Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) is a medical treatment for severe mental illness. ECT involves sending electrical impulses into the brain to induce a brief seizure.
ECT is an established, yet often misunderstood, therapy mainly used for major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia when other treatments have failed. It’s a controlled procedure that, while under anesthesia, aims to provide rapid and significant improvements in symptoms.
Medical professionals typically recommend ECT after careful evaluation, especially for patients who do not respond to medication or are at high risk for suicide. With rigorous safety protocols, ECT has evolved significantly since its inception. This treatment is often administered in a series, and patients are carefully monitored throughout the process. Recognizing the potential benefits, many patients and families consider ECT as a viable option after weighing their options for treatment-resistant mental illnesses.
Electroconvulsive Therapy: Shedding Light On The Shadows
In the realm of mental health treatments, few therapies evoke as many myths as Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT). Often shrouded in mystery, ECT might seem like a relic from another era. This piece aims to illuminate the facts and dispel the common misconceptions surrounding this treatment. It’s time to look ECT in the eye and understand it for what it truly is.
The Historical Context: Ect’s Journey
ECT has a long history in mental health care. Once depicted as a harsh procedure, it’s evolved significantly over the decades. Let’s embark on a journey through ECT’s evolution:
- 1930s: ECT emerges as a psychiatric treatment.
- Mid-20th Century: Its use peaks without proper regulations.
- Late 20th Century: Advances improve safety and efficacy.
- Today: ECT stands as a refined procedure for select disorders.
Breaking Down The Basis: What Ect Really Is
Understanding ECT means looking past the stigma. Below is a clear breakdown of the process:
- Patient undergoes a thorough evaluation.
- Meds are given to ensure comfort and safety during treatment.
- Electrical impulses are controlled and precise.
- These impulses cause a brief, therapeutic seizure.
- Sessions typically span a few weeks for full effect.
ECT is not a universal remedy, but for some, it can be life-changing. It treats major depression, bipolar disorder, and more. When medications fail, ECT may step in to provide relief.
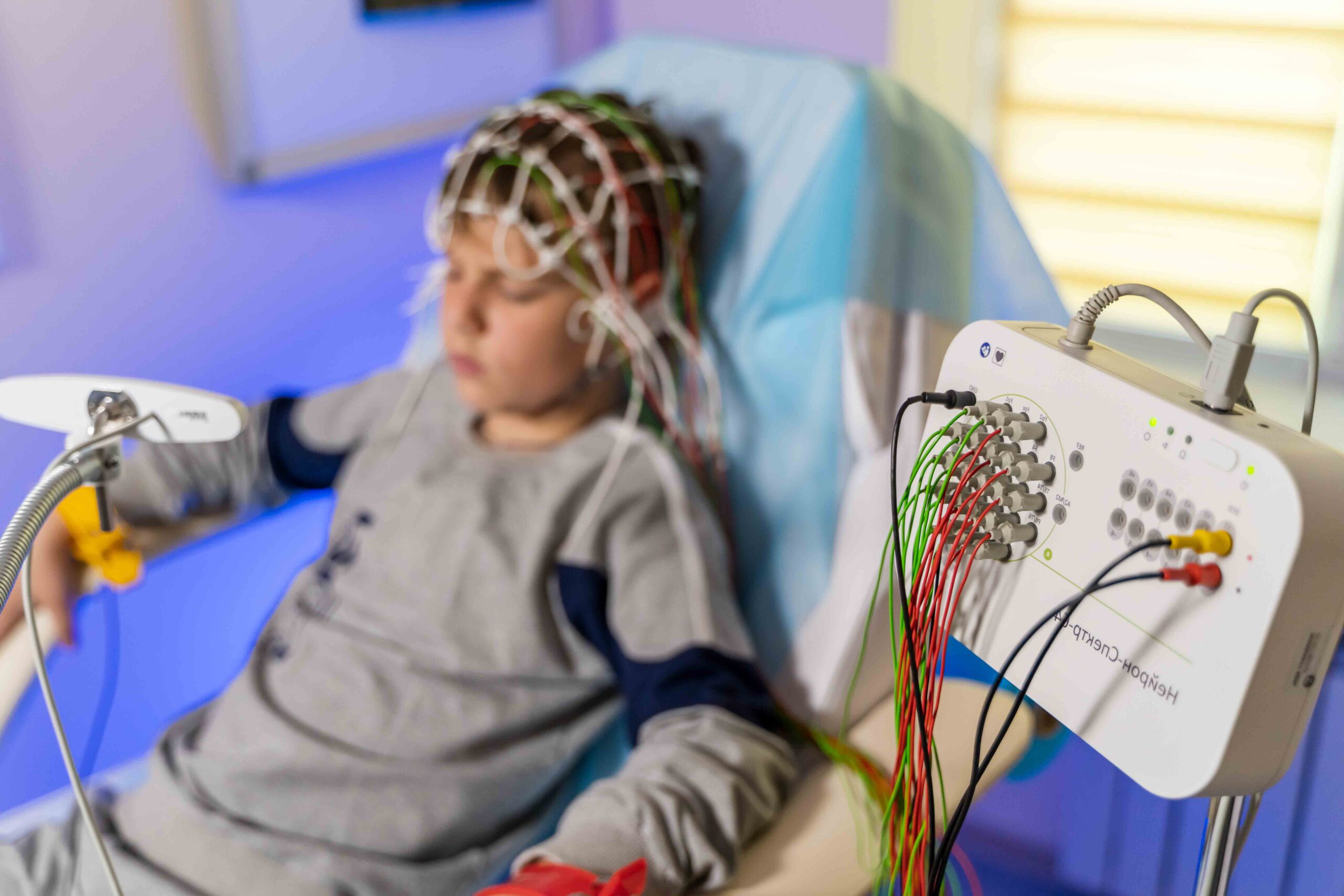
The Principle Of Ect: How It Works
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) is a medical treatment. It’s often used when other treatments don’t work. ECT is for severe mental health conditions. These include major depression, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia.
