Resistance Training: Unlock Strength and Endurance Benefits
Resistance is the opposition to the flow of electric current. It is measured in ohms (Ω). Resistance plays a crucial role in electrical circuits. It determines how much current flows […]
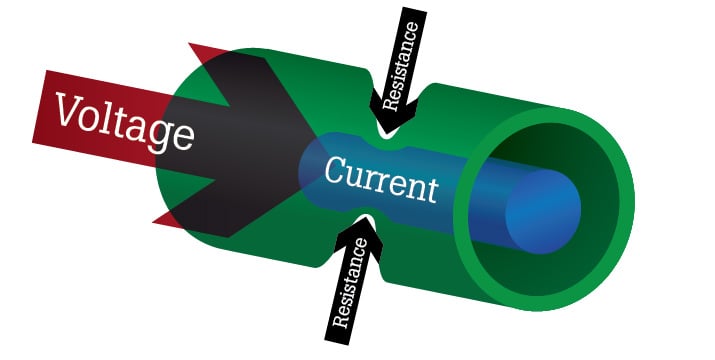
Resistance is the opposition to the flow of electric current. It is measured in ohms (Ω). Resistance plays a crucial role in electrical circuits. It determines how much current flows […]
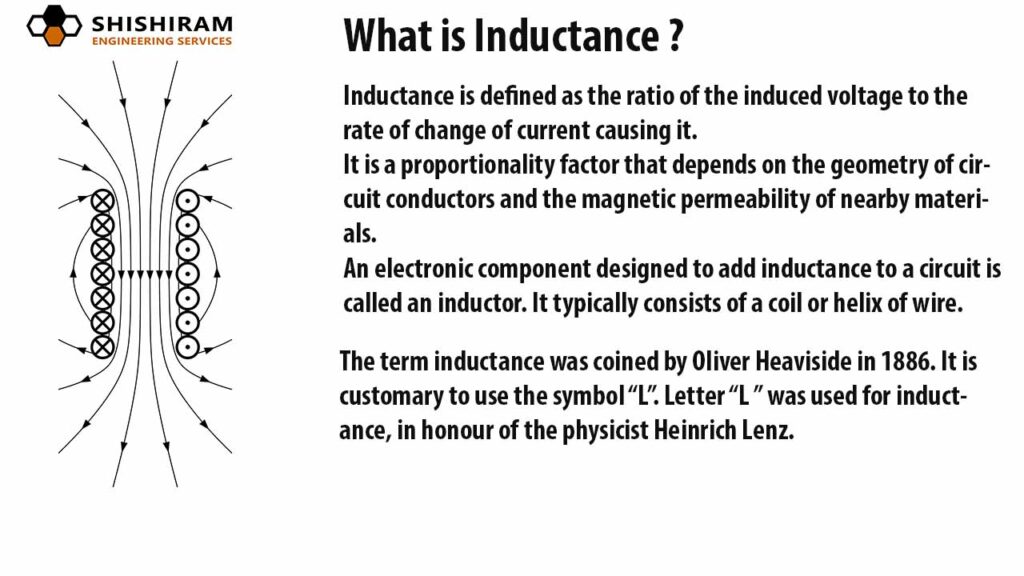
Inductance is the property of an electrical conductor that opposes changes in current. It is measured in henries (H). Inductance plays a crucial role in electrical circuits. It helps manage […]
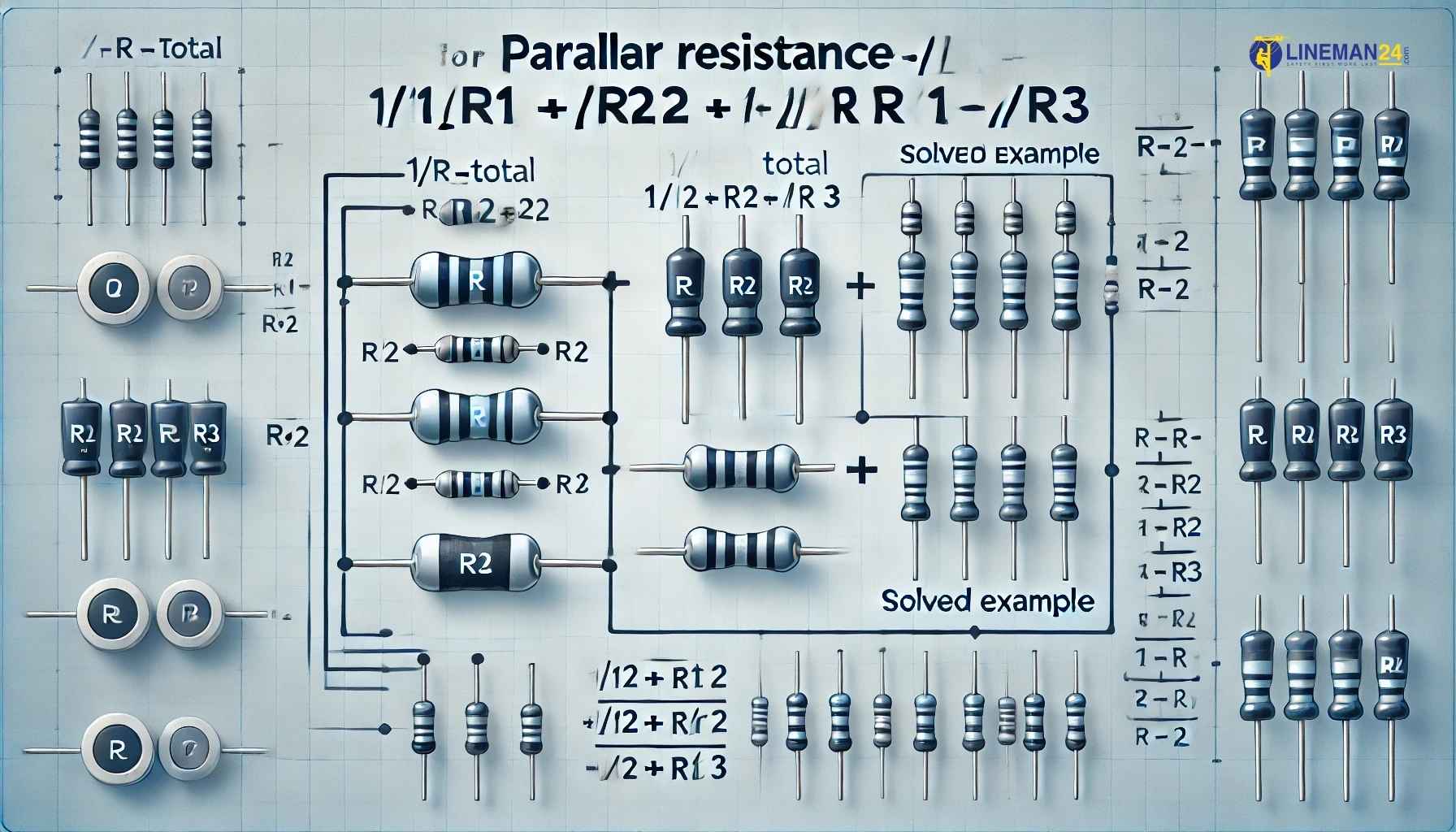
