An electrical installer sets up and maintains electrical systems in various settings. They ensure safety and compliance with regulations.
Electrical installers play a crucial role in residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. They handle wiring, lighting, and electrical equipment installations. Their expertise ensures that electrical systems function efficiently and safely. Proper installation prevents hazards like fires and electrical shocks. Electrical installers must stay updated with the latest codes and technologies.
Their work involves reading blueprints, troubleshooting issues, and using various tools. Excellent problem-solving skills and attention to detail are essential for this job. With growing reliance on electricity, the demand for skilled electrical installers remains high. This career offers job stability and opportunities for advancement.
Introduction To Electrical Installation
Electrical installation is essential in our daily lives. It involves setting up the electrical systems in homes and buildings. This task ensures that we get safe and reliable power.
Role Of An Electrical Installer
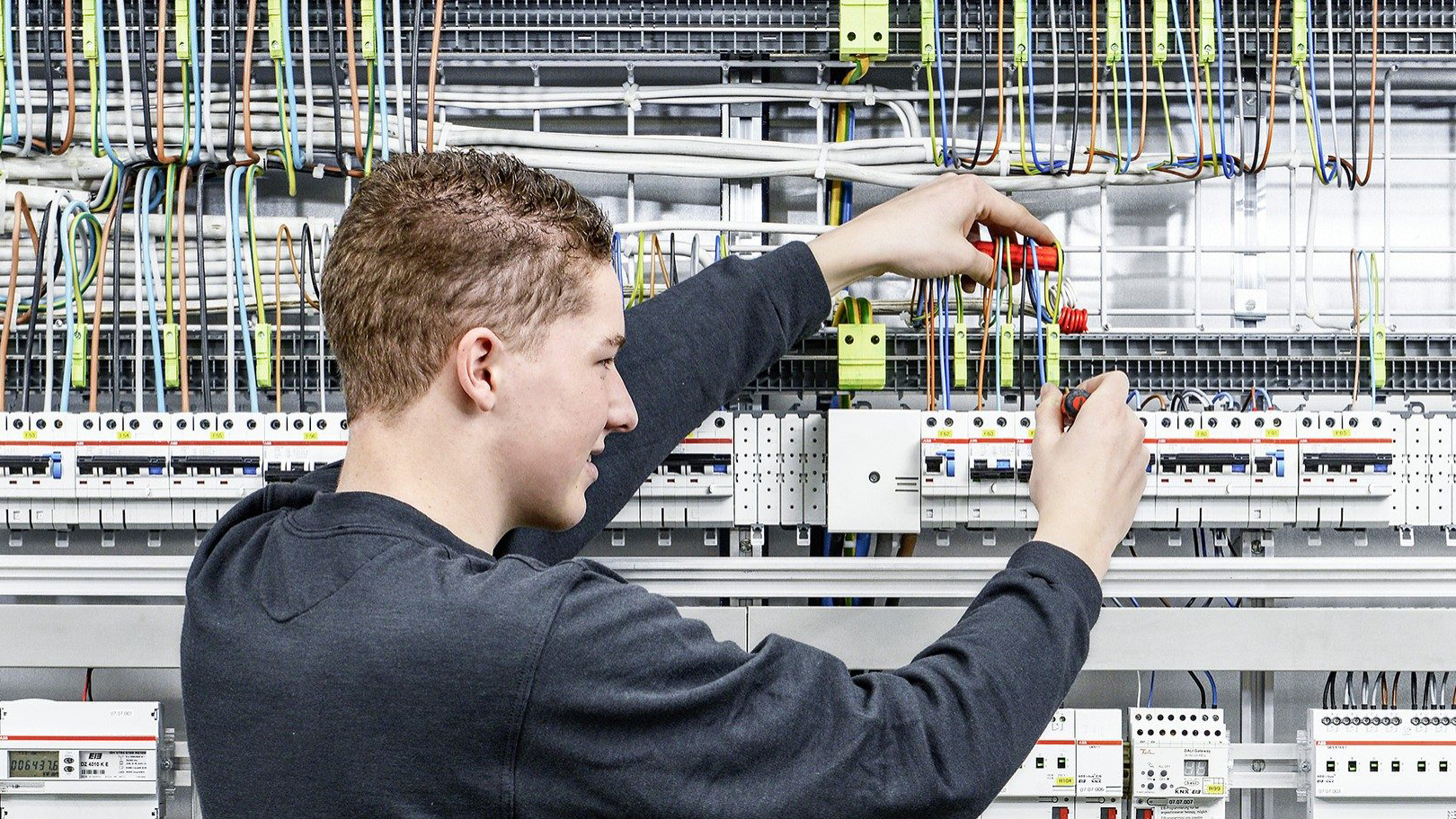
An electrical installer plays a key role in this process. They set up, maintain, and repair electrical systems. Their job ensures that lights, outlets, and appliances work. Without them, our homes and workplaces would lack power.
