Electricity is the flow of electrical power or charge. It is a basic part of nature and essential for modern living.
Understanding electricity requires a grasp of its properties and how it influences our world. Life without electricity would be vastly different. It powers our homes, runs our appliances, and drives technological innovation. Deeply intertwined with the physics of electrical charge and current, electricity operates on laws that scientists like Faraday and Ohm first detailed.
Due to its importance, electricity generation and distribution are critical areas in engineering, with a focus on sustainability and efficiency. From lighting our rooms to connecting us through phones and the internet, electricity is the unseen force that energizes our day-to-day life. Ensuring that this power is harnessed and utilized effectively remains a top priority in contemporary society. As a cornerstone of development and progress, electricity supports industries, healthcare systems, and educational infrastructures, underscoring its integral role in advancing human civilization.
The Current Flow: Electricity Basics
Electricity powers our world in amazing ways. It brightens our homes and runs our gadgets. To understand how, let’s dive into electricity basics.
Fundamental ConceptsFundamental Concepts
Electricity is the flow of electrical power or charge. It’s both a basic part of nature and one of the most used forms of energy.
- Current is the movement of electric charge.
- Voltage is the force that drives current through a conductor.
- Resistance is what slows current down.
Conductors Vs Insulators
| Conductors | Insulators |
|---|---|
| Materials that let electricity flow through them | Materials that resist electricity flow |
| Examples: Copper, Aluminum | Examples: Rubber, Glass |
Historic Sparks: The Discovery Of Electricity
The tale of electricity is a journey of wonder and brilliance. It has lit the path of human progress for centuries. From mystical forces to a household necessity, uncover the electric tale that changed the world.
Early Experiments
Electricity was once thought to be merely a curious trick of nature. The ancient Greeks found that rubbing amber attracted small objects. This was the start of our electric quest.
- 1600s: William Gilbert coins the term ‘electricus’.
- 1700s: Experiments with static electricity ignite interest.
- Benjamin Franklin: His kite experiment links lightning to electricity.
Key Figures And Breakthroughs
Electricity’s story is a tapestry woven by brilliant minds across decades.
| Scientist | Discovery | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Alessandro Volta | Invents the battery | 1800 |
| Michael Faraday | Unearths electromagnetic induction | 1831 |
| James Clerk Maxwell | Develops electromagnetic theory | 1873 |
| Thomas Edison | Creates the electric light bulb | 1879 |
| Nikola Tesla | Champions alternating current (AC) | 1888 |
This electric league of pioneers built the foundation of today’s electric world. They turned the mysterious into the essential, powering lives for generations to come.
Volts And Jolts: Understanding Voltage And Current
Welcome to “Volts and Jolts: Understanding Voltage and Current”, a journey into the electric world. Electricity is everywhere. It powers our homes, gadgets, and machines. To grasp its essence, one must understand voltage and current. These forces flow through wires like water in pipes, bringing energy to our devices. This section shines a light on the magic of voltage and current in electrical systems.
The Role Of Voltage In Electrical Systems
Voltage is the pressure that pushes electrical charges through a conductor. Like water pressure in a hose, it drives the flow of current. Without voltage, no current would move, and nothing electrical would work.
- Power sources – batteries, generators – supply voltage.
- High voltage means more force; low voltage, less force.
- Voltage can be steady (DC) or changing (AC).
Different devices need different voltages. A smartphone charger might need just 5 volts. A washing machine might need 240 volts.
The Nature Of Electrical Current
Electrical current is the flow of electric charge in a circuit. It’s measured in amperes or amps. Current works with voltage to power devices.
| Type of Current | Description |
|---|---|
| Direct Current (DC) | Flows in one direction. |
| Alternating Current (AC) | Changes direction periodically. |
In most homes, AC is the standard. Devices like LED lights, electric ovens, and TVs rely on it. Only the right amount of current makes devices work properly. Too much can damage them.