To calculate resistors in parallel, use the formula 1/R_total = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3. This gives the total resistance. Resistors in parallel circuits often find usage in electronic […]

An essential electrician’s tool list includes pliers, screwdrivers, wire strippers, and a multimeter. These tools are crucial for any electrical work. Electricians rely on a variety of tools to perform […]
To calculate current in a parallel circuit, use Ohm’s Law for each branch. Sum the currents to find the total. Parallel circuits are common in electrical systems. They allow multiple […]
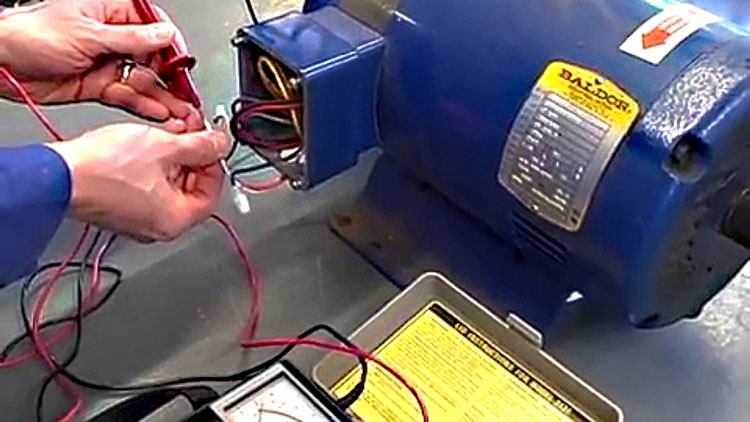
**What is Megger Testing? ** Megger testing measures the insulation resistance of electrical components. It ensures the safety and efficiency of electrical systems. **** Megger testing is crucial in maintaining […]
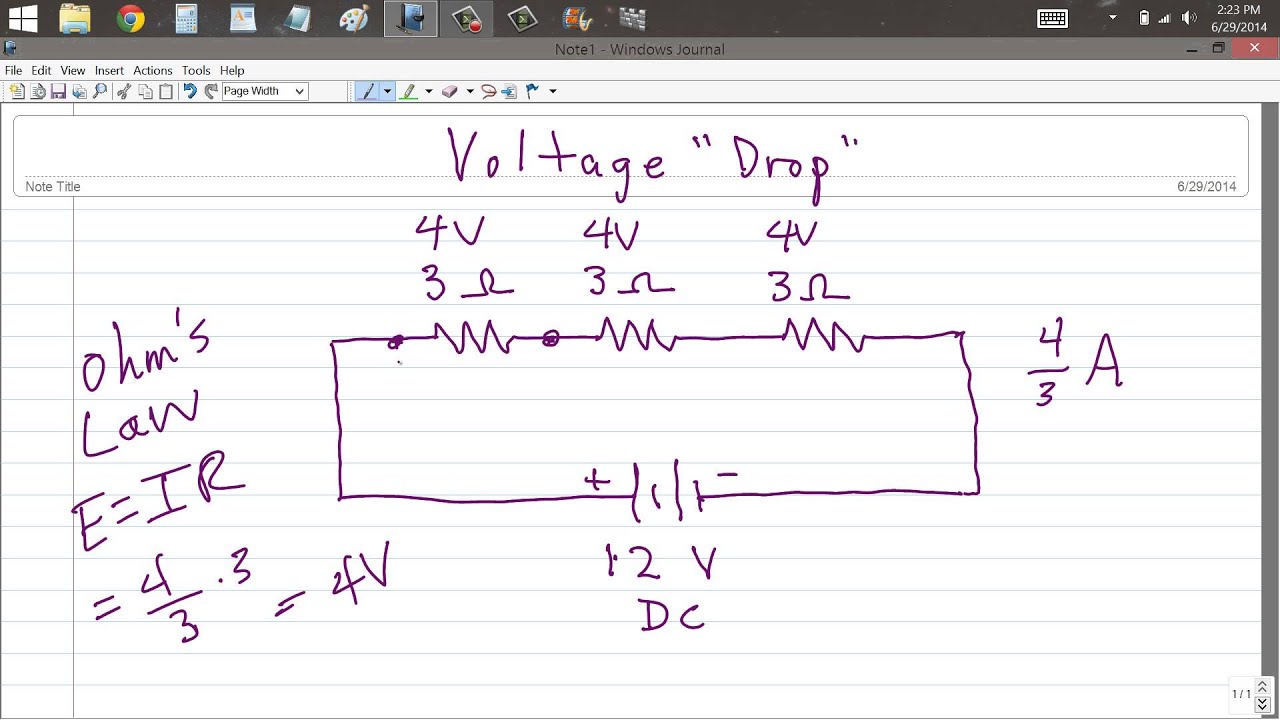
