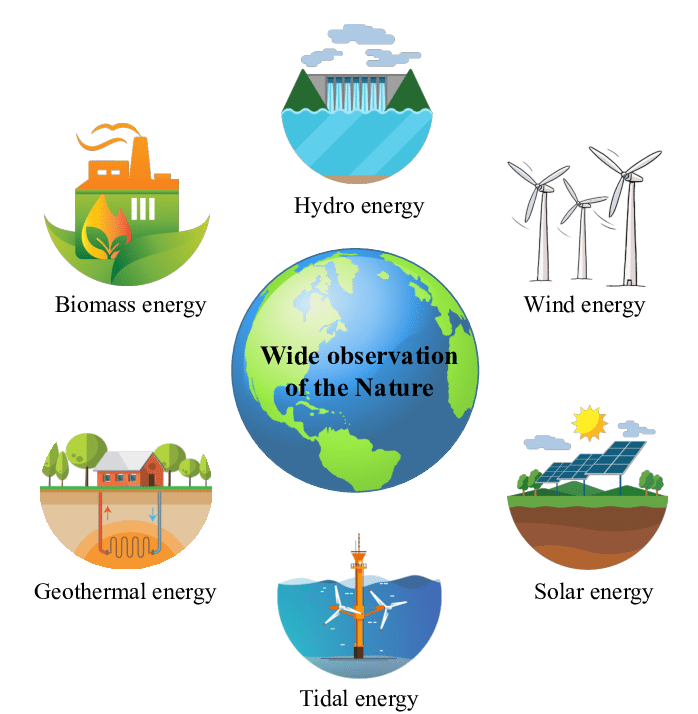
Renewable energy sources tap into natural processes to generate power. Examples include solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass.
Renewable energy sources are essential for sustainable power generation. They harness energy from ongoing natural phenomena like sunlight, wind flow, water currents, earth’s heat, and organic plant matter. Unlike fossil fuels, these sources replenish themselves naturally and reduce carbon emissions, mitigating climate change.
Transitioning to renewables is crucial for energy security, environmental protection, and economic growth. As technology advances, renewable energy becomes more efficient and cost-effective, encouraging widespread adoption. Governments and industries globally are investing in renewable infrastructure to move towards a low-carbon future, creating jobs and fostering innovation in the energy sector. Embracing renewable energy is key to achieving a harmonious balance between human activities and the earth’s ecological systems.
Renewable energy is a gift that keeps on giving. It’s like a superhero for the planet but without the cape. Using energy from the sun, wind, and other natural sources, we make sure there’s enough power for everyone, without hurting our home, Earth. Let’s explore how this energy is not only cool for the environment but also great for our wallets and our security.
Reducing Carbon Emissions
Think of carbon emissions like littering in the sky; the less we do it, the better our air. Renewable energy cuts down this ‘litter’, making the air cleaner for birds, trees, and us! With each gust of wind and ray of sun we harness, we say ‘no’ to dirty air and ‘yes’ to a happy, healthy planet.
Energy Security
Imagine if all your toys came from one friend, and they suddenly moved away. Renewable energy is like having many friends to borrow toys from, so you’re never without. It means our towns and cities can always light up because our energy doesn’t come from one place far away but from all around us, like the sun above and the wind that plays with your hair.
Cost-effectiveness
- Save money in the long run.
- Pay less for energy because the wind and sun are free.
- Once set up, these power plants cost less to run.
No more worries about rising energy bills! With renewable energy, the price for power stays friendly, just like the sun’s warm hello in the morning.
Types Of Renewable Energy Sources
Embracing renewable energy is critical for sustaining our planet. These clean sources reduce pollution and offer infinite power. Let’s explore the vibrant world of renewables.
Solar Energy
Solar panels capture sunlight, transforming it into electricity. This energy powers homes, industries, and even satellites in space. Its abundance makes solar a leading renewable source.
Wind Energy
Turbines harness wind power to produce energy. Wind farms can be on land or at sea. The wind’s natural force spins turbine blades, generating electricity with no harmful emissions.
Hydro Energy
Water flows drive hydroelectric plants. Dams create reservoirs. Water’s movement through turbines generates electricity. This method is highly efficient and reliable, although dependent on geographical locations.
Geothermal Energy
Earth’s heat is a powerful resource. Geothermal plants use steam from underground reservoirs. This steam rotates turbines, producing clean electricity. Iceland excels in using geothermal energy.
Biomass Energy
Biomass comes from organic materials like wood, plants, and waste. When burned, biomass releases energy used for heating and electricity. It’s a renewable cycle as plants regrow over time.
