Renewable resources examples include solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal, and biomass energy sources. These sustainable resources are replenished naturally and can provide an alternative to nonrenewable resources, such as oil and coal.
Investing in renewable energy can reduce carbon emissions, promote energy independence, and create job opportunities in the clean energy sector. Renewable resources are becoming increasingly important in the fight against climate change. As the world transitions to a more sustainable future, the need for clean, renewable energy sources is becoming more urgent.
Solar and wind power are the most popular forms of renewable energy, but hydropower, geothermal, and biomass energy are also viable options. These resources are abundant and can be harnessed to power homes, businesses, and even entire cities. We will explore the different types of renewable resources and how they can be used to benefit the environment and reduce our dependence on nonrenewable resources.
Solar Energy
Solar energy is an excellent example of a renewable resource. It uses the sun’s energy to power homes, businesses, and vehicles. By harnessing the power of the sun, we can reduce our reliance on non-renewable resources and move towards a more sustainable future.
Solar energy is one of the fastest-growing sources of renewable energy with enormous potential to fulfill global energy requirements sustainably. It is obtained from the radiant energy of the sun and can be harnessed using various technologies. Let’s explore the three primary methods of harnessing solar energy: Photovoltaic Cells, Concentrated Solar Power, and Solar Water Heating.

Photovoltaic Cells
Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are devices that convert sunlight directly into electricity. These cells are made of a semiconductor material, usually silicon, arranged in a thin film. When photons from sunlight hit the semiconductor, they knock loose electrons from their atoms, allowing them to flow freely. This flow of electrons generates direct current (DC) electricity. PV cells can power homes, vehicles, and even spacecraft, making them a versatile source of renewable energy.
Concentrated Solar Power
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) uses mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a small area, which then heats up a fluid, usually water, to create steam. The steam drives a turbine to generate electricity. CSP systems are of three types – parabolic trough, power tower, and dish/engine system. These systems are used in large power plants and are becoming increasingly popular because they can generate power even when the sun isn’t shining.
Solar Water Heating
Solar water heating is a technology that uses the sun’s energy to heat water. It is an excellent alternative to traditional water heating systems that consume electricity or gas to heat water. A solar water heating system consists of a solar collector that absorbs radiant energy from the sun and transfers it to the water. The heated water is then stored in an insulated tank and used for various applications, such as bathing, washing, and cooking. Solar water heating systems are widely used in residential and commercial buildings, especially in areas with abundant sunlight. In conclusion, Solar Energy is a reliable and sustainable source of renewable energy. These three techniques; Photovoltaic Cells, Concentrated Solar Power, and Solar Water Heating stand out as examples of alternative ways of producing power that meet modern-day environmental goals and requirements.
Wind Energy
Wind energy is a great example of a renewable resource. The energy harnessed from wind can be used to generate electricity and can be a sustainable alternative to non-renewable sources. It is clean, renewable, and produces no harmful emissions, making it a popular choice for reducing carbon footprints.
Renewable energy sources are becoming more popular as people are becoming aware of the importance of preserving our planet’s resources. Wind energy is one of the most rapidly growing renewable energy sources. It is clean and accessible, making it an excellent alternative to traditional sources of energy. Wind turbines are used to convert wind energy into electricity and they come in two main types: horizontal-axis wind turbines and vertical-axis wind turbines.
Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines
Horizontal axis wind turbines are the most commonly used type of wind turbine. These turbines have a rotor that spins around a horizontal axis. The blades are designed in a way that captures the wind and rotates the rotor, which is connected to a generator that converts the energy into electricity. These turbines range in size from small residential turbines to industrial-scale turbines that can generate enough energy to power entire communities.
Vertical Axis Wind Turbines
Vertical axis wind turbines have their rotor shaft positioned vertically. The blades have a helical twist that rotates around a vertical axis. The advantages of these turbines are their ability to operate in lower wind speeds, less noise pollution, and less bird mortality. These turbines work on a completely different principle than the horizontal-axis wind turbines. The rotor is connected directly to the generator, reducing mechanical complexity and maintenance requirements. Overall, wind turbines have unique capabilities of generating sustainable energy while being eco-friendly. They offer a great alternative to traditional energy sources, and through advancements in technology, wind turbines will continue to become more effective and efficient at generating clean energy for our planet.
