Ohm’s Law: Mastering Electrical Circuits Made Simple
Ohm’s Law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points. It is represented by the formula V = […]
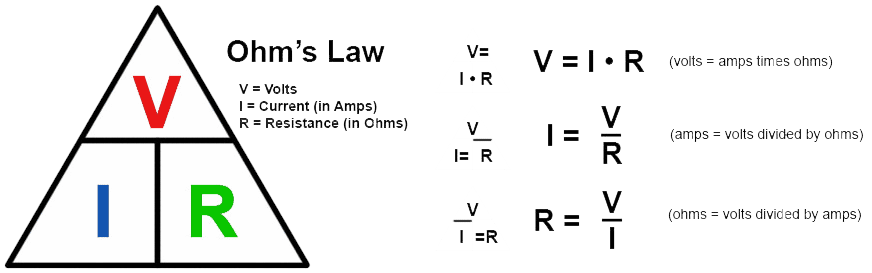
Ohm’s Law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points. It is represented by the formula V = […]
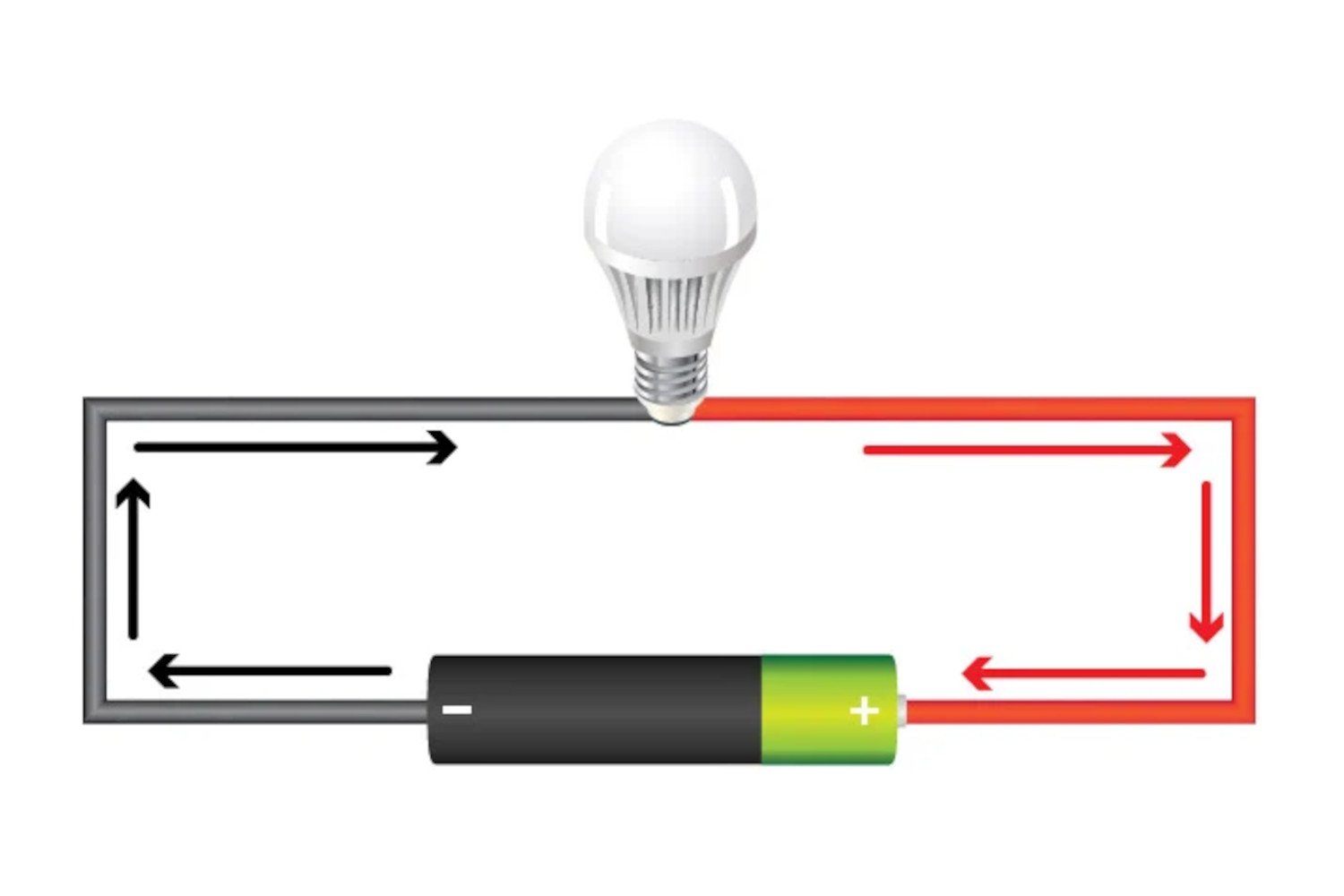