Electrodes And Electricity: Ect Mechanisms
ECT works by sending electric currents through the brain. This is done to cause a brief seizure. Doctors use electrodes to deliver the electricity. These are small, flat pieces that stick to the head.
- The placement of electrodes can change the ECT’s effects.
- They can go on one or both sides of the head.
- This choice depends on the condition treated.
The Brain’s Response: Neurological Effects Of Ect
When the brain gets this electric current, things change inside. First, chemicals called neurotransmitters increase. These help brain cells talk to each other.
| Before ECT | After ECT |
|---|---|
| Fewer neurotransmitters | More neurotransmitters |
| Brain regions less active | Brain regions are more active |
Brain growth factors also go up after ECT. This means the brain can heal and make new connections. As a result, patients can feel their moods improve and think clearer.
Common Misconceptions Surrounding Ect
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) often comes with a suitcase of misunderstandings. Despite its history and scientific evolution, many distortions about ECT persist. Let’s unpack some of these misconceptions and reveal the truths hidden by myths and media portrayals.
Hollywood vs. Reality: ECT in MediaHollywood Vs. Reality: Ect In Media
The silver screen paints ECT with broad, fear-inducing strokes. Films like “One Flew Over the Cuckoo’s Nest” have skewed public perception, depicting the therapy as barbaric and punitive. In reality, modern ECT is a regulated, humane procedure performed under anesthesia with muscle relaxants to ensure comfort and safety.
Distorted Perceptions: Separating Ect Myths From Facts
- Myth: ECT is a last resort for severe cases. Fact: ECT can be highly effective early on for certain conditions.
- Myth: ECT causes pain and physical trauma. Fact: Patients are asleep and feel no pain during the procedure.
- Myth: Memory loss from ECT is permanent. Fact: Most memory issues are short-term and often reversible post-therapy.

Credit: www.whiteswanfoundation.org
Scientific Verdict: Ect’s Effectiveness
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) stands out in mental health care. It’s a medical treatment that’s been sparking discussions for years. Scientific studies back its success. Many patients see big changes where other treatments have failed. We’re diving into how well ECT works. We especially focus on its effectiveness and various uses.
Efficacy In Severe Depression: Evidence And Outcomes
Severe depression can feel unbeatable. ECT has become a beacon of hope for those struggling. Here’s why:
- High Success Rate: Clinical trials show that ECT results in significant improvement in about 70-90% of cases.
- Fast-acting Relief: Unlike medication, ECT can lift symptoms in just a few weeks.
One study compared ECT to antidepressants. ECT helped more people and worked faster. These findings support ECT as a top choice for severe depression.
Beyond Depression: Other Conditions Treated With Ect
ECT isn’t just for depression. It’s proven effective for various conditions. Take a look at its diverse applications:
| Condition | Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| Bipolar Disorder | Works well in both manic and depressive episodes |
| Schizophrenia | Helpful, especially when paired with medication |
| Catania | Often brings rapid improvement |
Researchers also see ECT’s potential in treating Parkinson’s and neurologic disorders. It brings symptom relief when other treatments don’t work.
Safety And Side Effects: Evaluating Risks Of Ect
The consideration of safety and side effects is paramount when discussing Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT). It’s a treatment involving electrical stimulation of the brain, often resulting in remarkable improvements for those battling severe depression or other mental health conditions. But like any medical procedure, ECT comes with potential risks that warrant a thorough evaluation.
Short-term Side Effects: Acknowledging The Costs
While ECT is generally safe, recognizing the short-term side effects is necessary. Patients commonly experience:
- Confusion: Immediately after treatment, some patients may feel disoriented.
- Memory loss: Many report temporary memory issues, primarily affecting recent events.
- Physical side effects: These can include headaches, muscle aches, nausea, or fatigue.
