Electricians must always follow safety protocols to prevent accidents and ensure a safe working environment. Wear proper protective gear and adhere to electrical codes.
Electricians play a crucial role in maintaining and installing electrical systems. Their work involves inherent risks, making safety guidelines essential. Wearing appropriate protective gear like gloves, goggles, and insulated clothing can prevent injuries. Adhering to established electrical codes and regulations ensures compliance and safety.
Regularly inspecting tools and equipment can avoid malfunctions and hazards. Understanding the layout of electrical systems and de-energizing circuits before working on them is critical. Continuous education on safety practices helps keep electricians updated on the latest standards. Prioritizing safety not only protects electricians but also ensures the safety of everyone around them.
Credit: ayanelectricians.co.uk
Personal Protective Equipment
Electricians face various risks every day. To ensure safety, they must follow general safety guidelines. One crucial aspect is using Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). PPE helps protect electricians from electrical shocks, burns, and other hazards. Understanding and using the right PPE can save lives and prevent injuries. Let’s dive into the different types of PPE and how to use them properly.
Types Of Ppe
Electricians need different types of PPE to stay safe. Here are some essential items:
- Insulated Gloves: These gloves protect hands from electrical shocks. They are made of rubber and tested for high voltage.
- Safety Glasses: Glasses protect eyes from sparks and flying debris. They should be impact-resistant.
- Face Shields: Shields provide full-face protection. They are useful for tasks involving arc flashes.
- Hard Hats: These hats protect the head from falling objects. They also provide some protection against electrical shocks.
- Fire-Resistant Clothing: Clothes made from fire-resistant materials protect against burns. They are essential for working near live wires.
- Safety Boots: Boots with insulating soles protect feet from electrical currents. Steel toes provide additional protection.
Proper Usage
Using PPE correctly is just as important as having it. Here are some tips:
- Inspect PPE Regularly: Check for damage before each use. Look for cracks, tears, and wear.
- Wear the Right Size: PPE should fit well. Ill-fitting gear can be uncomfortable and less effective.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Use PPE as instructed by the manufacturer. This ensures maximum protection.
- Store PPE Properly: Keep gear in a clean, dry place. Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures.
- Replace Damaged PPE: Don’t use damaged or worn-out equipment. Replace it immediately to stay safe.
- Clean PPE After Use: Clean gear according to the manufacturer’s instructions. This maintains its effectiveness.
Remember, PPE is your last line of defense. Always use it correctly to stay safe on the job. Proper usage can prevent injuries and save lives.
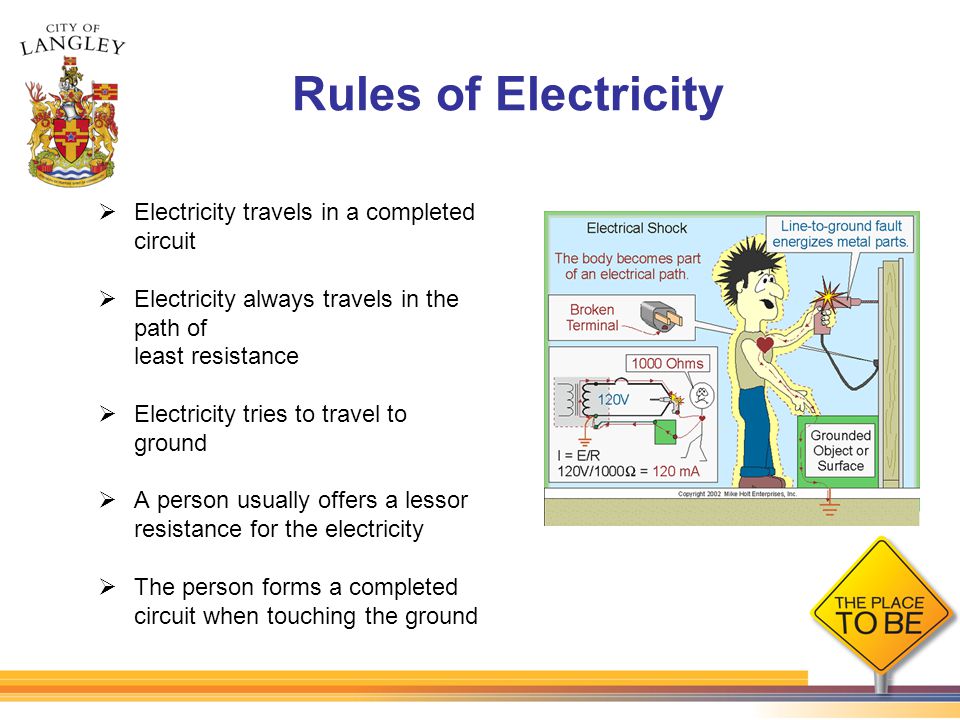
Electrical Hazards
Electricians face many dangers while working. Understanding electrical hazards is crucial for their safety. These hazards can cause serious injuries or even death. Knowing the risks and how to avoid them can save lives. Let’s delve into the types of hazards and how to recognize them.
