a step-by-step guide to using an online voltage drop calculator:
- Visit a reliable voltage drop calculator website.
- Enter the wire length in meters.
- Input the current in amperes.
- Select the wire material (copper or aluminum).
- Click on the “Calculate” button.
The calculator will display the voltage drop instantly. This method is quick and accurate.
Preventing Voltage Drop
Voltage drop can cause many problems in electrical systems. Proper techniques can help avoid these issues. Learn how to prevent voltage drop by choosing the right wire gauge, minimizing distance, and using voltage regulators.
Choosing The Right Wire Gauge
Using the correct wire gauge is essential. Thicker wires offer less resistance. Less resistance means less voltage drop.
| Wire Gauge | Maximum Current (Amps) |
|---|---|
| 10 AWG | 30 |
| 12 AWG | 20 |
| 14 AWG | 15 |
Choose a thicker wire if your current is higher. This helps in reducing voltage drop.
Minimizing Distance
Longer wire runs increase resistance. More resistance leads to more voltage drop. Keeping wires short can help avoid this.
Organize your layout to reduce wire lengths. This can be done by placing power sources closer to the load.
Using Voltage Regulators
Voltage regulators keep voltage levels stable. They adjust the voltage to the desired level. This ensures that devices receive the correct voltage.
- Linear Regulators: Simple but less efficient
- Switching Regulators: More efficient and versatile
Using voltage regulators can significantly reduce the effects of voltage drop. They are especially useful in sensitive electronics.
Tools And Equipment
Understanding voltage drop in electrical circuits is crucial. The right tools and equipment simplify this task. This section explores essential tools for measuring and managing voltage drops.
Voltage Drop Meters
Voltage drop meters are vital for checking electrical circuits. These meters measure voltage across components. They help identify potential issues. Using a voltage drop meter is simple. Connect the probes to the circuit and read the display. Some advanced meters offer additional features. They can log data and provide detailed analysis.
- Accuracy: Voltage drop meters are highly accurate. They ensure precise readings.
- Ease of Use: These meters are user-friendly. Even beginners can use them effectively.
- Portability: Most voltage drop meters are portable. They are easy to carry and use on-site.
Wire Gauge Measurement Tools
Correct wire gauge is crucial to prevent excessive voltage drops. Wire gauge measurement tools help determine the wire size. These tools are essential for any electrical project. They ensure the wire meets the required specifications.
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Wire Gauge Ruler | A ruler with marked wire sizes. It is simple to use. |
| Digital Caliper | Measures wire diameter accurately. It offers precise readings. |
These tools ensure you use the correct wire size. They reduce the risk of voltage drops. Always verify wire size before starting any project. This step ensures safety and efficiency.
Real-world Applications
Voltage drop impacts various real-world applications. It affects how devices perform. Understanding voltage drop helps ensure efficient and safe electrical systems. Let’s explore some real-world applications.
Residential Wiring
Voltage drop in residential wiring is common. It can lead to dim lights, malfunctioning appliances, and other issues. Proper wiring helps reduce voltage drop. Here are some tips to minimize it:
- Use thicker wires for long distances.
- Avoid overloading circuits with too many devices.
- Ensure all connections are secure and tight.
Industrial Settings
In industrial settings, voltage drop can cause serious problems. Machinery may not operate correctly. Production lines may halt. Here are some ways to manage voltage drop in industrial environments:
- Use high-quality cables and conductors.
- Regularly inspect and maintain electrical equipment.
- Install voltage regulators and stabilizers.
Solar Power Systems
Solar power systems are sensitive to voltage drop. It reduces efficiency and energy output. To optimize solar power systems, consider the following:
- Use low-resistance wires for connections.
- Ensure the solar panels are properly aligned.
- Maintain clean and dust-free panels for maximum efficiency.
Understanding voltage drop is crucial in various applications. It ensures electrical systems operate efficiently and safely.
Maintenance And Inspection
Voltage drop can cause many electrical problems. Regular maintenance and inspection are necessary. This helps ensure that your electrical system works properly and safely.
Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups are essential for maintaining electrical systems. Schedule these checks at least once a year. During the check-up, look for any signs of wear and tear.
- Inspect wires for damage.
- Check connections for tightness.
- Measure voltage levels at different points.
Use a multimeter to measure voltage. Compare readings with standard values. Any significant differences may indicate problems.
Identifying Potential Issues
Identifying potential issues early can prevent major problems. Look out for these signs:
- Flickering lights: Indicates voltage instability.
- Warm outlets: May suggest overloaded circuits.
- Frequent breaker trips: Points to possible short circuits.
If you notice any of these signs, take action immediately. Conduct a thorough inspection. Use the table below to track your findings.
| Check | Findings | Action Taken |
|---|---|---|
| Wire Damage | None | None |
| Connection Tightness | Loose at breaker | Tightened connection |
| Voltage Levels | Normal | None |
Future Trends
Voltage drop can impact the efficiency of electrical systems. As technology evolves, the future trends in managing voltage drop are promising. These trends focus on advancements in materials and the integration of smart grid technology.
Advancements In Materials
New materials are being developed to reduce voltage drop. These materials have better conductivity and lower resistance. Using these materials can significantly improve energy efficiency.
Copper and aluminum have been the standard conductors. Now, researchers are exploring graphene and carbon nanotubes. These new materials have higher conductivity than traditional metals.
Graphene is a single layer of carbon atoms. It is incredibly strong and highly conductive. Graphene could revolutionize electrical systems by reducing voltage drop.
Carbon nanotubes are tiny cylindrical structures. They are also made of carbon atoms. These nanotubes offer excellent conductivity and flexibility. They could be used in various electrical applications to enhance performance.
Smart Grid Technology
Smart grid technology is another future trend. It aims to modernize the electrical grid. A smart grid uses digital communication to detect and react to changes in electricity usage.
This technology helps in managing voltage drop more effectively. Smart grids can monitor and control the flow of electricity. They can adjust the supply based on demand, reducing voltage drop.
Smart meters are a key component of smart grids. They provide real-time data on electricity usage. This data helps in optimizing the distribution of electricity.
Advanced sensors are used to detect voltage drops and other issues. These sensors send alerts to the control center. The control center can then take immediate action to resolve the problem.
Smart grid technology also supports renewable energy sources. Solar panels and wind turbines can be integrated into the grid. This integration helps in balancing the supply and demand of electricity.
Overall, smart grid technology offers a more efficient and reliable electrical system. It can greatly reduce voltage drop, leading to energy savings and improved performance.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Credit: www.interpower.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Voltage Drop?
Voltage drop is the reduction in electrical potential along a circuit. It occurs due to resistance in the conductors.
Why Does Voltage Drop Happen?
Voltage drop happens because of resistance in the electrical wires. Longer wires and higher currents increase resistance.
How To Calculate Voltage Drop?
To calculate voltage drop, use the formula V = I x R. Where V is voltage, I is current, and R is resistance.
Can Voltage Drop Cause Problems?
Yes, voltage drop can cause inefficient operation of electrical devices. It may lead to overheating and energy loss.
Conclusion
Understanding voltage drop is crucial for efficient electrical systems. It helps prevent potential issues and maintains safety. Regular checks and proper calculations ensure optimal performance. Stay informed and keep your electrical systems running smoothly. Remember, a well-maintained system saves time, money, and energy.
Implement these practices and enjoy a more reliable setup.




I truly appreciate this post. I have been looking everywhere for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You have made my day! Thx again!