Circuitry Unveiled: Components And Design
Understanding how electricity moves through devices is like unlocking a puzzle. Circuitry Unveiled: Components and Design explores this hidden world. Let’s dive into the basics and discover what makes our gadgets tick!
Basic Circuit Components
Circuits are like paths for electricity. They consist of different parts that work together. Think of them as puzzle pieces creating a complete picture.
- Resistors: These control the electricity flow, like brakes in cars.
- Capacitors: They store and release energy, akin to batteries.
- Inductors: Working like magnets, they manage the energy in the circuit.
- Diodes: They make sure electricity only goes one way, like a one-way street.
- Transistors: Tiny switches that turn the current on or off.
Each part has a role. Together, they allow devices to do amazing things!
Circuit Design Principles
When building circuits, designers follow key rules. These ensure circuits work well and are safe.
| Principle | Description |
|---|---|
| Simple Paths | Electricity needs a clear path to move. |
| Controlled Flow | Paths must have elements like resistors to manage the current. |
| Stable Connections | All components must connect well to prevent errors. |
| Right Power | The voltage must suit the circuit’s needs. |
Designers also use diagrams called schematics. These show where each part goes.
Creating a circuit is an art. It’s about mixing these components for the perfect result. Like a recipe, the right combination makes everything work!
Power Generation: From Mechanical To Electrical Energy
The journey of power generation is a fascinating one that involves converting raw mechanical force into usable electrical energy. This transformation lights up our homes, powers our industries, and fuels the technology that makes modern life possible. Electricity generation is an intricate dance between nature, technology, and human ingenuity, harnessing forces to create power on a massive scale.
Types Of Power Plants
Power plants are the heart of electricity generation. They come in various types, each with their way of transforming energy. Below is an overview:
- Coal-fired: Burns coal to create steam that drives turbines.
- Natural Gas: Uses gas combustion to turn turbines.
- Nuclear: Relies on nuclear fission to produce steam for turbines.
- Hydroelectric: Utilizes flowing water to generate mechanical energy.
- Wind: Converts wind movement into electrical power.
- Solar: Transforms sunlight into electricity using solar cells.
Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources are vital for a sustainable future. They have a reduced environmental impact and provide a cleaner alternative to fossil fuels. Some popular renewable sources include:
| Solar Energy | Generated from sunlight using photovoltaic cells. |
|---|---|
| Wind Energy | Produced through wind turbines that capture wind’s kinetic energy. |
| Hydro Energy | Created by harnessing the power of water in rivers and dams. |
| Geothermal Energy | Derived from the Earth’s internal heat to generate power. |
| Biomass Energy | Comes from organic materials like plant and animal waste. |
The Grid: Distributing Electrical Power
An electrical power grid is a vast network.
It connects power plants to various consumers.
This network ensures electricity travels from its generation point to homes, businesses, and industry.
Structure Of The Electrical Grid
The structure is like a city’s road system.
Main roads are high-voltage transmission lines.
Smaller roads are distribution lines.
Electricity moves from the power station over transmission lines.
Transformer stations act as intersections.
They reduce electricity voltage for safe home use.
- Step 1: Power generated at a plant.
- Step 2: High voltage for long-distance travel.
- Step 3: Transformer stations lower voltage.
- Step 4: Distribution lines carry power to users.
Challenges In Power Distribution
Power distribution faces several hurdles.
Physical obstacles, such as landscapes, affect lines.
Weather events can cause outages.
The demand for electricity is ever-growing.
Old infrastructure needs upgrades.
Maintenance and upgrades require time and money.
Smart grids are one solution to improve reliability.
| Challenge | Impact | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Weather Events | Power Outages | Grid Reinforcement |
| Increasing Demand | Stressed Grid | Capacity Expansion |
| Aging Infrastructure | Efficiency Loss | Technology Upgrades |
Magnetic Influence: Electromagnetism
The topic of electromagnetism bridges the gap between electricity and magnetism, two fundamental forces that shape the world of physics. This invisible but powerful force influences many aspects of our daily lives. Its discovery marked a turning point in how we harness energy and light the corners of modern innovation.