Types Of Hazards
Electricians encounter various electrical hazards. Some common types include:
- Electric Shock: This occurs when electric current passes through the body. It can cause burns, nerve damage, or even stop the heart.
- Arc Flash: A sudden release of electrical energy through the air. It can cause severe burns and blast injuries.
- Fire Hazards: Faulty wiring or overloaded circuits can lead to fires. These fires can quickly spread, causing significant damage.
- Explosions: Sparks from electrical equipment can ignite flammable materials. This can result in dangerous explosions.
- Faulty Equipment: Using old or damaged tools can be dangerous. They may not work correctly, leading to accidents.
Understanding these hazards helps in taking preventive measures. Awareness and proper training are key to avoiding accidents. Electricians should always use safety gear and follow protocols. Below is a table summarizing these hazards:
| Hazard | Impact |
|---|---|
| Electric Shock | Burns, nerve damage, heart failure |
| Arc Flash | Severe burns, blast injuries |
| Fire Hazards | Fire damage, potential fatalities |
| Explosions | Injuries, property damage |
| Faulty Equipment | Accidents due to malfunction |
Recognizing Risks
Recognizing electrical risks is crucial for electricians. Here are some signs and preventive measures:
- Frayed Wires: Look for exposed or damaged wires. Replace them immediately to prevent shocks.
- Burn Marks: Check outlets and switches for burn marks. This indicates overheating or short circuits.
- Strange Smells: Smelling burning plastic or rubber? This could mean an electrical fault. Turn off power and investigate.
- Flickering Lights: Lights flickering could signal wiring issues. Inspect and fix any loose connections.
Use safety equipment always. Wear insulated gloves and shoes. Use tools with insulated handles. Follow these guidelines:
- Inspect tools before use.
- Turn off power before starting work.
- Use a voltage tester to check circuits.
- Work in pairs for added safety.
- Keep a safe distance from live wires.
Training and awareness can prevent accidents. Stay alert and follow safety protocols. This ensures a safer working environment for all electricians.
Safe Work Practices
Electricians face numerous hazards daily. Following general safety guidelines can prevent accidents and injuries. One key aspect is adhering to safe work practices. These practices ensure that electricians work in a controlled and safe environment. Two crucial elements of these practices are Lockout/Tagout Procedures and Working Near Live Circuits.
Lockout/tagout Procedures
Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) procedures are critical for preventing accidental energy release. This process involves isolating electrical energy sources and ensuring they remain isolated during maintenance. Here are the steps for a proper LOTO procedure:
- Prepare for Shutdown: Identify the energy sources and the control methods.
- Notify Affected Employees: Inform all employees about the shutdown.
- Shutdown Equipment: Turn off the machine or equipment.
- Isolate Energy Sources: Disconnect the energy sources.
- Apply Lockout/Tagout Devices: Attach locks and tags to each energy-isolating device.
- Release Stored Energy: Ensure all stored energy is released or restrained.
- Verify Isolation: Check if the isolation is complete and effective.
Following these steps ensures no accidental energy release occurs. It protects electricians from unexpected power-ups. Below is a table summarizing the LOTO steps and their purpose:
| Step | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Prepare for Shutdown | Identify energy sources |
| Notify Affected Employees | Inform about shutdown |
| Shutdown Equipment | Turn off machines |
| Isolate Energy Sources | Disconnect energy |
| Apply Lockout/Tagout Devices | Attach locks and tags |
| Release Stored Energy | Ensure energy is released |
| Verify Isolation | Check isolation effectiveness |
Working Near Live Circuits
Working near live circuits poses significant dangers. Electricians must follow stringent safety protocols to minimize risks. Here are some key safety practices:
- Use Insulated Tools: Always use tools with proper insulation to prevent electrical shock.
- Wear Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): This includes gloves, safety glasses, and flame-resistant clothing.
- Maintain Safe Distance: Keep a safe distance from live circuits. Use barriers if necessary.
- De-energize Circuits: If possible, de-energize circuits before working on them.