Voltage is the electrical potential difference between two points. It drives the flow of electric current in a circuit. Voltage, often measured in volts, is crucial in electrical systems. […]

Amperes measure the flow of electric current in a circuit. One ampere equals one coulomb of charge passing a point per second. Amperes, commonly abbreviated as “A,” are a fundamental […]
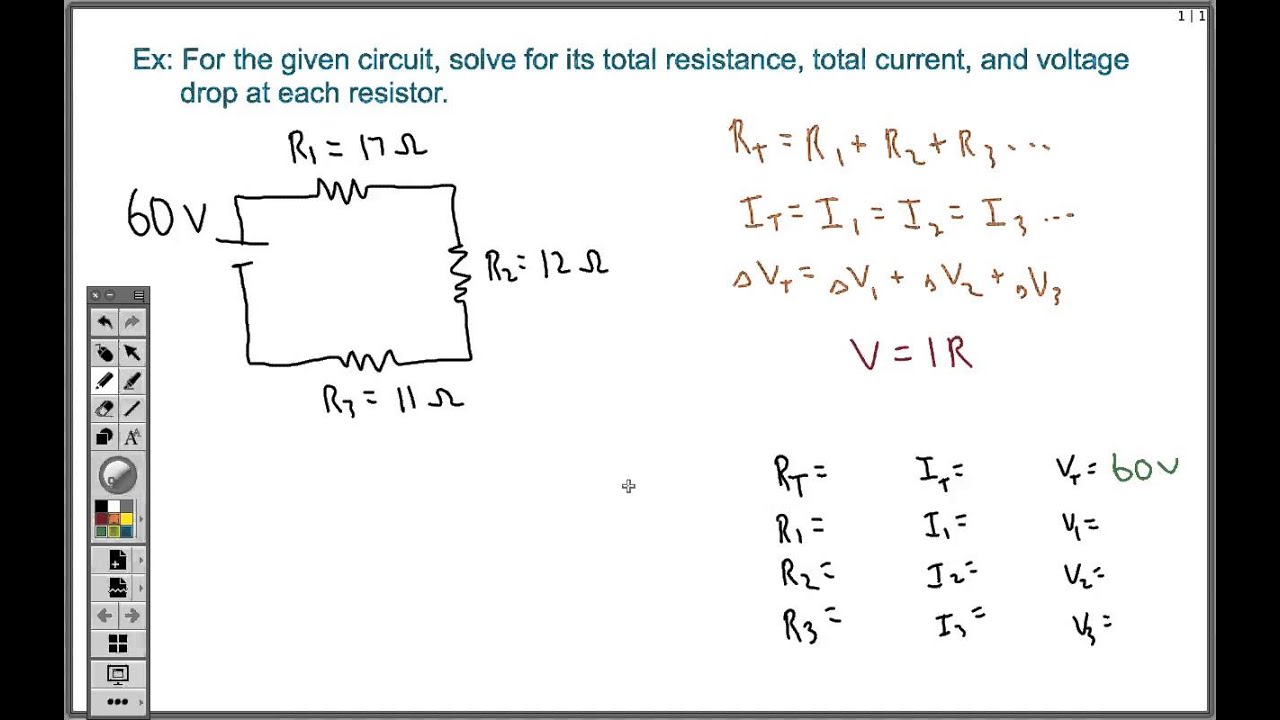
