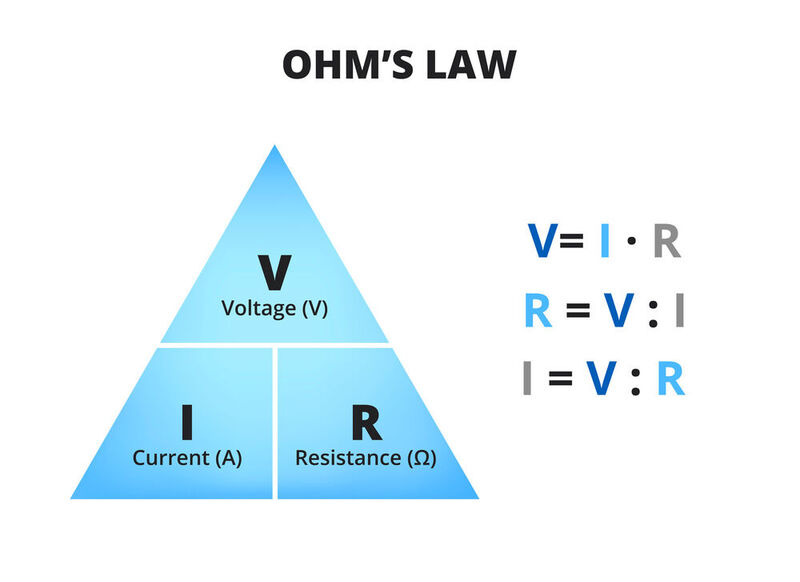
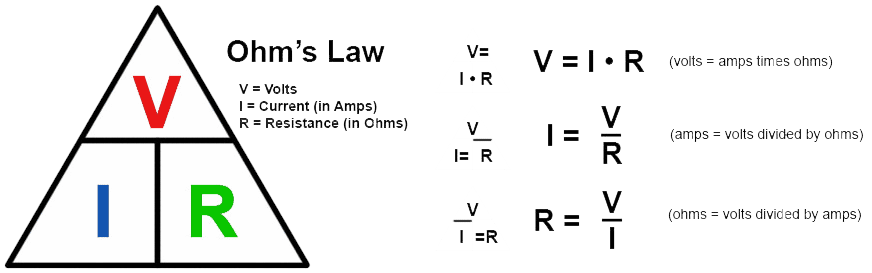
Ohm’s Law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points. It is represented by the formula V = IR, where V is voltage, I is current, and R is resistance.
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering and physics. It helps understand the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in an electric circuit. Georg Simon Ohm, a German physicist, formulated this law in 1827. His work has since become a cornerstone in the study of electricity.
The law simplifies circuit analysis and design, making it easier to predict how electrical components will behave. Understanding Ohm’s Law is crucial for anyone working with electrical systems, from hobbyists to professional engineers.
Introduction To Ohm’s Law
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental concept in electrical engineering. This law helps to understand the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance. It forms the basis of many electrical principles and calculations. Knowing Ohm’s Law is essential for anyone dealing with electrical circuits.
Origins And History
Ohm’s Law was named after Georg Simon Ohm, a German physicist. He discovered the law in the early 19th century. Ohm published his findings in 1827. His work was groundbreaking at the time. Today, Ohm’s Law is a standard part of electrical engineering.
Importance In Electrical Engineering
Ohm’s Law is crucial in electrical engineering. It helps engineers design circuits and solve problems. The law states that voltage (V) equals current (I) times resistance (R).
V = I × R
This simple formula is used in countless applications. It helps determine the correct values for circuit components. Ohm’s Law also aids in troubleshooting and repairing electrical systems.
Here’s a quick reference table for understanding the relationships:
| Parameter | Symbol | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage | V | Volts (V) |
| Current | I | Amperes (A) |
| Resistance | R | Ohms (Ω) |
Understanding these relationships is key in electrical engineering. Whether designing new circuits or fixing old ones, Ohm’s Law is a vital tool. It ensures safety and efficiency in electrical systems.
Basic Principles
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental concept in electricity. It explains the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance. Understanding these principles helps us in everyday tasks and electronics.
Voltage
Voltage is the force that pushes electric charges through a circuit. It is measured in volts (V). Think of voltage as the pressure that moves water through a pipe. Higher voltage means more pressure, pushing charges faster.
Current
Current is the flow of electric charges through a circuit. It is measured in amperes (A), or amps. Imagine current as the amount of water flowing through a pipe. More current means more charges are flowing.
Resistance
Resistance is what slows down the flow of electric charges. It is measured in ohms (Ω). Resistance is like a narrow pipe that restricts water flow. Higher resistance means less current flows through the circuit.
| Term | Symbol | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage | V | Volts |
| Current | I | Amperes (Amps) |
| Resistance | R | Ohms |
The relationship between these three is given by Ohm’s Law formula:
V = I RThis means voltage equals current times resistance. Understanding this formula helps in solving electrical problems easily.
The Ohm’s Law Equation
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering. It describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit. This equation is simple yet powerful. Understanding this law can help you solve many electrical problems.