- Verify Voltage Absence: Use a voltmeter to check if the circuit is live before starting work.
These practices ensure electricians stay safe while working near live circuits. Here’s a quick reference table for necessary PPE:
| PPE | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Insulated Gloves | Prevent electrical shock |
| Safety Glasses | Protect eyes from sparks |
| Flame-Resistant Clothing | Protect against burns |
By adhering to these guidelines, electricians reduce the risk of injury. Safe work practices are essential for any electrician’s daily routine.
Credit: www.staccard.com
Tool Safety
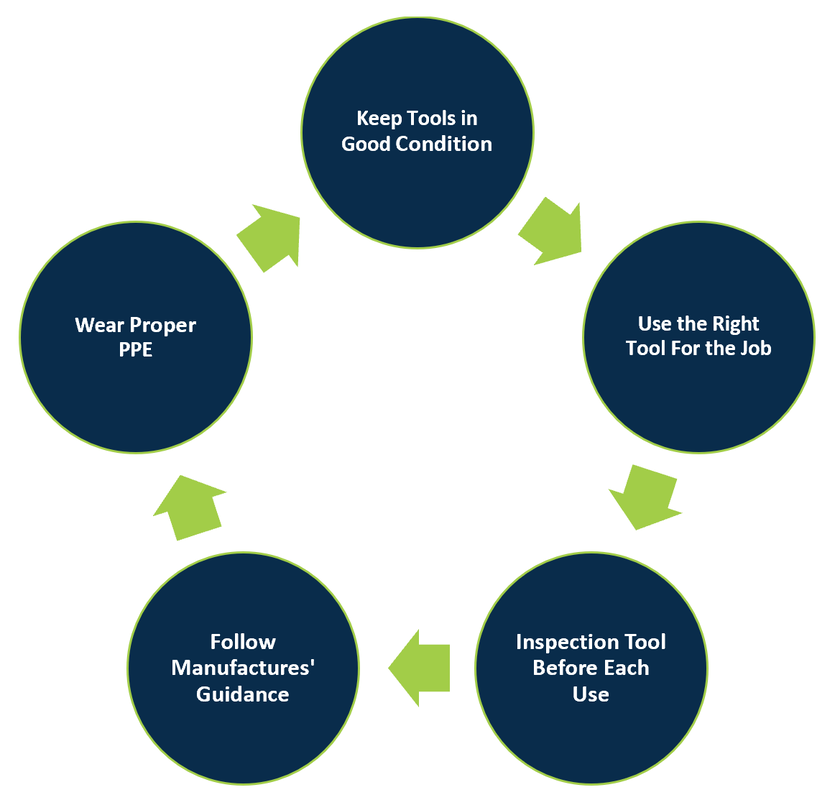
Electricians face various hazards daily, making safety a top priority. One critical aspect of safety is Tool Safety. Using tools correctly reduces the risk of injury and ensures efficient work. Below, we discuss essential guidelines under two main topics: Inspection and Maintenance and Safe Handling Techniques.
Inspection And Maintenance
Regular inspection and maintenance of tools are crucial for electricians. Faulty tools can lead to serious accidents. Always check tools before use to ensure they are in good condition. Follow these steps for proper inspection:
- Visual Inspection: Look for cracks, frayed cords, and worn-out parts.
- Functionality Test: Ensure tools operate smoothly and efficiently.
- Electrical Safety: Test for proper insulation and grounding.
Maintaining tools is just as important. Here are some maintenance tips:
- Clean Tools Regularly: Remove dirt and debris to prevent malfunctions.
- Lubricate Moving Parts: Apply oil or grease to reduce wear and tear.
- Store Tools Properly: Keep tools in a dry, safe place to avoid damage.
Below is a simple table highlighting key maintenance tasks:
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Daily |
| Cleaning | Weekly |
| Lubrication | Monthly |
| Storage Check | As Needed |
Safe Handling Techniques
Using tools safely protects electricians from injuries. Here are some safe handling techniques to follow:
- Wear Protective Gear: Always use gloves and safety glasses.
- Use Tools as Intended: Do not misuse tools for tasks they are not designed for.
- Keep a Firm Grip: Hold tools securely to prevent slips.
Other important tips include:
- Avoid Wet Conditions: Do not use electrical tools in wet environments.
- Disconnect Power: Unplug tools when not in use or during maintenance.
- Keep Workspace Clean: A tidy area reduces the risk of tripping or knocking over tools.
Following these techniques ensures a safer working environment. Remember, proper tool handling not only protects you but also enhances your efficiency and productivity.