Current in a series circuit is the same through all components. It is calculated using Ohm’s Law: I = V/R. A series circuit is a simple electrical circuit in which […]
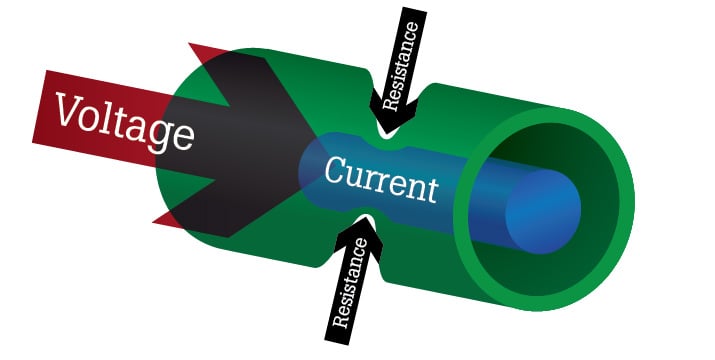
Resistance is the opposition to the flow of electric current. It is measured in ohms (Ω). Resistance plays a crucial role in electrical circuits. It determines how much current flows […]
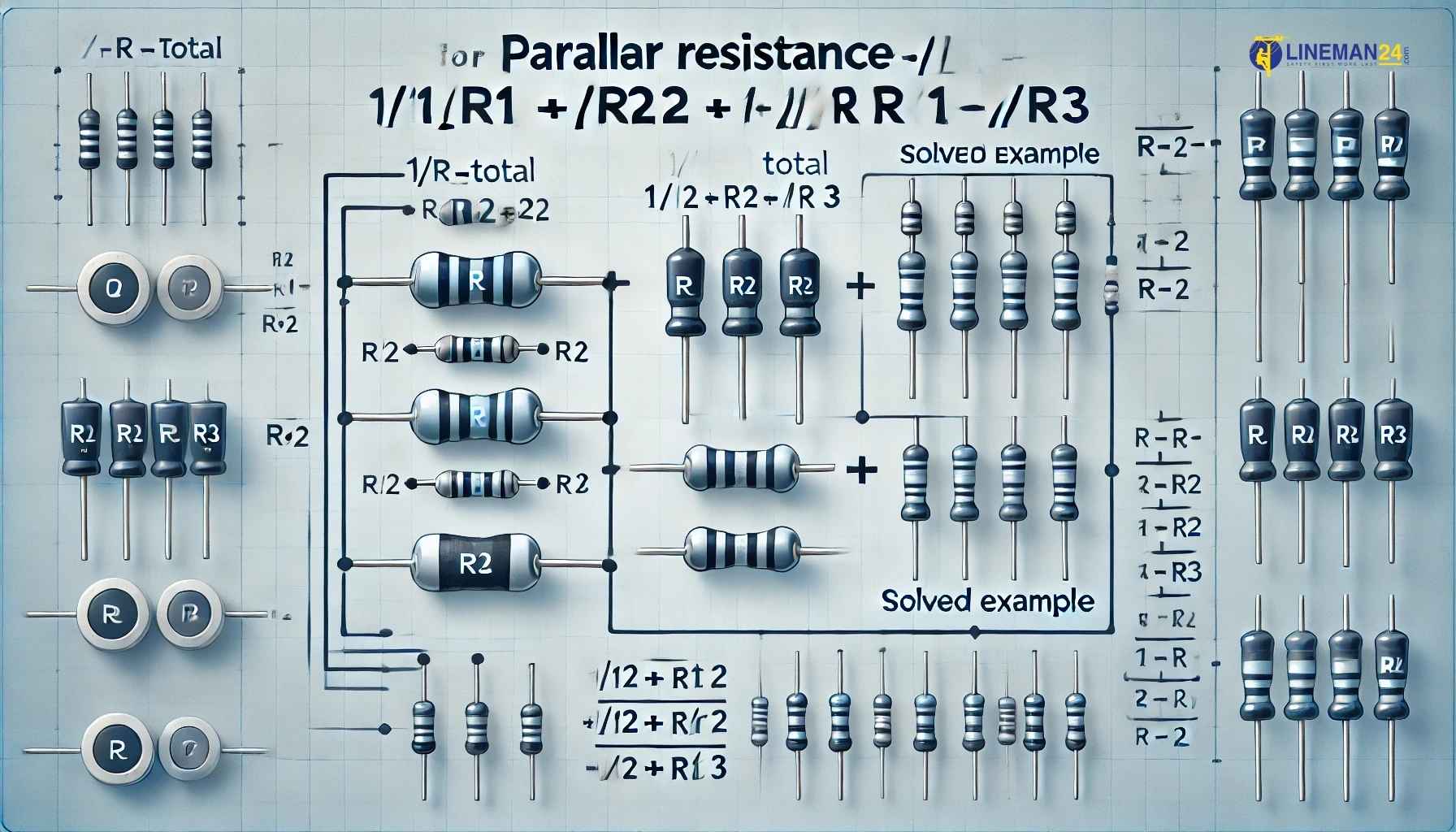