Magnetism And Electricity Connection
Electricity can create magnetism, and magnetism can create electricity. This relationship begins at the atomic level, where electric currents generate magnetic fields. These fields then exert force on other magnets and conductive materials around them.
| Element | Role in Electromagnetism |
|---|---|
| Electric Current | Generates a magnetic field |
| Magnetic Field | Influences other materials |
- Flowing electrons produce magnetic force.
- This force acts over a distance, affecting other objects.
Applications Of Electromagnetism
Electromagnetism powers many devices. It makes our lives easier and our work more efficient. Below are key applications:
- Electric Motors: Convert electrical energy to mechanical energy.
- Transformers: Change the voltage levels of electric current.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Offer detailed body scans.
- Maglev Trains: Utilize magnetic levitation for smooth rides.
Each use shows the versatility of electromagnetism. From healthcare to transportation, it shapes countless industries.
- Telecommunication
- Relies on electromagnetic waves to transmit data.
- Electronic Storage
- Employs magnetic media to store information.
Understanding electromagnetism opens doors to technological advancements. It allows us to envision a future with endless possibilities.
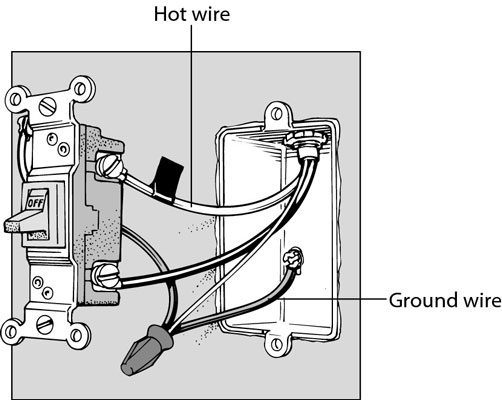
Household Wiring: Bringing Power Indoors
Electricity powers your home, bringing light, warmth, and convenience. Wiring is the network that makes this possible. It must be safe, reliable, and well-planned to handle daily demands. Let’s dive into how wiring powers your home and the essentials for a safe electrical system.
Safety In Home Electrical Systems
To ensure safety, specific standards and codes apply to home wiring. Electricians follow these to protect you and your family. Here are key points for safe electrical systems:
- Use circuit breakers to prevent overloads.
- Install ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) in wet areas.
- All outlets must have proper grounding.
- Regularly check for damaged cords or outlets.
These practices keep electricity running smoothly. They also prevent accidents. Remember, professional installation and maintenance are musts for electrical safety.
Common Wiring Configurations
Different spaces need different wiring setups. The two most common types are series and parallel circuits. How do they work?
| Circuit Type | Features | Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Series | Components connected one after another | Simple devices |
| Parallel | Components connected across common points | Most home circuits |
Series circuits are for simpler tasks. They can be limiting. If one device fails, the current stops. Parallel circuits, on the other hand, allow continuous flow even if one device goes out. They are ideal for home use, ensuring that a single failure doesn’t cut power to an entire room.
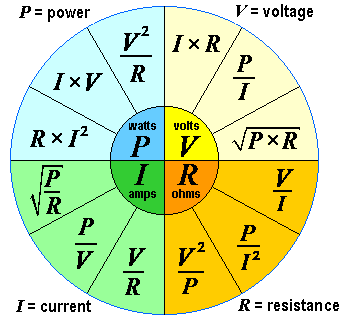
Measuring Electricity: Tools And Techniques
Understanding how to measure electricity is key in many fields. Homes, schools, and businesses all rely on electricity. Knowing the right tools and techniques ensures safety and efficiency. Let’s explore the essentials of measuring electricity.
Multimeters And Usage
A multimeter is a handy device. It measures voltage, current, and resistance. There are two types: analog and digital. Digital multimeters (DMMs) are popular due to their accuracy and ease of use.
- Turn off power before connecting the multimeter.