First Aid Procedures
Electricians work in environments where safety risks are high. Understanding general safety guidelines is crucial to ensure their well-being. One of the most important aspects of these guidelines is knowing First Aid Procedures. Immediate and effective first aid can be the difference between a minor injury and a severe one. This section will cover the essential first aid skills every electrician should know and the importance of having emergency contact information readily available.
Basic First Aid Skills
Every electrician should be equipped with basic first aid skills. These skills can help manage injuries until professional medical help arrives. Here are some key points:
- CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation): Knowing how to perform CPR can save lives, especially in cases of electric shock.
- Wound Care: Properly cleaning and dressing wounds prevents infections.
- Burn Treatment: Apply cool water to burns and cover with a sterile bandage. Do not use ice.
- Fracture Management: Immobilize the injured area using a splint or other supportive materials.
- Poison Management: Identify the substance and seek immediate medical advice.
It’s also beneficial to have a well-stocked first aid kit on hand. Here’s a simple checklist for an electrician’s first aid kit:
| Item | Quantity |
|---|---|
| Adhesive Bandages | 20 |
| Gauze Pads | 10 |
| Antiseptic Wipes | 15 |
| Burn Gel | 1 tube |
| Scissors | 1 |
| CPR Mask | 1 |
Regular training ensures electricians stay updated on the latest first aid techniques. Practice mock drills and refresh your knowledge periodically.
Emergency Contact Information
Having emergency contact information easily accessible is vital. In an emergency, time is of the essence. Here are the key details to keep handy:
- Local Emergency Services: Know the direct dial numbers for police, fire, and medical services.
- Company Contacts: List the phone numbers of your supervisor and HR department.
- Personal Emergency Contacts: Include phone numbers for family members or close friends.
- Medical Information: Note any allergies, medications, and medical conditions.
Use the table below to organize your emergency contact information:
| Contact Type | Contact Name | Phone Number |
|---|---|---|
| Emergency Services | Fire Department | 911 |
| Company Contact | John Doe (Supervisor) | 555-123-4567 |
| Personal Contact | Jane Smith (Wife) | 555-987-6543 |
| Medical Information | Dr. Adams (Physician) | 555-222-3344 |
Label emergency contact sheets clearly and place them in accessible locations. Make sure everyone on the team knows where to find this information. This ensures quick and efficient response in case of any mishap.
Training And Certification
Working as an electrician requires a deep understanding of electrical systems and strict adherence to safety protocols. Training and certification are critical components for ensuring both personal safety and the safety of others. These guidelines help electricians navigate complex electrical environments while minimizing risks.
Importance Of Training
Training is essential for electricians to develop the skills and knowledge needed to perform their job safely and efficiently. The following points highlight the importance of comprehensive training:
- Safety Awareness: Training programs teach electricians to recognize and mitigate potential hazards.
- Technical Skills: Electricians learn to handle various tools and equipment, ensuring proper use and maintenance.
- Regulatory Compliance: Electricians are educated on local and national electrical codes, ensuring legal and safe practices.
- Problem-Solving: Training enhances an electrician’s ability to troubleshoot and resolve electrical issues.
Training can be conducted in different formats, including:
| Type of Training | Benefits |
|---|---|
| On-the-Job Training | Hands-on experience under the guidance of seasoned professionals |
| Classroom Training | Structured learning environment with theoretical and practical components |
| Online Courses | Flexible learning options for continued education |
Investing in quality training ensures electricians are well-prepared to handle the demands of their job safely.
Certification Programs
Certification programs validate an electrician’s expertise and adherence to industry standards. These programs are essential for career advancement and legal compliance. Key benefits of certification include:
- Professional Credibility: Certifications enhance an electrician’s reputation and trustworthiness.
- Higher Earning Potential: Certified electricians often command higher salaries.
- Access to Better Job Opportunities: Many employers prefer or require certified electricians.
Common certification programs for electricians include:
- Journeyman Electrician Certification: Requires a combination of classroom education and on-the-job training.
- Master Electrician Certification: Advanced certification requiring several years of experience and passing a comprehensive exam.
- Specialty Certifications: Focus on specific areas such as residential, commercial, or industrial electrical work.
Certification programs often include a mix of written exams and practical assessments. Maintaining certification may require continuing education to stay updated with the latest industry standards and technologies.
Participating in reputable certification programs ensures electricians are recognized as qualified professionals, capable of performing their duties safely and effectively.