Solar Energy
Solar energy stands out among renewable sources for its vast potential and accessibility. It’s the power extracted from the sun’s rays. This energy is a key player in the global shift towards clean, renewable power. Houses and businesses harness this clean energy using various technologies.

How Solar Energy Works
Solar power begins with the sun. Photovoltaic cells catch sunlight and convert it into electricity. These cells are part of solar panels. Panels come together to form solar systems. These systems convert sunlight instantly into power for use in our homes and gadgets.
Solar Panel Technology
- Monocrystalline Solar Panels: Made from pure silicon, high efficiency.
- Polycrystalline Solar Panels: Blended silicon, cost-effective with moderate efficiency.
- Thin-Film Solar Panels: Flexible and light, but less efficient and degrade faster.
Advantages Of Solar Energy
- Environmentally Friendly: Zero emissions while generating power.
- Reduces Electricity Bills: Generate your own power and save money.
- Low Maintenance Costs: Solar systems need little upkeep.
- Renewable: Unlimited source of energy as long as the sun shines.
Disadvantages Of Solar Energy
| Disadvantage | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Initial Costs: | The initial investment for solar panels and installation is high. |
| Weather Dependent: | Efficiency drops on cloudy days and at night. |
| Space Requirement: | Large areas are needed for panels to produce substantial power. |
| Energy Storage Costs: | Batteries to store energy are an added expense. |
Wind Energy
Embarking on the path of sustainability, wind energy emerges as a beacon of hope. Harnessing the power of the wind is an innovative approach to generating electricity. This eco-friendly energy source plays a significant role in our quest for a greener planet.
How Wind Energy Works
Simply put, wind energy converts airflow into electricity. When the wind blows, it spins the blades of a wind turbine. This motion triggers a generator to produce electrical power. The stronger the wind, the more electricity is generated.
Wind Turbine Technology
At the heart of wind power lies advanced technology. Wind turbines have evolved significantly. Modern turbines are more efficient than ever, capturing wind at various speeds. They consist of three main parts:
- Blades: Capture the wind’s energy
- Nacelle: Houses the generator and gearbox
- Tower: Elevates the turbine to access better wind speeds
Advantages Of Wind Energy
- Clean and Sustainable: Wind power produces no harmful emissions
- Cost-effective: After installation, operational costs are low
- Abundant: The wind is a plentiful resource worldwide
Disadvantages Of Wind Energy
- Intermittent: Wind is not always predictable or constant
- Space Requirements: Large areas needed for wind farms
- Impact on Wildlife: Potential threat to birds and bats
Hydro Energy
Imagine a world where water not only quenches our thirst but also lights up our homes. Hydro energy, also known as hydropower, harnesses the power of moving water to create electricity. It’s one of the oldest and largest sources of renewable energy in the world.
How Hydro Energy Works
Converting water power to electricity, hydro energy relies on the water cycle. Rain or melted snow, usually from mountains, travels into rivers and lakes. Man-made dams help to direct this water through turbines, which spin generators to produce electricity.
Hydro Turbine Technology
The heart of hydro energy lies in the hydro turbines. They work much like a windmill submerged in water. Their blades turn as water flows over them. The blades are coupled to a generator. The movement transforms into electrical power.
| Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Impulse | Handles high-flow rate | More suitable for small-scale |
| Reaction | High efficiency | Complex construction |
Advantages Of Hydro Energy
- Clean energy: Hydroelectric power is a green energy source.
- Reliable: It generates power steadily, unlike solar or wind.
- Cost-effective: After construction, operating costs are low.
- Flexibility: It adjusts quickly to changing energy demands.
- Storage: Water can be stored and used when needed.
Disadvantages Of Hydro Energy
- Environmental impact: Can alter local ecosystems.
- High upfront costs: Constructing dams and facilities require significant investment.
- Limited reservoirs: Suitable locations are finite.
- Weather dependent: Droughts can limit water availability.

Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy taps into the Earth’s internal heat as a reliable, clean power source. Unlike other renewable resources, geothermal energy offers a continuous flow of power, unaffected by the weather. Below, we explore the inner workings, the various applications, and the pros and cons of this powerful energy source.
How Geothermal Energy Works
Deep beneath the Earth’s crust, heat from the molten core creates hot water and steam. Wells drilled into geothermal reservoirs bring this steam to the surface. We then use it to turn turbines, creating electricity. This process makes use of an endless energy supply, just a drill away.
