Electrician math involves calculations essential for electrical work. These include Ohm’s Law, voltage, current, resistance, and power formulas.
Electrician math is crucial for ensuring safe and efficient electrical installations. Electricians need to perform accurate calculations to determine the correct wire sizes, circuit loads, and component ratings. Mastery of basic math skills, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, is necessary.
Additionally, electricians must understand algebra and geometry to solve complex problems. They use formulas like Ohm’s Law to calculate voltage, current, and resistance. Accurate math skills help prevent electrical failures and hazards, ensuring systems operate smoothly. Electricians also need to stay updated on the latest codes and standards, which often involve mathematical considerations.
Introduction To Electrician Math
Understanding Electrician Math is crucial for anyone in the electrical field. This specialized math helps electricians perform their job safely and efficiently. It combines basic arithmetic, algebra, and geometry to solve electrical problems.
Why Math Matters
Math is essential for electricians for several reasons. First, it ensures accurate measurements. Electricians need to measure lengths, angles, and distances precisely. Second, it helps in calculating electrical loads. Knowing how much power is needed prevents overloading circuits. Third, math aids in understanding electrical codes. These codes ensure safety and compliance with standards.
Real-world Applications
Electrician Math is used daily in various tasks. For instance, calculating the right wire size is crucial. Using the wrong wire size can cause overheating and fires. Another example is determining the voltage drop. This ensures that devices receive the correct voltage. Electricians also use math to design circuits. This involves calculating the total resistance and current flow.
| Task | Math Involved |
|---|---|
| Measuring Wire Length | Addition and Subtraction |
| Calculating Electrical Load | Multiplication |
| Determining Voltage Drop | Division |
| Designing Circuits | Algebra |
Understanding these tasks makes an electrician’s job easier and safer. Mastering Electrician Math leads to greater efficiency and fewer errors.

Credit: www.iec-cincy.com
Basic Arithmetic Skills
Electricians need strong basic arithmetic skills. Simple math helps them with everyday tasks. They use math for measuring and calculating. This ensures safety and accuracy in their work.
Addition And Subtraction
Electricians often use addition and subtraction. They calculate total lengths of wire. For example, if you have two wires of 10 meters each, the total length is 20 meters.
Subtraction helps them figure out remaining lengths. If you start with 20 meters and use 8 meters, you have 12 meters left.
Example:
- 10 meters + 10 meters = 20 meters
- 20 meters – 8 meters = 12 meters
Multiplication And Division
Multiplication helps electricians with larger quantities. If one wire costs $2, then 10 wires cost $20.
Division is essential for even distribution. If you have 100 meters of wire for 5 rooms, each room gets 20 meters.
Example:
- $2 per wire × 10 wires = $20
- 100 meters ÷ 5 rooms = 20 meters per room
Understanding Fractions And Decimals
Electricians use math every day. Understanding fractions and decimals is crucial. These skills help solve electrical problems. Knowing these basics can make your job easier and safer.
Converting Fractions
Fractions show a part of a whole. You often see fractions in measurements. For example, a wire might be 3/4 inch thick.
- To convert a fraction to a decimal, divide the top number by the bottom number.
- For example, 3/4 becomes 0.75.
Below is a simple conversion table:
| Fraction | Decimal |
|---|---|
| 1/2 | 0.5 |
| 1/4 | 0.25 |
| 3/4 | 0.75 |
Working With Decimals
Decimals are another way to show parts of a whole. They are often used in electrical work.
- For example, a voltage might be 12.5 volts.
- To add or subtract decimals, align the decimal points first.
- For example, 12.5 + 3.25 = 15.75.
Decimals can make calculations faster and more accurate.
Mastering Algebra
Algebra is a vital skill for electricians. Understanding algebra helps them solve complex problems. It is essential for electrical calculations and circuit design. Let’s explore key algebra concepts that electricians need to master.
Solving Equations
Electricians often solve equations to find unknown values. This skill is crucial for tasks like determining resistance or current. Let’s dive into some examples:
V = IR
If V = 12 volts and I = 2 amps, find R.
12 = 2R
R = 12 / 2
R = 6 ohms
In this example, solving the equation gives the resistance value. Electricians use such calculations daily.
Using Formulas
Formulas are essential tools for electricians. They help calculate various electrical parameters. Here are some important formulas:
- Ohm’s Law: V = IR
- Power Formula: P = VI
- Energy Formula: E = Pt
Let’s see a practical example using the power formula:
P = VI
If V = 120 volts and I = 10 amps, find P.