Hydro Energy
Hydro energy is a prime example of a renewable energy sources as it relies on the continuous flow of water to generate electricity. With the increasing demand for clean energy, hydro energy has become an attractive alternative to fossil fuels and is expected to continue to grow in popularity.
Hydro energy, also known as hydroelectric power, is a renewable resource that utilizes the kinetic and potential energy of running water to generate electricity. It is one of the most widely used and reliable sources of renewable energy, accounting for nearly one-fifth of the world’s electricity supply. In this section, we’ll take a closer look at two types of hydro energy: large and small hydroelectric dams and tidal and wave energy.
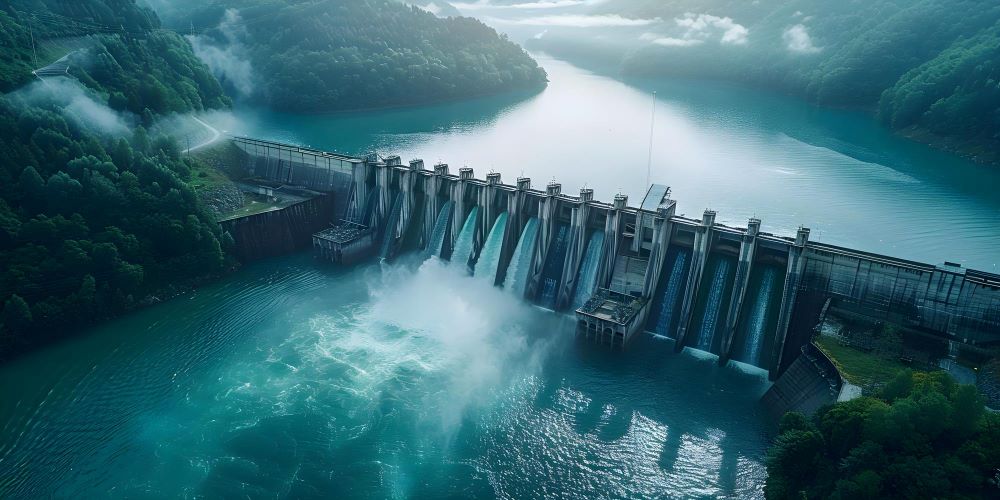

Large And Small Hydroelectric Dams
Large hydroelectric dams are typically built on large rivers and provide a significant amount of energy. These dams have a storage reservoir that can generate power on demand, making them incredibly useful for meeting peak electricity demands. Small hydroelectric dams, on the other hand, are built on small streams and rivers and generate power for local communities. They’re used to supplement power from larger power grid systems and reduce overall energy costs.
Tidal And Wave Energy
Tidal and wave energy are forms of hydroenergy that harness the natural movements of the ocean to generate electricity. Tidal energy is generated by large tidal barrages or tidal turbines that utilize the ebb and flow of ocean tides to generate power. Wave energy, on the other hand, uses the motion of waves to generate electricity. While tidal and wave energy currently account for a small fraction of renewable energy production, they have enormous potential for growth and could become significant sources of renewable energy in the future. Overall, hydroenergy is an important and reliable source of renewable energy that has been utilized for over a century. Large and small hydroelectric dams and tidal and wave energy are just a few examples of how we can harness the power of water to create clean, sustainable energy. As we continue to look for sustainable ways to power our homes and businesses, hydro energy will likely remain an important part of the renewable energy mix.
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy is one of the most popular renewable resources examples. It is an environmentally friendly and sustainable form of energy that harnesses the heat from the earth’s core to generate electricity without producing greenhouse gases. The use of geothermal power can help to reduce our dependence on non-renewable sources of energy and contribute to a cleaner and greener future.