- Select the correct setting on the device for what you’re measuring.
- Connect the probes to the circuit—black to ground, red to power.
- Read the display for a digital reading of the measurement.
For safety, always start with the highest range. Use protective gear. A multimeter is a must-have tool for any electrical work.
Electrical Measurements Standards
Standards ensure consistency in electrical measurements. Organizations like IEC and NIST provide guidelines.
| Standard | Organization | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| IEC standards | International Electrotechnical Commission | International guidelines |
| NIST standards | National Institute of Standards and Technology | U.S. measurements |
These standards ensure that equipment calibration and measurements are accurate. They also make sure that electrical devices are safe to use. Following standards is critical for anyone involved with electricity.
Energy Efficiency: Conservation And Management
Electricity lights up our homes and powers our lives. Yet, using it smartly is key. Energy efficiency means using less power to perform the same tasks. This practice not only saves money but also helps the planet. Let’s explore how to manage and conserve energy effectively.
Efficient Appliances And Devices
Choosing the right appliances makes a big difference. Look for Energy Star labels when buying. This mark means the device uses less electricity than standard models. Consider replacing older items with more efficient ones.
| Appliance | Energy Saving Feature | Estimated % Savings |
|---|---|---|
| Refrigerator | Energy Star Certified | Up to 50% |
| Dishwasher | Eco-friendly cycles | Up to 30% |
| LED Bulbs | Long-lasting | Up to 75% |
Remember, even charging cables draw power when plugged in. Unplug them when not in use. This small step saves energy.
Energy Saving Strategies
Here are tactics to keep your electric bills down:
- Turn off lights when leaving a room.
- Use natural light during the day.
- Set thermostats to an economic temperature.
- Seal windows and doors to avoid heat loss.
In addition, a programmable thermostat adjusts temperatures and saves energy. Insulation is another smart move. Properly insulating your home helps maintain temperature.
- Insulate your attic and walls.
- Consider double-pane windows.
- Install door sweeps to prevent drafts.
By employing these strategies, you can lead a more energy-efficient lifestyle. It’s about making smarter choices for a sustainable future. Start small and watch the savings grow.
Safety Protocols: Avoiding Electrical Hazards
Electricity powers our lives, but it’s vital to respect its power. Knowing how to stay safe around electricity prevents accidents and saves lives. This section dives into keeping homes and workplaces secure by highlighting common electrical hazards and prevention measures, alongside essential safety equipment and procedures.
Common Hazards And Prevention
Electrical hazards can be silent but deadly. Awareness is key to prevention. Here’s a look at what to watch for and how to keep safe:
- Overloaded outlets: Ignite fires.
- Use one plug per outlet.
- Worn cords: Cause shocks and fires.
- Check regularly. Replace if damaged.
- Wet areas: Increase electrocution risk.
- Keep electronics away from water.
| Hazard | Action |
|---|---|
| Overloaded circuits | Install more outlets |
| Damaged insulation | Use electrical tape |
| Improper grounding | Get professional checks |
Safety Equipment And Procedures
Right tools and knowledge promote safety. Implement these items and actions:
- Use insulated gloves when handling wires.
- Wear safety goggles to protect eyes.
- Fire extinguishers: Place them in accessible locations.
- Routine Inspections:
- Prevent malfunctions and identify issues early.
- Emergency Plan:
- Prepare and practice for electrical emergencies.
Following these safety protocols reduces risk and fosters a secure environment where electricity becomes a helpful servant instead of a hazardous master.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/lightbulblit-57a5bf6b5f9b58974aee831e.jpg)
Credit: www.thoughtco.com
Sustainable Advances: The Future Of Electricity
Imagine a world powered by clean, infinite energy. The future of electricity shines bright with sustainable advances that promise a healthier planet. Our journey into this future is exciting, led by bold innovations and transformative power solutions. This world is not a dream; it’s the horizon of our collective efforts.