P = 120 10
P = 1200 watts
Using these formulas, electricians can determine power, resistance, and energy. This knowledge ensures safe and efficient electrical work.
Geometry In Electrical Work
Electricians use geometry daily in their work. Understanding shapes, angles, and distances helps them plan and install electrical systems accurately. This knowledge ensures safety and efficiency in every project.
Shapes And Angles
Electricians often deal with various shapes and angles. They need to measure and cut materials to fit specific spaces. For example, they use right angles to install outlets and switches.
- Right angles for outlets and switches.
- Triangles for cable runs.
- Circles for junction boxes.
Using the correct angles ensures that electrical components fit properly. This prevents safety hazards and ensures the system works efficiently.
Measuring Distances
Measuring distances accurately is essential for electricians. They use tools like tape measures and rulers to ensure precision. For instance, they measure the distance between outlets to meet code requirements.
| Tool | Use |
|---|---|
| Tape Measure | Measure distances between outlets and fixtures. |
| Ruler | Ensure straight lines for wiring. |
Accurate measurements ensure that wires are the correct length. This prevents excess wire, which can be dangerous and wasteful.

Credit: electacourse.com
Trigonometry For Electricians
Understanding trigonometry is crucial for electricians. It helps them make accurate calculations and ensures safety. This section covers the essential trigonometric functions: sine, cosine, and tangent.
Sine, Cosine, And Tangent
Electricians use sine, cosine, and tangent to calculate angles and lengths. These functions help solve many electrical problems.
- Sine (sin) is the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse in a right triangle.
- Cosine (cos) is the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse.
- Tangent (tan) is the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side.
Practical Examples
Here are some practical examples where electricians use these trigonometric functions:
| Scenario | Function Used | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Determining cable length | Sine | If the opposite side is 5m and the hypotenuse is 10m, sin(θ) = 0.5. |
| Finding the height of a pole | Cosine | If the adjacent side is 8m and the hypotenuse is 10m, cos(θ) = 0.8. |
| Calculating slope of a roof | Tangent | If the opposite side is 3m and the adjacent side is 4m, tan(θ) = 0.75. |
These examples show how trigonometry helps electricians in various tasks. Knowing these functions ensures accuracy and efficiency.
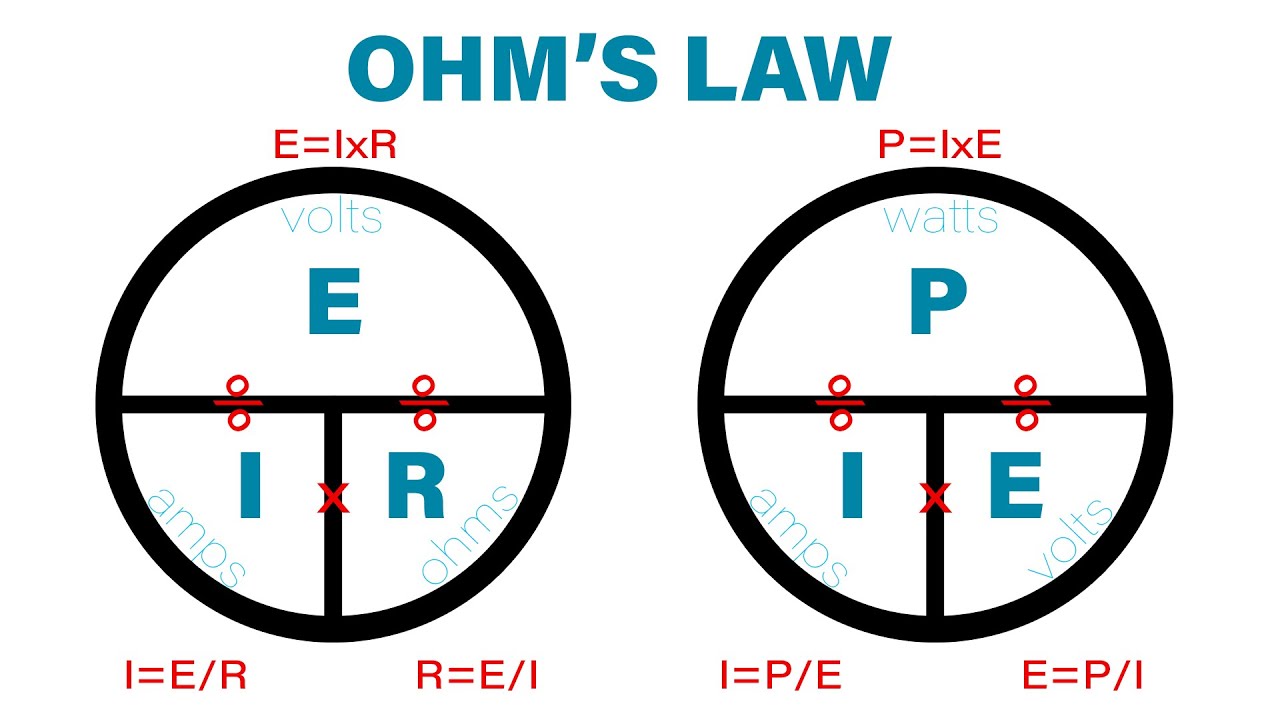
Ohm’s Law And Electrical Calculations
Electricians rely on Ohm’s Law for accurate electrical calculations. This law helps in understanding the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance. Mastering Ohm’s Law ensures safe and efficient electrical work.