Formula Breakdown
The Ohm’s Law equation is:
In this formula:
- V stands for voltage.
- I stands for current.
- R stands for resistance.
This equation shows how voltage, current, and resistance are related. If you know two of these values, you can find the third.
Units Of Measurement
Each part of Ohm’s Law uses specific units.
| Variable | Unit | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage | Volt | V |
| Current | Ampere | A |
| Resistance | Ohm | Ω |
Using the correct units is crucial. It ensures your calculations are accurate. Always double-check your units before solving problems.

Credit: byjus.com
Practical Applications
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental concept in electrical engineering. It helps us understand how voltage, current, and resistance interact. This law is not just theoretical; it has many practical uses.
Household Circuits
Ohm’s Law is essential in designing household circuits. Knowing the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance ensures safe and efficient electrical systems. For example, it helps determine the right fuse rating.
Consider a typical light bulb circuit at home:
| Component | Voltage (V) | Current (I) | Resistance (R) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light Bulb | 120V | 0.5A | 240Ω |
By using Ohm’s Law (V = IR), we can ensure that the bulb operates safely within its limits.
Electronics Projects
Ohm’s Law is crucial for electronics projects. It helps in designing and troubleshooting circuits. Hobbyists and professionals use it to calculate the values of resistors, capacitors, and other components.
For instance, in a simple LED circuit:
- Supply Voltage: 9V
- LED Forward Voltage: 2V
- Desired Current: 20mA
Using Ohm’s Law, we find the resistor value:
R = (9V - 2V) / 0.02A = 350ΩThis calculation ensures the LED operates safely without burning out.
Using Ohm’s Law In Calculations
Ohm’s Law is vital for electrical calculations. It links voltage, current, and resistance. The formula is simple but powerful: V = I x R.
Finding Voltage
To find voltage, multiply current by resistance. This is useful for understanding electrical circuits.
V = I x RFor example, if the current is 2 amps and the resistance is 3 ohms, the voltage is:
V = 2A x 3Ω = 6VCalculating Current
To calculate current, divide voltage by resistance. This helps you know how much current flows through a circuit.
I = V / RIf the voltage is 12 volts and resistance is 4 ohms, the current is:
I = 12V / 4Ω = 3ADetermining Resistance
To find resistance, divide voltage by current. This is crucial for designing circuits.
R = V / IIf the voltage is 10 volts and the current is 2 amps, the resistance is:
R = 10V / 2A = 5Ω| Formula | Example |
|---|---|
| Finding Voltage: V = I x R | 2A x 3Ω = 6V |
| Calculating Current: I = V / R | 12V / 4Ω = 3A |
| Determining Resistance: R = V / I | 10V / 2A = 5Ω |
- Voltage (V): The electrical potential difference
- Current (I): The flow of electric charge
- Resistance (R): The opposition to current flow
Common Misconceptions
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental concept in electrical engineering. Many people misunderstand it. Let’s clear up some common misconceptions.
Overlooking Temperature Effects
Many believe Ohm’s Law is always accurate. This isn’t true. Temperature changes can affect resistance.
| Temperature | Resistance |
|---|---|
| Low | Decreases |
| High | Increases |
For example, metals conduct better at low temperatures. At high temperatures, they resist more. So, always consider temperature.
Misinterpreting Circuit Diagrams
Some people struggle to read circuit diagrams. They might think components are connected differently.
- Always check the direction of current flow.
- Identify all resistors and their values.
- Ensure you understand series and parallel connections.
Reading the diagram correctly ensures you apply Ohm’s Law accurately. Practice makes perfect. Study various circuit diagrams to get better.
Advanced Concepts
Ohm’s Law is fundamental in understanding electrical circuits. Advanced concepts expand this basic knowledge to more complex applications. This section delves into power calculations, series circuits, and parallel circuits, providing a deeper understanding of these essential topics.
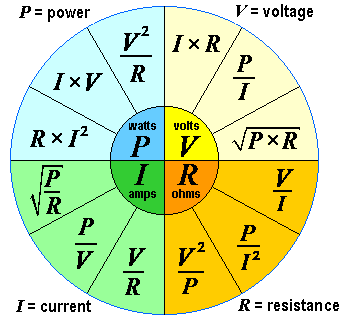
Power Calculations
Power in electrical circuits is crucial. It shows how much energy is used. Power (P) is calculated using the formula:
P = V IWhere P is power in watts, V is voltage in volts, and I is current in amperes. Another important formula is:
P = I2 RHere, R is resistance in ohms. These formulas help in designing efficient circuits.