Emerging Technologies In Power Generation
The power generation landscape is undergoing remarkable change. Groundbreaking technologies aim to harvest energy in ways we never thought possible.
- Solar paint – a coat that captures sunlight and turns it into electricity.
- Wave energy converters – machines that seize the power of ocean waves.
- Nano-generators – small devices turning mechanical energy into power.
These advancements show we can get electricity from the world around us. It is clean, sustainable, and lets us look to a future without pollution.
The Shift To Sustainable Power Solutions
All over the world, there’s a shift happening. We are moving from old, harmful ways of making electricity to new, green methods. This movement has massive support and excitement.
Renewable energy is at the center of this shift. Here’s what countries are doing:
| Country | Renewable Source | Target Year |
|---|---|---|
| Iceland | Geothermal | 2040 |
| Germany | Wind & Solar | 2050 |
| China | Hydropower & Solar | 2060 |
More countries are joining this movement. They are making big plans to change how we get electricity. The future is bright and full of hope.
The Electric Economy: Impact On Industries
Electricity is not just flipping light switches. It powers our world in amazing ways. Today, we’re seeing a revolution. This revolution is changing factories and how we travel. It’s the electric economy, and it’s huge.
Electrification of TransportationElectrification Of Transportation
Cars and buses are going electric. It’s not just about being green. It’s also about being smart with money. Let’s see how:
- Electric vehicles (EVs) save on gas costs.
- They need less maintenance than petrol cars.
- Batteries get better and cheaper every year.
Charging stations are popping up everywhere. From cities to highways, they make traveling easy. Countries are saying goodbye to diesel and petrol. They’re saying hello to clean, electric transport.
Electrical Technology in ManufacturingElectrical Technology In Manufacturing
Manufacturing is smarter with electricity. Robots work 24/7. They make things fast. They don’t make mistakes. Here’s what’s changing:
| Technology | Benefits |
|---|---|
| 3D Printing | Makes complex parts, lowers waste. |
| Programmable Automation | Quick changes in production, saves time. |
| Energy Efficient Machines | Uses less power, saves money. |
Data is key. Sensors collect info. They help prevent mistakes. They keep machines running without stopping.
Electricity makes manufacturing clean and precise. This leads to better products for everyone.
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/50911339/electricity.0.jpg)
Credit: www.vox.com
Blackouts And Brownouts: Understanding Power Outages
Power outages can plunge our world into darkness unexpectedly. Whether due to a storm or an unexpected malfunction, understanding blackouts and brownouts is key. These sudden losses of electricity affect daily life and safety. In the next sections, we explore power failures, their effect on communities, and possible solutions.
Causes Of Power Failures
Multiple factors may lead to a blackout or a brownout:
- Weather events: Strong winds, ice, or lightning can damage power lines.
- Operational errors: Mistakes by power company employees can disrupt service.
- Equipment failure: Over time, transformers and other equipment may break down.
- High demand: Overloading power systems during peak times can cause outages.
- Wildlife: Animals can accidentally cause short circuits in equipment.
Impact On Communities
Power outages impact everyone’s life:
- Homes lose light, heat, or air conditioning, making them uncomfortable or unsafe.
- Schools may close, disrupting education.
- Hospitals rely on backup generators for critical care.
- Businesses suffer from lost sales and productivity.
- Food spoils without refrigeration, leading to waste and extra costs.
Solutions
Several steps can reduce power outage risks:
| Strategy | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Infrastructure updates | Modern equipment resists weather damage. |
| Tree trimming | Reduces risk of branches falling on lines. |
| Energy conservation | Lessens the load on power grids at peak times. |
| Backup power | Schools and hospitals continue to function. |
Communities can prepare better with these solutions to ensure continuous power.
Wireless Electricity: Cutting The Cord
Imagine charging your phone just by placing it on the table. No plugs, no cables, no hassle. Wireless electricity is reshaping how we think about energy transfer. This innovation means we can say goodbye to the jungle of cords tangling our lives. It’s simple, clean, and incredibly convenient.