**Accurate Answer:** Voltage drop occurs when electrical current flows through a conductor, causing a loss of voltage. This can affect the performance of electrical devices. **** Voltage drop is a […]
Capacitance in series results in a lower overall capacitance than any single capacitor in the series. The formula is 1/C_total = 1/C1 + 1/C2 + 1/C3. Capacitance in series is […]
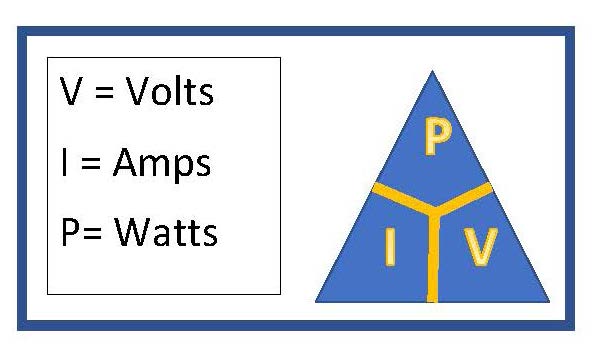
Watt’s Law states that power equals voltage multiplied by current (P = V * I). This fundamental principle links electrical power, voltage, and current. Watt’s Law is a cornerstone concept […]
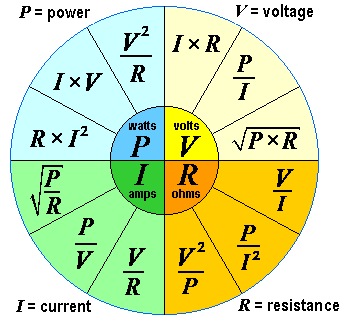
The Power Formula is P = IV, where P is power, I is current, and V is voltage. It calculates electrical power in circuits. Understanding the Power Formula is essential […]