Geothermal energy is a renewable resource that can be harnessed from the earth’s internal heat by extracting it and converting it into usable energy. This sustainable source of energy has a low impact on the environment making it an ideal solution to reduce harmful emissions and dependence on fossil fuels.

Direct Use Of Geothermal Energy
Direct use of geothermal energy involves using naturally occurring steam or hot water for space heating, industrial processes, and agriculture. It is the oldest form of geothermal energy usage and has been employed for thousands of years. Today, direct use of geothermal energy is used to heat greenhouses, swimming pools, homes, and buildings.
Geothermal Heat Pumps
Geothermal heat pumps or ground source heat pumps have gained popularity in recent years because of their high energy efficiency and the ability to use them in any region. They work by harnessing the earth’s constant temperature to heat and cool buildings. Geothermal heat pumps use underground pipes that circulate water or refrigerant to transfer heat to and from the ground.
Geothermal Power Plants
Geothermal power plants are used to convert geothermal energy into electricity. There are three types of geothermal power plants: dry steam, flash steam, and binary cycle. Dry steam plants utilize steam from underground wells to directly drive the turbines. Flash steam plants utilize high-pressure hot water to generate steam to turn the turbines, while binary cycle plants use a heat exchanger to transfer geothermal heat to a secondary fluid for use in generating electricity. In conclusion, geothermal energy is a sustainable resource that offers different ways to harness and use it. By employing direct use, geothermal heat pumps, and geothermal power plants, we can reduce dependence on fossil fuels, limit harmful emissions, and secure a sustainable future for generations to come.
Bioenergy
Bioenergy is a form of renewable energy derived from natural and organic matter that has undergone photosynthesis. It is a reliable and sustainable source of power that can reduce carbon emissions by substituting non-renewable energy sources. Bioenergy can either be converted into electricity, heat, or fuel, making it a versatile option. Among the forms of bioenergy, biofuels, biogas, and biomass are the most prevalent.
Biomass
Biomass is the organic matter obtained from living organisms, such as plants and animals, and their by-products. It is regarded as a renewable energy resource because it can be replenished by natural processes. Biomass can be used to generate electricity, heat, and fuel. Some examples of biomass include wood chips, leaves, corn, and agricultural waste. The use of biomass as a fuel source is known as bioenergy.
Biofuels
Biofuels are derived from biomass conversion and used as an alternative to fossil fuels. The two primary types of biofuels are ethanol and biodiesel. Ethanol is made by fermentation processes using crops like corn, wheat, or sugar cane, while biodiesel is produced from vegetable oil or animal fat. The use of biofuels has gained popularity in recent years as an attempt to reduce carbon emissions and make transportation more sustainable.
Biogas
Biogas is a renewable energy source obtained from the decomposition of organic matter in the absence of oxygen. It is composed of methane, carbon dioxide, and trace amounts of other gases. Biogas is typically produced by anaerobic digestion of agricultural waste, sewage, waste food, and crops. It can be used as a fuel for heating, cooking, and electricity generation.
In summary, bioenergy is a sustainable energy source that can play a significant role in achieving global climate goals. Among its various forms, biomass, biofuels, and biogas are the most used. Countries should explore and implement bioenergy to meet their energy demands and contribute to the fight against climate change.
Hydrogen Fuel Cells
One example of a renewable resource is hydrogen fuel cells, which can be used to generate electricity and power vehicles. These cells use hydrogen and oxygen to create energy, with the only byproduct being water.
Hydrogen fuel cell technology is making significant progress as researchers continue to explore it as a clean energy source for transportation. Hydrogen fuel cells convert the chemical energy stored in hydrogen into usable electricity by chemically reacting with oxygen from the air. Here are two types of hydrogen fuel cells:
Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells
Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) fuel cells are one of the most common types of fuel cells used in vehicles and stationary power. PEM fuel cells work by passing hydrogen gas through a catalyst that separates it into protons and electrons. The protons pass through a special membrane, while the electrons create an electric current. PEM fuel cells can operate at low temperatures and respond quickly to changes in power demand. Its efficiency and reliability have made it a preferred choice in the automotive sector.