| Formula | Description |
|---|---|
P = V I |
Calculates power using voltage and current. |
P = I2 R |
Calculates power using current and resistance. |
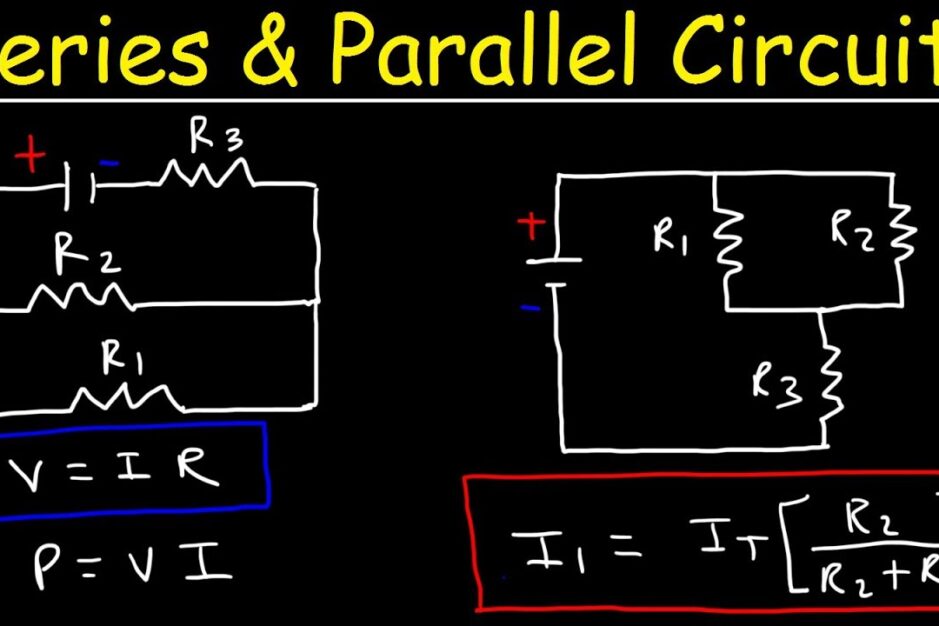
Series And Parallel Circuits
Circuits can be connected in two ways: series and parallel. In a series circuit, components are connected end-to-end. The same current flows through each component. The total resistance is the sum of individual resistances:
Rtotal = R1 + R2 + ... + RnIn parallel circuits, components are connected across the same voltage. The total resistance is found using the formula:
1 / Rtotal = 1 / R1 + 1 / R2 + ... + 1 / Rn- Series circuits: Same current, total resistance is the sum.
- Parallel circuits: Same voltage, total resistance is reciprocal of the sum of reciprocals.
Understanding these types of circuits is key in circuit design. It helps in predicting circuit behavior.
Practical Tips And Best Practices
Understanding Ohm’s Law is crucial for anyone dealing with electrical circuits. This law helps to calculate the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance. Let’s dive into some practical tips and best practices to use Ohm’s Law effectively.
Safety Precautions
Safety should always be your top priority. Here are some essential safety tips:
- Turn off power before working on any circuit.
- Use insulated tools to avoid electrical shocks.
- Wear protective gear like gloves and goggles.
- Double-check connections to prevent short circuits.
- Avoid working with wet hands or in damp conditions.
Troubleshooting Techniques
Effective troubleshooting can save you time and effort. Follow these steps:
- Check power supply: Ensure the power source is working.
- Inspect connections: Look for loose or broken wires.
- Measure voltage: Use a multimeter to check voltage levels.
- Test components: Verify resistors, capacitors, and other parts.
- Document findings: Keep a log of your measurements and observations.
Using these tips and best practices will help you apply Ohm’s Law effectively and safely in your projects. Always prioritize safety and follow systematic troubleshooting techniques to achieve accurate results.
Conclusion And Further Reading
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental concept in the field of electronics and electrical engineering. It plays a crucial role in understanding the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance. This section will summarize the key points and provide resources for further learning.
Key Takeaways
- Ohm’s Law states that voltage is equal to current times resistance.
- The formula is
V = I R. - Ohm’s Law helps in designing and troubleshooting electrical circuits.
- It is essential for both beginners and professionals in electronics.
Recommended Resources
For those interested in diving deeper into Ohm’s Law, the following resources are highly recommended:
| Resource | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Khan Academy | Website | Interactive lessons on electrical engineering concepts. |
| Basic Electronics | Book | Comprehensive guide on basic electronics and circuits. |
| Coursera | Online Course | Free course covering the basics of electronics. |
These resources will help deepen your understanding of Ohm’s Law and its applications.

Credit: www.digikey.com
Credit: www.power-and-beyond.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Ohm’s Law?
Ohm’s Law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points. It is represented by the formula V = IR.
How Is Ohm’s Law Used?
Ohm’s Law is used to calculate the voltage, current, or resistance in an electrical circuit. It helps in designing and analyzing electrical systems.
What Is The Formula For Ohm’s Law?
The formula for Ohm’s Law is V = IR, where V is voltage, I is current, and R is resistance. This equation helps in understanding the relationship between these three quantities.
Why Is Ohm’s Law Important?
Ohm’s Law is essential for understanding and designing electrical circuits. It provides a simple way to calculate electrical parameters, ensuring safety and efficiency.
Conclusion
Understanding Ohm’s Law is crucial for anyone dealing with electrical circuits. It simplifies complex concepts into manageable equations. With this knowledge, troubleshooting becomes easier and safer. Whether you are a student or a professional, mastering Ohm’s Law is essential. Keep exploring to deepen your understanding of electrical principles.





2 thoughts on “Ohm’s Law: Mastering Electrical Circuits Made Simple”