Principles Of Wireless Power
Wireless power relies on fascinating physics. It works through magnetic fields that are harmless to humans. Two coils, one in the device and one in the charger, interact. When electricity passes through the charger’s coil, it creates a magnetic field. This field reaches the device coil and creates electricity. Voilà, your battery charges without wires!
- Magnetic Resonance: Power moves over short distances between coils.
- Induction: The process that converts magnetic fields to electricity.
Prospects Of Wireless Charging
Wireless charging is not just for phones. It’s shaping our future in exciting ways. Picture roads that charge electric cars as they drive. Think of pacemakers getting power without surgery. Imagine offices with desks that power laptops, tablets, and more.
| Application | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics | No cords; devices charge when on surfaces |
| Medical Devices | Less invasive, more comfort for patients |
| Automotive | Continuous charging, longer travel |
| Industrial | Better safety, no exposed wires |
The potential is massive, and researchers are pushing boundaries every day. As wireless technology improves, we will see more devices cutting the cord, making life simpler and safer.

Credit: www.electricrate.com
Global Electrification: Bridging The Power Gap
Imagine a world where everyone flips a switch, and the light floods their home. Yet, for many, this is a distant dream. Global Electrification aims to turn this dream into reality. By bridging the power gap, nations unite to light up lives across the globe. This journey of electrification is not just about powering homes, but also empowering economies and communities.
Access To Electricity Worldwide
As we forge ahead into the 21st century, access to electricity remains uneven. It is crucial in shaping a country’s development. Still, thousands of communities live without it.
- Global Coverage: As of today, around 90% of the world has access to electricity.
- Rural vs Urban Divide: Urban areas enjoy better electrification rates compared to rural regions.
- Continental Challenges: Africa and Asia have the largest populations without access to power.
International Electrification Projects
To bridge the vast power gap, international projects are crucial. They bring innovation and investment to the table.
| Project | Region | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Home Systems | Sub-Saharan Africa | Million homes lit |
| Grid Expansion Programs | Southeast Asia | Connect remote villages |
| Wind Farm Projects | Latin America | Renewable power generation |
International cooperation plays a pivotal role. Noteworthy, NGOs and governments partner regularly. Their goal? To light up the dark and enable progress.
Battery Technology: Storing Electrical Energy
Imagine a world where every spark of electricity matters. That’s our world, and batteries are the superheroes. They grab energy and hold onto it until we need to power our lives. Let’s dive into how batteries have grown smarter and stronger over time!
Evolution Of Batteries
From simple to complex, batteries have evolved. Long ago, we only had basic cells. Now, we brag about lithium-ion champions. This is their story:
- Volta’s pile – The first step in battery life.
- Lead-acid – Cars’ best friends since 1859.
- Nickel-cadmium – Rechargeable and handy.
- Lithium-ion – The star, with more energy, less weight.
Innovations In Energy Storage
Exciting times are here! New battery tech bursts onto the scene. We’re not just storing energy; we’re doing it better:
| Technology | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Solid-state batteries | Safe and pack more power. |
| Graphene batteries | Charge super fast! |
| Flow batteries | Last for decades, wow! |
These breakthroughs in battery technology make our gadgets run longer and charge faster. They even help our planet with cleaner energy storage.
Smart Grids: Intelligent Power Distribution
Imagine a world where power flows through a web of intelligence, dynamically responding to the demands of homes, factories, and cities. Smart Grids represent this leap in electrical power distribution, utilizing real-time data to optimize energy consumption and streamline electricity supply.
Features Of The Smart Grid
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI): Delivers precise energy use data to both utility providers and consumers.
- Automated Fault Detection: Quickly locates and isolates issues, minimizing downtime.
- Integrated Communication Systems: Ensures seamless data exchange across the grid.
- Energy Management Systems: Allows for efficient use of renewable energy sources.
- Peak Load Management: Balances demand and reduces strain during high usage times.