Site Safety Protocols
Electricians face various hazards daily. Following site safety protocols is crucial to ensure everyone’s safety. These protocols help minimize risks and create a safer working environment. Here, we discuss important aspects of site safety, focusing on site assessment and emergency evacuation plans.
Site Assessment
A thorough site assessment is the foundation of safety on any job site. Electricians must evaluate the site to identify potential hazards. This step helps in planning safe work practices.
Key elements of site assessment include:
- Identifying Electrical Hazards: Look for exposed wires, overloaded circuits, and faulty equipment.
- Assessing Work Area: Ensure the workspace is clean and free of obstacles.
- Checking Safety Equipment: Verify that all safety gear, such as gloves and helmets, are in good condition.
- Evaluating Environmental Factors: Consider weather conditions and lighting that may affect work.
Electricians should document their findings in a safety report. This report should be shared with the entire team.
| Hazard | Action |
|---|---|
| Exposed Wires | Insulate or cover wires |
| Overloaded Circuits | Distribute load evenly |
| Faulty Equipment | Repair or replace equipment |
Emergency Evacuation Plans
Having a clear emergency evacuation plan is crucial for electricians. This ensures everyone knows what to do in case of an emergency.
Steps to create an effective evacuation plan:
- Establish Exit Routes: Identify and mark all exit routes clearly.
- Assign Roles: Designate responsibilities to team members, such as a fire warden.
- Conduct Drills: Regularly practice evacuation drills to ensure everyone is familiar with the process.
- Communicate the Plan: Ensure all team members understand the evacuation plan and their roles.
Emergency contact numbers should be easily accessible. Keep a list of important contacts, such as fire department and medical services, on-site.
| Contact | Number |
|---|---|
| Fire Department | 123-456-7890 |
| Medical Services | 098-765-4321 |
| Site Supervisor | 555-555-5555 |
Regularly review and update the evacuation plan to address any changes in the site layout or team composition.

Credit: pt.pinterest.com
Staying Informed
Electricians must always prioritize safety. Staying informed is a key part of this. By keeping up with the latest regulations and engaging in continuous education, electricians can ensure they are working safely and effectively.
Updates On Regulations
Electricians must stay updated on the latest regulations. New rules can come out often. These updates can affect how electricians do their jobs. Missing out on these updates can lead to unsafe practices and legal issues. Here are some ways to stay informed:
- Subscribe to Industry Newsletters: Many organizations send out regular updates about new regulations and safety guidelines.
- Join Professional Associations: Associations like the National Electrical Contractors Association (NECA) provide timely updates and resources.
- Attend Webinars and Workshops: These events often cover the latest changes in regulations and best practices.
Here’s a table summarizing key resources for regulation updates:
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Industry Newsletters | Regular updates on regulations and safety guidelines |
| Professional Associations | Access to resources and timely updates |
| Webinars and Workshops | In-depth coverage on regulatory changes |
Continuous Education
Continuous education is essential for electricians. The industry is always evolving. New technologies and methods are introduced regularly. Keeping skills up-to-date ensures safety and efficiency. Here are some ways to engage in continuous education:
- Enroll in Certification Programs: These programs provide in-depth knowledge and practical skills.
- Participate in Online Courses: Many platforms offer courses on the latest electrical technologies and safety practices.
- Attend Industry Conferences: Conferences are great for learning about the latest trends and networking with other professionals.
A well-informed electrician is a safe electrician. Continuous education helps in mastering new skills and staying ahead in the industry. Below is a list of some valuable education resources:
- Certification Programs: Offered by various educational institutions and professional bodies.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and LinkedIn Learning.
- Industry Conferences: Events like the National Electrical Code (NEC) Conference and Electrical Safety Workshop (ESW).
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Basic Electrical Safety Tips?
Basic electrical safety tips include wearing protective gear, using insulated tools, and turning off power sources. Always check equipment for damage before use.
How Can Electricians Prevent Electrical Hazards?
Electricians can prevent hazards by following safety protocols, using proper tools, and regularly inspecting equipment. Proper training is essential.
Why Is Ppe Important For Electricians?
PPE, or Personal Protective Equipment, protects electricians from electrical shocks, burns, and other injuries. It’s crucial for safety.
What Should Electricians Do In An Emergency?
In an emergency, electricians should shut off power, call emergency services, and provide first aid if safe. Stay calm and focused.
Conclusion
Practicing safety is essential for electricians. Following these guidelines can prevent injuries and ensure a secure work environment. Always prioritize proper training and use the right tools. Stay updated with safety standards and wear appropriate protective gear. By doing so, electricians can perform their duties safely and efficiently.




