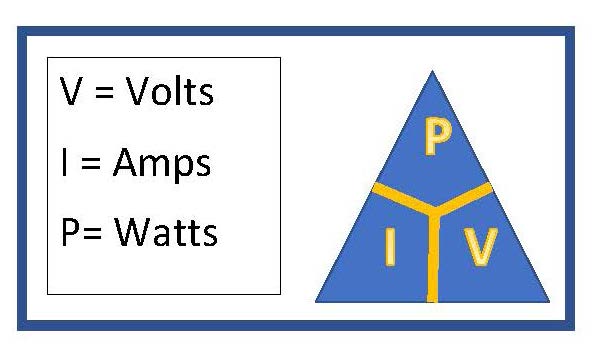
Watt’s Law states that power equals voltage multiplied by current (P = V * I). This fundamental principle links electrical power, voltage, and current.
Watt’s Law is a cornerstone concept in electrical engineering and physics. It helps in understanding how electrical power works within circuits. Knowledge of this law is essential for designing and troubleshooting electrical systems. Watt’s Law is crucial for calculating the power consumption of devices, making it integral to energy efficiency.
This law provides a straightforward method for determining the relationship between power, voltage, and current. By mastering Watt’s Law, you can optimize electrical systems for better performance. This understanding is vital in many applications, from household electronics to industrial machinery.
Introduction To Watt’s Law
Watt’s Law is a fundamental concept in electrical engineering. It helps us understand the relationship between power, voltage, and current. This law is named after James Watt, a pioneer in the field of power measurement.
Historical Background
James Watt, a Scottish inventor, made significant contributions to the study of power. He is best known for improving the steam engine in the 18th century. His work laid the groundwork for modern electrical power measurement. Watt’s Law, named in his honor, is essential in understanding electrical systems.
Importance In Modern Electrical Engineering
Watt’s Law is crucial in designing and analyzing electrical circuits. It helps engineers calculate the power consumption of various devices. Understanding this law is essential for efficient energy use.
| Component | Symbol | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Power | P | Watts (W) |
| Voltage | V | Volts (V) |
| Current | I | Amperes (A) |
Watt’s Law can be expressed with the formula:
P = V I- P: Power in Watts
- V: Voltage in Volts
- I: Current in Amperes
Using this formula, engineers can predict how much power a circuit will use. This is critical for safe and efficient electrical system design.
Basic Principles
Understanding the basic principles of Watt’s Law is important for electrical engineering. This law helps explain the relationship between power, voltage, and current. It is simple and easy to apply.
Power, Voltage, And Current Relationship
Power is the rate at which electrical energy is consumed or generated. It is measured in watts (W). Voltage is the electrical potential difference between two points. It is measured in volts (V). Current is the flow of electric charge. It is measured in amperes (A).
Watt’s Law shows a direct relationship between these three. Power depends on both voltage and current. If you increase voltage, power increases. If you increase current, power also increases.
Mathematical Expression
The mathematical expression of Watt’s Law is very straightforward. It is:
P = V × IHere:
- P stands for Power in watts.
- V stands for Voltage in volts.
- I stands for Current in amperes.
To find power, multiply voltage by current. To find voltage, divide power by current. To find current, divide power by voltage.
| Parameter | Symbol | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Power | P | Watts (W) |
| Voltage | V | Volts (V) |
| Current | I | Amperes (A) |
Applications In Daily Life
Watt’s Law is essential in understanding electrical power. It helps us calculate power usage in various devices. This is crucial for energy efficiency. Let’s explore its applications in daily life.
Household Appliances
Watt’s Law helps us determine the power consumption of household appliances. Knowing this can save on electricity bills. For example, consider a refrigerator:
- Voltage: 120V
- Current: 5A
Using Watt’s Law:
Power (P) = Voltage (V) x Current (I)The power consumption is: 600W.
This knowledge helps choose energy-efficient devices.
Industrial Equipment
In industries, Watt’s Law is crucial. It ensures machines run efficiently. Consider an electric motor:
- Voltage: 240V
- Current: 10A
Using Watt’s Law:
Power (P) = Voltage (V) x Current (I)The power consumption is: 2400W.
Knowing this helps manage energy costs. It also ensures safe operation of equipment.