Geothermal Power Plants
- Flash Steam Plants pull high-pressure hot water into cooler, low-pressure water. The drop in pressure causes the hot water to become steam, turning turbines.
- Binary Cycle Plants transfer heat through a secondary liquid that boils at a lower temperature than water. This system generates electricity without significant emissions.
- Dry Steam Plants use pure steam extracted from geothermal reservoirs to power turbines directly.
Advantages Of Geothermal Energy
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Environmentally Friendly | Minimal carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels. |
| Renewable | A practically inexhaustible source of energy from Earth’s heat. |
| Stable | Provides consistent power, unlike solar or wind energy. |
| Low Operating Costs | After initial setup, generating electricity is low-cost. |
Disadvantages Of Geothermal Energy
- High Initial Cost for establishing infrastructure, including drilling and plant construction.
- Location-specific since not all regions have accessible geothermal resources.
- Environmental Concerns such as the release of greenhouse gases trapped deep under the surface.
- Potential Depletion of local geothermal sources if not managed carefully.
Biomass Energy
Biomass energy is a renewable energy source with a secret power. It comes from organic materials, such as plants, animals, and waste products. This type of energy is unique because it turns natural resources into power and heat.
How Biomass Energy Works
Converting biomass to energy is like magic, but it’s science. Plants grow using sunlight. When burned, they release that solar energy as heat. There are other ways too, like changing waste into gas or liquid fuels. These can create electricity or power engines.
Types Of Biomass Energy
- Wood and wood waste: Used for heating or electricity.
- Agricultural residues: Leftovers from farms converted to energy.
- Biogas: Made from animal manure and other organic wastes.
- Biofuels: Liquids produced from plants for transportation.
- Landfill gas: Harvested from waste decomposing in landfills.
Advantages Of Biomass Energy
Biomass energy is always available and can reduce reliance on fossil fuels. It’s a way to turn waste into something useful. And, it helps with waste management by using up stuff that might otherwise just sit in landfills.
Disadvantages Of Biomass Energy
Even with its benefits, biomass energy is not perfect. It can lead to deforestation if not managed responsibly. There are concerns about air quality as burning materials can release pollutants. And, there’s a space issue; growing biomass crops takes land that could be used for food.
Challenges In Adopting Renewable Energy
While renewable energy sources offer a path to a cleaner environment, their adoption comes with obstacles. These challenges range from economic to technical difficulties. They often slow the transition from fossil fuels to sustainable energy. Let’s explore some of the hurdles facing renewable energy adoption.
High Initial Costs
Renewable energy technologies require significant upfront investment. Solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable installations often come with high price tags. These costs include not only the technology itself but also the installation and integration into existing power grids.
Intermittency
The sun does not always shine, and the wind does not always blow. This intermittency means that renewable energy sources are not always available. Backup systems or energy storage solutions are necessary to ensure a continuous power supply. These solutions are still being developed and can be costly.
Lack Of Infrastructure
Many places lack the needed infrastructure to support renewable energy. This includes everything from transmission lines to electric vehicle charging stations. Building new infrastructure is expensive and time-consuming. Investments and planning must consider future energy needs.
Policy Barriers
Renewable energy policies differ widely across regions. Some have incentives and supportive regulations. Others have barriers that make it hard for renewable energy to compete. It is crucial for lawmakers to understand the long-term benefits of renewable energy. They must craft policies that encourage its growth over time.
Credit: medium.com
Frequently Asked Questions Of Renewable Energy Sources
What Are The 5 Main Renewable Energy Sources?
The five main renewable energy sources are solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass energy. These sources are sustainable and environmentally friendly.
What Are 7 Renewable Energy Sources?
Seven renewable energy sources include solar power, wind energy, hydropower, geothermal energy, biomass, ocean energy, and hydrogen.
What Are The 9 Types Of Renewable Energy Sources?
The nine types of renewable energy sources are solar, wind, hydroelectric, biomass, geothermal, ocean, hydrogen, tidal, and biofuels. Each harnesses natural processes to generate energy sustainably.
What Are The 6 Main Types Of Renewable Energy?
The six main types of renewable energy are solar, wind, hydroelectric, geothermal, biomass, and ocean (tidal and wave) energy. Each harnesses natural processes to generate power sustainably.
Conclusion
Embracing renewable energy sources is no longer a choice but a necessity for a sustainable future. By investing in solar, wind, and hydropower, we chart a path towards cleaner, more efficient energy use. Let’s harness these natural gifts, ensuring a brighter tomorrow for the coming generations.
Our planet deserves no less.