Alkaline Fuel Cells
Alkaline fuel cells have been around since the 1960s and were the first type of fuel cell used in the American space program. Alkaline fuel cells use an electrolyte made up of a solution of potassium hydroxide dissolved in water to conduct ions between the electrodes. The high-temperature operation of alkaline fuel cells makes them ideal for underwater vehicles, but their high sensitivity to carbon dioxide limits their use in other applications. Hydrogen fuel cell technology is a promising solution for transportation and energy needs, caused by the drive for cleaner, renewable energy sources that can help mitigate climate change effects. As a writer, it’s crucial to understand and keep up-to-date with renewable resources, especially examples like hydrogen fuel cells, that have the potential to revolutionize our planet’s energy production.
Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion
Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) is a renewable energy technology that utilizes the temperature difference between cooler deep ocean water and warmer surface water to generate electricity. It is a promising example of how we can harness renewable resources to meet our energy demands sustainably.
Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) is a process that converts the temperature difference between warm surface seawater and cold deep seawater into electricity. OTEC is a renewable resource, which is an alternative to fossil fuel resources. It is a clean and reliable source of energy that can be used to produce electricity. OTEC technology is mainly used in countries that are located in the tropical regions.
Open Cycle Otec
In the open cycle, OTEC seawater is introduced into a low-pressure chamber, where it is vaporized by the warm surface seawater. The steam produced is used to drive a turbine connected to the generator to produce electricity. The cold deep seawater is then pumped to condense the steam.
Closed Cycle Otec
The closed cycle uses a working fluid such as ammonia or propylene to vaporize at a low temperature. This vapor is then used to drive the turbine, generating electricity. The warm surface seawater is used to heat the fluid in the evaporator. The cold deep seawater is used to condense the working fluid, which is then returned to the evaporator. OTEC has significant potential for generating energy. It is suitable for tropical maritime environments where the temperature difference between the surface and deep seawater is greater than 20°C. The energy generated from OTEC can be used to power desalination plants, air-conditioning systems, and other industrial processes, which are essential for countries located in tropical regions.
Waste-to-energy
Waste-to-Energy is a prime example of renewable resources. It involves the process of converting waste materials like garbage and biomass into usable energy sources such as electricity, heat, and fuel. This not only reduces waste but also helps in sustainable energy production.
Waste-to-energy is the process of generating energy from waste materials. It refers to any technology that converts waste, including organic wastes and biomass, into heat, electricity, or fuel. This technology is gaining popularity as it helps in reducing the dependence on fossil fuels and at the same time, managing waste products responsibly.
Incineration
Incineration is a waste-to-energy conversion process where waste materials are burned at high temperatures to produce steam and electricity. The process is widely used in waste management systems to reduce the amount of waste going into landfills. Incineration can handle various types of waste materials, including municipal, medical, and hazardous wastes.
Gasification
Gasification is a process that converts solid carbon-based materials into synthetic gas or syngas. The process involves heating waste materials such as wood chips or agricultural residues in the absence of oxygen to produce syngas and other solid by-products. The syngas can be used as fuel in power plants or for heating purposes.
Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a process that converts waste materials, such as biomass or plastic, into liquid fuel, gas, and biochar. The process involves heating the waste materials in the absence of oxygen, creating a chemical reaction that breaks down the waste molecules into the desired outputs. Biofuels produced through pyrolysis can be used directly for energy or refined further to produce transportation fuels such as gasoline and diesel.
These waste-to-energy technologies offer practical solutions for creating clean energy and reducing waste. By adopting these technologies, we can create a cleaner and sustainable future.
Energy Storage
Energy storage using renewable resources is a crucial factor in the transition towards a more sustainable future. Examples of energy storage include batteries, pumped hydro storage, and thermal storage, all of which play a vital role in maximizing the potential of renewable energy sources.
Renewable sources such as solar and wind energy have one downside: they are not always available on demand. One way to combat this issue is through the use of energy storage. Energy storage technologies include chemical, mechanical, and thermal methods. Energy storage systems are capable of smoothing out the power output of renewable sources, allowing for a steady supply to the grid.