They read blueprints and technical diagrams. They know the right wires and tools to use. They connect wires to circuit breakers, transformers, and other components. They test electrical systems to ensure they work safely.
They also follow local building regulations. This ensures all electrical work is up to code. Here are some tasks they perform:
- Reading and interpreting blueprints
- Installing wiring and lighting systems
- Maintaining electrical equipment
- Ensuring compliance with safety standards
Importance Of Safe Wiring
Safe wiring is crucial in electrical installation. It prevents electrical fires and shocks. It ensures the safety of people and property.
Using the right materials is important. Wires must be of the correct size and type. Proper insulation is necessary to avoid short circuits. Safe wiring practices also include proper grounding.
Regular inspections help maintain safe wiring. An electrical installer checks for wear and tear. They replace damaged wires and components. This keeps the electrical system in good working order.
| Importance | Details |
|---|---|
| Prevents Fires | Reduces the risk of electrical fires. |
| Prevents Shocks | Protects people from electric shocks. |
| Compliance | Ensures compliance with safety codes. |
Basic Electrical Concepts
Understanding basic electrical concepts is crucial for any electrical installer. These concepts form the foundation of all electrical work. They help in troubleshooting and ensuring safety during installations.
Voltage, Current, And Resistance
Voltage, current, and resistance are the three core components of electricity. They work together to power our homes and devices.
- Voltage (V) is the potential difference between two points. It’s like the pressure pushing electrical charges through a conductor.
- Current (I) is the flow of electrical charge. Measured in amperes (A), it represents how fast the electrons are moving.
- Resistance (R) opposes the flow of current. Measured in ohms (Ω), it determines how much the material resists the electric flow.
These three elements are interrelated and crucial in understanding circuits.
Ohm’s Law And Circuit Basics
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental principle in electricity. It states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points.
The formula for Ohm’s Law is:
V = I RThis means:
- Voltage (V) = Current (I) Resistance (R)
- Current (I) = Voltage (V) / Resistance (R)
- Resistance (R) = Voltage (V) / Current (I)
Understanding these basics helps in designing and troubleshooting circuits. It ensures efficient and safe electrical installations.
| Component | Symbol | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage | V | Volts |
| Current | I | Amperes |
| Resistance | R | Ohms |
Tools Of The Trade
Electrical installers rely on a specific set of tools to perform their tasks efficiently and safely. These tools help in ensuring that electrical systems are installed correctly and function properly. Below, we explore some essential tools and safety gear that every electrical installer should have.
Essential Tools For Installers
Every electrical installer needs a set of essential tools. These tools make the job easier and ensure high-quality work.
- Multimeter: This device measures voltage, current, and resistance.
- Wire Strippers: These are used to strip the insulation from electrical wires.
- Pliers: Pliers help in gripping, twisting, bending, and cutting wires.
- Screwdrivers: Different types of screwdrivers are needed for various screws.
- Fish Tape: Fish tape helps in pulling wires through conduits.
- Cable Cutters: These are essential for cutting thick cables.
- Voltage Tester: This tool checks if a wire is live.
Safety Gear And Equipment
Safety is paramount for electrical installers. Using proper safety gear can prevent accidents and injuries.
- Insulated Gloves: These gloves protect against electric shocks.
- Safety Glasses: These protect the eyes from debris and sparks.
- Hard Hats: Hard hats protect the head from falling objects.