To calculate resistors in parallel, use the formula 1/R_total = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3. This gives the total resistance. Resistors in parallel circuits often find usage in electronic […]
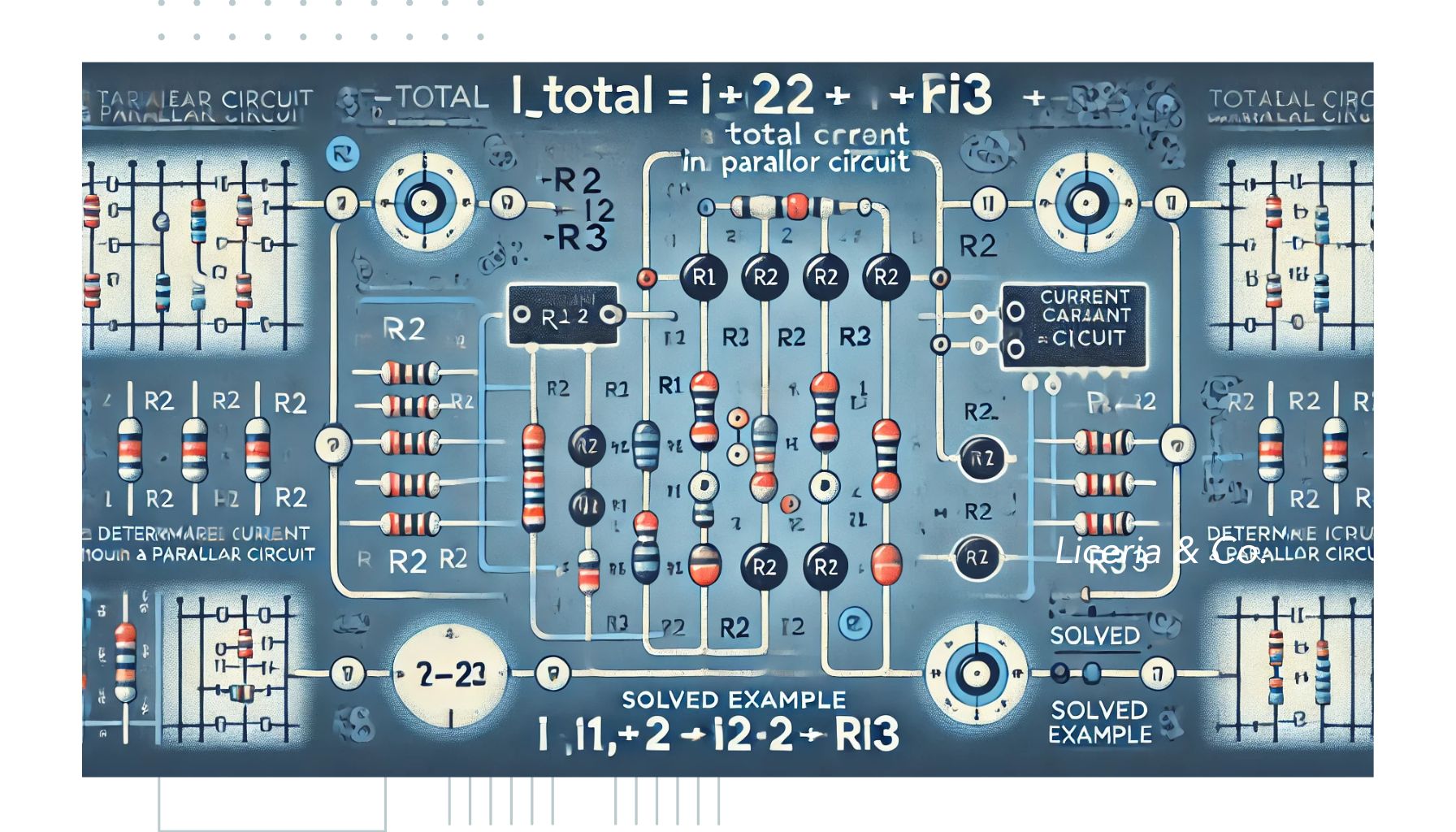
To calculate current in a parallel circuit, use Ohm’s Law for each branch. Sum the currents to find the total. Parallel circuits are common in electrical systems. They allow multiple […]