Voltage, Current, And Resistance
Ohm’s Law is simple yet powerful: V = I R. Here, V stands for voltage, I represents current, and R is resistance. Understanding these terms is crucial for electricians.
Voltage is the potential difference between two points in a circuit. It is measured in volts (V).
Current is the flow of electric charge. It is measured in amperes (A).
Resistance opposes the flow of current. It is measured in ohms (Ω).
| Term | Symbol | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage | V | Volts (V) |
| Current | I | Amperes (A) |
| Resistance | R | Ohms (Ω) |
Power Calculations
Power in an electrical circuit is calculated using the formula: P = V I. Here, P stands for power, V is voltage, and I represents current. Power is measured in watts (W).
To determine the power, follow these steps:
- Measure the voltage (V) across the component.
- Measure the current (I) flowing through the component.
- Multiply the voltage (V) by the current (I) to get the power (P).
For example, if the voltage is 12V and the current is 2A, the power is:
P = V I
P = 12V 2A
P = 24WUnderstanding these calculations ensures electricians work safely and efficiently. Mastering Ohm’s Law and electrical calculations is essential for every electrician.

Credit: m.youtube.com
Tips And Tools For Success
Electrician math is vital for success in the electrical industry. Mastering it can lead to accurate and safe electrical work. This section provides tips and tools to excel in electrician math.
Useful Calculators
Calculators are essential for electricians. They help with complex calculations quickly and accurately. Here are some useful calculators:
- Ohm’s Law Calculator: Computes voltage, current, resistance, and power.
- Voltage Drop Calculator: Determines voltage drop in a circuit.
- Load Calculator: Calculates electrical load for circuits.
- Conduit Fill Calculator: Helps in determining conduit fill capacity.
Study Resources
Having the right study resources can make a big difference. These resources can enhance your electrician math skills:
- Textbooks: Books like “Electricity and Basic Electronics” are great.
- Online Courses: Websites like Khan Academy offer free courses.
- Practice Worksheets: Printable worksheets for daily practice.
- Tutorial Videos: YouTube channels for visual learning.
Below is a table of online courses and their features:
| Course | Platform | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Electrician U | Udemy | Video tutorials, quizzes, certification |
| Electrician Math | Coursera | Interactive lessons, practice problems |
| Basic Electrical Engineering | edX | Expert instructors, downloadable resources |
Frequently Asked Questions
What Math Do Electricians Use?
Electricians use basic arithmetic, algebra, and geometry. They calculate voltage, current, and resistance. Math helps in ensuring safe and efficient electrical systems.
Why Is Math Important For Electricians?
Math ensures precise measurements and calculations. It helps electricians plan and install electrical systems safely. Accurate math reduces risks and improves efficiency.
How Do Electricians Calculate Voltage Drop?
Electricians use Ohm’s Law to calculate voltage drop. They consider wire length, gauge, and current. Accurate calculations prevent electrical issues and ensure safety.
Do Electricians Need To Know Algebra?
Yes, electricians often use algebra. Algebra helps in solving equations related to electrical circuits. It’s essential for understanding and applying electrical concepts.
Conclusion
Mastering electrician math is essential for accuracy and safety in the field. It ensures proper installations and efficient troubleshooting. By understanding basic math concepts, electricians can enhance their skills and confidence. Keep practicing these calculations to excel in your career and provide top-notch service to your clients.