- Ear Protection: Ear protection is necessary in noisy environments.
- Fire Extinguisher: An extinguisher is crucial for tackling electrical fires.
- First Aid Kit: A first aid kit is essential for treating minor injuries.
By using these tools and safety gear, electrical installers can perform their tasks efficiently and safely.

Credit: www.ukcareersfair.com
Wiring Basics
Understanding wiring basics is essential for any electrical installer. This knowledge ensures safe and efficient electrical systems. We will explore the types of wires and cables, and the importance of color coding and labels.
Types Of Wires And Cables
Different projects require different wires and cables. Selecting the right type is crucial for safety and functionality.
| Type | Use |
|---|---|
| Non-Metallic (NM) Cable | Residential wiring |
| Armored Cable (AC) | Commercial buildings |
| Underground Feeder (UF) Cable | Outdoor wiring |
Color Coding And Labels
Color coding helps identify wires quickly. Different colors indicate different wire functions.
- Black: Hot wire, carries current.
- White: Neutral wire, completes the circuit.
- Green or Bare: Ground wire, safety feature.
Labels provide additional information. They indicate wire type, size, and other important details.
- Check the label for wire gauge.
- Look for insulation type.
- Ensure the wire is rated for the intended use.
Common Wiring Techniques
Understanding common wiring techniques is essential for every electrical installer. These techniques ensure safe and efficient electrical connections. Let’s explore some key methods used in the field.
Series And Parallel Circuits
Series and parallel circuits are fundamental in wiring. In a series circuit, components are connected end-to-end. The current flows through each component in turn. This means a break affects the entire circuit.
In a parallel circuit, components are connected across the same voltage source. The current divides among the paths. A break in one path does not affect the others. This makes parallel circuits more reliable for certain applications.
| Type of Circuit | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Series Circuit | Single path for current. One break stops all current. |
| Parallel Circuit | Multiple paths for current. One break does not stop all current. |
Splicing And Connecting Wires
Proper splicing and connecting wires is crucial for safe electrical systems. Splicing involves joining two or more wires together. This can be done using wire nuts, crimp connectors, or soldering.
Here are some common wire splicing techniques:
- Twist-on Wire Connectors: Also known as wire nuts, these are simple to use.
- Crimp Connectors: Provide a secure and permanent connection.
- Soldering: Offers a strong and reliable bond.
Always ensure connections are tight and properly insulated. This prevents short circuits and reduces the risk of fire.
Safety Practices
Safety practices are crucial for any electrical installer. They help prevent accidents and ensure smooth operations. Following proper safety protocols keeps everyone safe.
Identifying Hazards
Identifying hazards is the first step in safety. Look for exposed wires. Check for damaged insulation. Be aware of wet areas. Wet surfaces can conduct electricity. Use proper lighting to spot dangers. Always inspect tools before use. Ensure they are in good condition.
Avoid working in dark areas. Poor visibility can hide hazards. Make sure all circuit breakers are off. Double-check before starting any work. Keep a safe distance from live wires. Mark hazardous areas clearly.
Preventing Electrical Shock
Preventing electrical shock is vital. Always wear protective gear. Use insulated gloves and boots. Never touch electrical devices with wet hands. Keep your workspace dry. Use proper tools designed for electrical work. Never use damaged tools.
Follow a safety checklist. Ensure all safety measures are in place. Disconnect power before starting any job. Test the circuit with a voltage tester. Make sure it is not live. Use Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs). They cut off power quickly. This prevents shocks.
Stay alert and focused. Avoid distractions while working. Regularly attend safety training. Stay updated on best practices. Protect yourself and others. Follow these simple steps and stay safe.
Troubleshooting And Repairs
Electrical installers often face challenges in troubleshooting and repairing systems. Diagnosing common issues and repairing faulty wiring are essential skills. This guide provides insights into solving these problems effectively.
Diagnosing Common Issues
Diagnosing issues involves a systematic approach. Common problems include:
- Tripped circuit breakers
- Blown fuses
- Faulty outlets
- Lighting problems
Start with the simplest checks. Verify if the circuit breaker is tripped. Then, inspect fuses for any signs of damage.