Benefits Of Smart Grid Technology
The adoption of smart grids brings myriad advantages. Consumers relish lower energy bills and enhanced service reliability. Meanwhile, environmental impacts are significantly curbed due to optimized energy consumption.
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Reduction in energy waste, saving resources. |
| Cost Reduction | Lower operational costs for utility providers. |
| Reliability | Less downtime and consistent power supply. |
| Renewable Integration | Smarter integration of solar and wind power. |
| Grid Security | Enhanced protection against cyber threats. |
Electricity In Nature: Bioelectricity
Imagine a world where creatures create their own sparkle, not just with colors, but with real electricity! Bioelectricity is this amazing power in nature. From the deep oceans to the human body, electricity thrives within living organisms. Get ready to explore how life on Earth uses electricity to survive and communicate.
Electric Phenomena In Organisms
Did you know that some fish can generate electric shocks? This is just one example of electric phenomena in organisms. Other examples include:
- Electric Eels: Strong shocks for defense and hunting
- Sharks: Sensing prey with electric fields in water
- Humans: Our brains use electric signals to think and move
Even plants have electric signaling to respond to damage or stress. This shows how electricity is vital for many life processes.
Study Of Bioelectricity
The study of bioelectricity is a field that combines biology and physics. Scientists in this field work to uncover:
| Research Area | Focus |
|---|---|
| Neuroscience | Brain and nerve electricity |
| Cardiology | Heart’s electrical patterns |
| Eco-electricity | Electricity in ecosystems |
This exciting study can lead to medical breakthroughs and a deeper understanding of life itself.
Regulations And Standards: Governing Electrical Systems
Electricity lights up our world, but it must stay safe. Rules and standards make sure of that. They’re like a rule book that electricians follow. This rule book helps avoid accidents with electricity. It keeps buildings and people safe. Let’s explore the key codes and compliance measures.
National And International Electrical Codes
Electricity rules vary around the globe. Some rules are for towns, and some are for countries. There are even rules for the whole world.
- National Electrical Code (NEC): This code is a big deal in the USA. Electricians must use it to install electricity safely. It gets updated every three years.
- International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC): Countries around the world follow these standards. They help make sure products work well together and are safe.
Countries choose these rules to suit their needs. Yet, the goal remains the same: keep electricity safe for everyone.
Compliance And Certification
It’s not just about knowing the rules. You must also show you follow them. This is where compliance and certification come in. Let’s look at what that means.
| Compliance | Certification |
|---|---|
| It means following the rules. Inspections make sure of that. | Getting a certificate proves you did the job right. |
| It happens at different stages of work. Each stage must pass a check. | You get a certificate after all checks are passed. |
Certificates are proof that everything is correct. It’s like a gold star for electricians. If they don’t have this, they may have to redo the work.
Frequently Asked Questions For Electricity
How Does Electricity Power A Home?
Electricity enters a home via the electrical grid, powering appliances, lighting, and other electronic devices through a network of wires and panels safely installed.
Can Electricity Be Generated At Home?
Home electricity generation is possible with solar panels, wind turbines, or small-scale hydro systems, becoming increasingly popular for energy independence.
What Is The Cost Of Electricity?
The cost of electricity varies by location, provider, and usage, typically measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh) and reflected in monthly utility bills.
How To Save On Electricity Bills?
To reduce electricity bills, one should use energy-efficient appliances, switch to LED lighting, unplug devices when not in use, and improve home insulation.
Is Electricity Eco-friendly?
Electricity can be eco-friendly if generated from renewable sources like solar, wind, or hydro, which produce minimal greenhouse gases compared to fossil fuels.
Conclusion
Electricity shapes our modern existence, powering homes, industries, and innovations. Embrace its potential for a sustainable future. As we progress, responsible use and renewable energy integration become crucial. Keep exploring this dynamic force; it promises a brighter, more efficient tomorrow.
Let’s harness electricity’s power, mindfully and innovatively.






1 thought on “Electricity”