Battery Storage
Battery storage systems are one of the most commonly used energy storage systems because of their versatility and efficiency. Batteries store energy in chemical form, which can be converted back to electrical energy when needed. The most prevalent type of battery used for energy storage is the lithium-ion battery, known for its high energy density and long cycle life.
Flywheels
A flywheel is a mechanical energy storage system that stores kinetic energy in the form of rotational motion. The flywheel is typically made up of a heavy rotating disc, which spins very fast on mechanically levitated bearings. When energy is needed, the stored kinetic energy in the flywheel can be converted back into electrical energy.
Thermal Energy Storage
Thermal energy storage refers to the storage of thermal energy in materials such as water, ice, and rocks. Thermal energy storage can be used in combination with solar power plants to produce electricity even when the sun is not shining. When the sun is available, the thermal energy storage materials are heated, and the stored energy is later used to generate electricity. Overall, energy storage is becoming an increasingly important component of renewable energy systems. It enables us to capture and store energy from renewable sources more efficiently, ultimately making renewable energy a more reliable and consistent source of power.
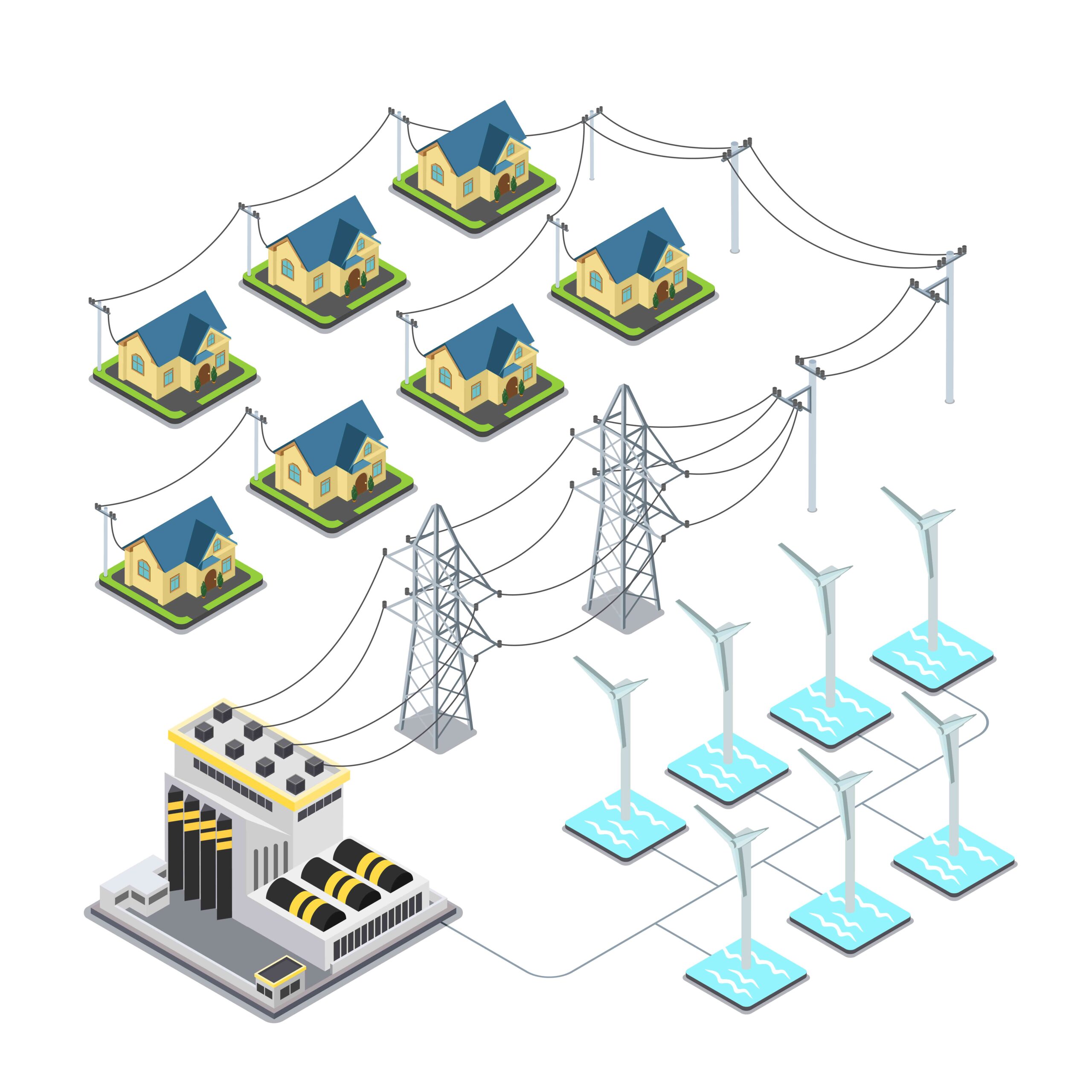
Smart Grid
Smart Grid technology utilizes renewable resources such as wind, solar, and geothermal power to provide efficient and sustainable energy solutions. This enables power companies to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and minimize the overall carbon footprint.