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Tripped Breaker | Overload | Reduce load, reset breaker |
| Blown Fuse | Short Circuit | Replace fuse, check wiring |
| Faulty Outlet | Loose Connections | Tighten connections |
| Lighting Issues | Burnt Bulb | Replace bulb |
Repairing Faulty Wiring
Repairing wiring requires caution and precision. Follow these steps:
- Turn off the power supply.
- Inspect the wiring for visible damage.
- Use a multimeter to check for continuity.
- Replace or repair damaged wires.
- Secure all connections tightly.
- Restore power and test the system.
Always ensure safety during repairs. Wearing protective gear and using insulated tools is crucial.

Credit: www.meritize.com
Advanced Wiring Projects
Advanced wiring projects require skill and precision. These projects go beyond basic electrical tasks. They involve complex systems and ensure the smooth running of your home. Let’s dive into two key areas: installing circuit breakers and home automation systems.
Installing Circuit Breakers
Installing circuit breakers is a critical task. Circuit breakers protect your home from electrical overloads. Here’s a simple guide to installing them:
- Turn off the main power supply.
- Remove the panel cover.
- Identify the empty slot for the new breaker.
- Insert the new circuit breaker into the slot.
- Connect the circuit wire to the breaker.
- Secure the breaker and replace the panel cover.
- Turn on the main power supply.
Ensure all connections are tight and secure. Proper installation prevents electrical hazards. Always follow safety protocols.
Home Automation Systems
Home automation systems bring convenience and efficiency. These systems control lighting, heating, and security. Here’s how to get started:
- Choose a home automation platform.
- Install the central hub.
- Connect smart devices like lights and thermostats.
- Configure settings using the platform’s app.
- Test each device for proper operation.
Smart home devices are often wireless. They communicate through Wi-Fi or Bluetooth. This makes installation easier and less invasive.
For advanced wiring projects, always consult a professional electrician. They ensure safety and compliance with local codes.
Staying Updated
Electrical installers must stay updated to excel in their field. This helps them provide the best service and ensures safety. They need to keep up with new technologies and continue their education. This section explores the importance of staying updated.
Continuing Education
Continuing education is vital for electrical installers. It helps them learn new skills and understand updated regulations. Many institutions offer courses for electricians. These courses cover new techniques and safety measures.
- Online courses for flexible learning
- Workshops for hands-on experience
- Certification programs for advanced skills
Taking these courses regularly keeps electricians knowledgeable. It also ensures they meet industry standards and regulations. Continuing education is a key part of an electrician’s career.
New Technologies In Electrical Installation
New technologies are changing the electrical installation field. Electricians must learn about these advancements to stay relevant. Some of these technologies include:
- Smart home systems
- Energy-efficient lighting
- Renewable energy sources
Smart home systems are becoming popular. Electricians need to know how to install and troubleshoot them. Energy-efficient lighting reduces energy use and costs. Electricians should understand these systems to provide better solutions.
Renewable energy sources like solar panels are also on the rise. Electricians need to learn how to install and maintain these systems. Staying updated with new technologies ensures electricians can offer the best services to their clients.
Credit: www.schindler-berufsbildung.ch
Frequently Asked Questions
What Does An Electrical Installer Do?
An electrical installer installs, maintains, and repairs electrical systems. They work in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. They ensure electrical systems are safe and up to code.
How To Become An Electrical Installer?
To become an electrical installer, you need a high school diploma. Then, complete an apprenticeship or technical school program. Obtain necessary licenses and certifications.
What Skills Do Electrical Installers Need?
Electrical installers need strong problem-solving skills. They must understand blueprints and electrical codes. Physical stamina and manual dexterity are also important.
How Much Do Electrical Installers Earn?
Electrical installers’ earnings vary based on experience and location. On average, they earn between $40,000 and $70,000 annually. Specialized skills can increase earnings.
Conclusion
Choosing the right electrical installer ensures safety and efficiency. Always verify credentials and experience before hiring. A skilled installer can prevent costly mistakes. Invest in quality work for long-term peace of mind. Trust a professional to handle your electrical needs safely and effectively.