Credit: shopsolarkits.com
Enhancing Energy Efficiency
Watt’s Law is crucial for understanding electrical power. It helps optimize energy usage. Enhancing energy efficiency is vital for both cost savings and environmental protection. Let’s explore how Watt’s Law can enhance energy efficiency.
Optimizing Electrical Devices
Using Watt’s Law, you can optimize electrical devices. Knowing the relationship between power, voltage, and current helps in device selection. Choose devices with lower power consumption to save energy.
Watt’s Law Formula:
P = V × I
Where:
P = Power (Watts)
V = Voltage (Volts)
I = Current (Amperes)
Let’s see an example:
| Device | Voltage (V) | Current (I) | Power (P) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LED Bulb | 120 | 0.1 | 12 Watts |
| Incandescent Bulb | 120 | 0.83 | 100 Watts |
From the table, LED bulbs consume less power. This means they are more energy-efficient.
Reducing Energy Loss
Energy loss happens due to resistance in wires and devices. Using Watt’s Law helps identify and reduce energy loss. Choose materials with low resistance to minimize loss.
Factors Affecting Energy Loss:
- Wire material
- Wire length
- Current flow
Here are some tips to reduce energy loss:
- Use copper wires. They have low resistance.
- Shorten wire lengths. This reduces resistance.
- Limit current flow. Lower current means less energy loss.
By following these tips, you can significantly reduce energy loss.
Case Studies
Watt’s Law is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering. Understanding its application in real-world scenarios is crucial. This section highlights case studies that demonstrate Watt’s Law in action.
Real-world Examples
Electric circuits in homes follow Watt’s Law. For instance, a 100-watt light bulb running on 120 volts draws a current of 0.83 amperes.
| Appliance | Power (Watts) | Voltage (Volts) | Current (Amperes) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light Bulb | 100 | 120 | 0.83 |
| Refrigerator | 200 | 120 | 1.67 |
| Microwave | 1200 | 120 | 10 |
Lessons Learned
From these examples, we learn that Watt’s Law helps in calculating current. This ensures the safe operation of electrical devices.
- Safety: Knowing current prevents circuit overloads.
- Efficiency: Accurate calculations enhance energy efficiency.
- Cost Savings: Proper understanding reduces electricity bills.
Implementing Watt’s Law in daily life improves electrical safety and efficiency.

Credit: www.engineeringclicks.com
Common Misconceptions
Understanding Watt’s Law is crucial for anyone in electronics. However, there are many common misconceptions that can lead to confusion. Let’s clarify these misunderstandings for better comprehension.
Myth Vs. Reality
Many people believe Watt’s Law is complicated. In reality, it’s simple. Watt’s Law states that power (P) equals voltage (V) times current (I). This formula is P = V x I. Some think Watt’s Law is only for advanced users. But it’s useful for everyone, even beginners.
- Myth: Watt’s Law is only for experts.
- Reality: Anyone can use Watt’s Law easily.
- Myth: Watt’s Law is different from Ohm’s Law.
- Reality: Both laws are related and equally important.
Clarifying Common Errors
There are frequent mistakes in applying Watt’s Law. These errors can lead to incorrect calculations. Let’s look at the most common ones:
- Incorrect Units: Always use volts for V, amps for I, and watts for P.
- Ignoring Resistance: Resistance affects voltage and current. Consider it in your calculations.
- Confusing Formulas: Remember, P = V x I. Do not mix it with other formulas.
Here is a table to help you remember the correct units:
| Variable | Unit |
|---|---|
| Voltage (V) | Volts (V) |
| Current (I) | Amps (A) |
| Power (P) | Watts (W) |
Understanding these points ensures accurate use of Watt’s Law. It helps in real-life applications and projects.
Future Trends
Watt’s Law is fundamental in electrical engineering. It defines the relationship between power, voltage, and current. As technology evolves, new trends are emerging in its application.
Innovations In Electrical Engineering
Innovations are shaping the future of electrical engineering. These advancements improve efficiency and performance.
- Smart Grids: Smart grids use digital technology for better power distribution. They enhance reliability and efficiency.
- Wireless Power Transfer: This technology allows devices to charge without cables. It’s useful for electric vehicles and mobile gadgets.
- Advanced Semiconductors: New materials like graphene are revolutionizing semiconductors. They offer higher speeds and lower power consumption.
Sustainable Practices
Sustainability is crucial in modern electrical engineering. New practices aim to reduce environmental impact.
| Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Renewable Energy Sources | Using solar, wind, and hydropower reduces reliance on fossil fuels. |
| Energy Efficiency | Improving systems to use less energy while maintaining performance. |
| Recycling Electronics | Proper disposal and recycling of electronics prevent e-waste pollution. |
These trends showcase how Watt’s Law continues to influence modern engineering. They highlight the importance of innovation and sustainability in the field.

Credit: www.elprocus.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Watt’s Law?
Watt’s Law relates power, voltage, and current. It states that power equals voltage multiplied by current. It helps calculate electrical power in circuits.
How To Apply Watt’s Law?
To apply Watt’s Law, multiply the voltage by the current. This provides the power in watts. It’s crucial for electrical engineering.
Why Is Watt’s Law Important?
Watt’s Law is vital for understanding electrical power. It helps design and troubleshoot electrical systems. It’s fundamental in electrical engineering.
Can Watt’s Law Be Used In Ac Circuits?
Yes, Watt’s Law applies to both AC and DC circuits. However, for AC, consider power factor. It’s essential for accurate calculations.
Conclusion
Understanding Watt’s Law is crucial for anyone working with electrical systems. It helps ensure safety and efficiency. By mastering this fundamental concept, you can make better decisions in your projects. Keep learning and applying Watt’s Law to achieve optimal performance and reliability in your electrical endeavors.