Distribution Automation
Demand Response
Advanced Metering Infrastructure
The Smart Grid is an advanced electrical grid that uses digital technologies to regulate the generation, distribution, and consumption of power in an efficient and sustainable manner. It is characterized by the use of two-way communication technologies that enable utilities, consumers, and renewable energy providers to interact with the grid in real time. One of the benefits of the Smart Grid is the integration of renewable resources, which can help reduce the carbon footprint of electricity production. Here are some examples of renewable resources that can be integrated into the Smart Grid.
Distribution Automation
Distribution Automation is a technology that enables utilities to monitor and control the flow of electricity on the distribution network using advanced sensors, switches, and software. This technology allows utilities to identify and address power outages quickly, minimize disruptions, and improve the reliability of the grid. By integrating renewable resources such as solar and wind power into the distribution network, utilities can optimize the distribution of electricity and reduce the need for conventional energy sources.
Demand Response
Demand Response is a program that encourages consumers to reduce their electricity consumption during periods of high demand by offering them economic incentives. By participating in the program, consumers can reduce their energy bills and help utilities avoid blackouts or brownouts during peak periods. By integrating renewable resources into the grid, utilities can reduce their dependence on fossil fuels and improve the efficiency of the demand response program.
Advanced Metering Infrastructure
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) is a system that uses digital meters to collect and transmit electricity consumption data in real time. This technology allows utilities to monitor and control the distribution of electricity more effectively, identify areas of high demand, and reduce the risk of power outages. By integrating renewable resources into the AMI system, utilities can optimize the distribution of electricity and reduce their carbon footprint while improving the reliability and efficiency of the grid.
Frequently Asked Questions For Renewable Resources Examples
What Are 10 Examples Of Renewable Resources?
Ten examples of renewable resources include solar energy, wind energy, hydroelectric power, geothermal energy, tidal energy, biomass, biofuels, geothermal heat pumps, wave energy, and hydrogen fuel cells.
What Are 5 Renewable Resources?
Renewable resources are those that can be replenished or replaced in a relatively short period of time. The five most common types are solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass. These resources are sustainable and have a lower environmental impact compared to non-renewable resources like oil and coal.
What Are The 7 Types Of Renewable Resources?
The 7 types of renewable resources are solar energy, wind energy, geothermal energy, hydropower, biomass, ocean energy, and hydrogen & fuel cells. They are all-natural, replenishable, and environmentally friendly sources of energy.
What Are 4 Renewable Resources?
Four renewable resources are solar energy, wind energy, hydro energy, and biomass energy.
Conclusion
By now, you must have a thorough understanding of what renewable resources entail and the various examples of these resources. From solar power to wind energy, hydroelectric power, and geothermal energy, the importance of using renewable resources simply cannot be overstated at a time when environmental conservation is becoming increasingly crucial.
The efforts towards reducing carbon footprints and promoting sustainable living depend on the use and promotion of renewable resources, and it is up to everyone to adopt these resources and help create a sustainable future for all.