Patient experiences vary, and symptoms typically subside over time. Monitoring by healthcare professionals ensures these effects are managed effectively.
Long-term Consequences: Assessing The Risks
Analyzing the long-term risks is vital for those considering ECT as a treatment option. Potential risks include:
| Risk | Description |
|---|---|
| Persistent memory loss | Some may experience lasting gaps in memory. |
| Cognitive changes | ECT can cause difficulty in learning or processing new information. |
Long-term side effects are less common and determinable through careful monitoring and follow-up. Dialogue with a healthcare provider is crucial in understanding personal risk factors and making informed decisions.
Patient Testimonials: Personal Ect Experiences
Many people have strong opinions about Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT). Some say it saved their lives; others did not have a positive experience. Let’s explore the real stories of those who have undergone ECT.
Success Stories: When Ect Changes Lives
Miraculous turnarounds can happen with ECT. Real people like Sarah and John share their journeys.
- Sarah: “Depression kept me bedridden. ECT gave me my life back.”
- John: “I was skeptical, but after ECT, I felt like a fog lifted from my mind.”
These are but two of countless life-altering tales. ECT’s electric waves often rebuild what mental distress destroyed.
Challenges And Adversities: When Ect Falls Short
ECT is not a surefire cure for all. Some individuals face hurdles despite the therapy.
| Patient | Challenge |
|---|---|
| Emily | Memory gaps post-ECT |
| Mark | Minimal symptom relief |
Emily and Mark highlight that not all walks through ECT are ones of triumph. Difficulties such as memory loss or insufficient treatment effects show that ECT’s success is not guaranteed.
Advances In Ect Techniques: Modern Practices
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) has evolved significantly from its early days. Today’s medical professionals focus on enhancing the procedure’s safety and effectiveness. These advancements have transformed ECT into a much-refined treatment option. Modern practices combine state-of-the-art technology with personalized care, aiming to deliver the best results while minimizing risks.
Refinements In Procedure: Minimizing Risks
The latest developments in ECT are all about safety. Here’s what’s new:
- Anesthesia advancements make the treatment more comfortable.
- Precision in electrical dosage ensures just the right amount is given.
- Brief pulse technology is gentler on the brain.
- Monitoring brain activity gives real-time feedback for safer outcomes.
These innovations mean that patients experience fewer side effects. Memory issues, once common, are now much rarer. Each step is meticulously planned to keep risks at a minimum.
Tailored Approaches: Personalizing Treatment
Just as in fashion, one size does not fit all in ECT. Customized treatment is crucial:
| Patient’s Profile | Treatment Customization |
|---|---|
| Medical history | Dosage adjusted for individual health needs |
| Previous response to ECT | Treatment frequency tailored to past outcomes |
| Co-existing conditions | Sync with medications and other treatments |
Doctors now can tailor the ECT techniques to suit each individual. They look at a wide array of factors. These include health history and how one responded to past treatments. This approach means better results with fewer sessions. It also means creating a unique treatment course for each patient.
The Decision To Undergo Ect: Considerations
Making the choice to pursue Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) is significant. It often comes as a last resort. Patients and doctors may consider it after other treatments fall short. This part of the journey involves careful thought about benefits and risks.
Weighing The Benefits Against The Risks
ECT has a history of success in treating certain psychiatric conditions. It’s crucial to balance this against potential side effects. Here’s an overview:
- Benefits:
- Quick improvement in severe depression
- Relief when medications don’t work
- Potential lifesaver for risk of suicide
- Risks:
- Memory loss, often short-term
- Confusion right after treatment
- Rare medical complications
Consulting With Experts: When Ect Is An Option
ECT isn’t for everyone. It’s vital to talk with medical professionals. Doctors specializing in mental health can tell when ECT may help.
| Conditions ECT Treats | Consult Necessary |
|---|---|
| Severe depression | Psychiatrist |
| Bipolar disorder | Psychologist |
| Schizophrenia | Neurologist |
Approach the decision with care. The right information and advice matter. A team of health care providers can guide the choice.
Regulatory Perspectives: Ect Protocols And Policies
In the world of mental health treatment, Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) stands as a critical intervention for numerous psychiatric conditions. Yet, it is not without controversy. A comprehensive understanding of the regulatory landscape is vital for patient welfare. Here, we delve into the protocols and policies governing ECT, reflecting on how these regulations shape its safe and ethical application.
Governmental Oversight: Ensuring Patient Safety
Governments worldwide recognize the potential risks and benefits of ECT. As such, they implement stringent oversight to safeguard patients. This protection extends from approving ECT devices, monitoring treatment facilities, and regulating practitioner credentials. Patient safety is the cornerstone of regulatory objectives. Specific focus areas include:
- Informed Consent: Clear communication of ECT’s risks and benefits ensures informed decisions.
- Treatment Protocols: Regulations dictate specific methods and conditions under which ECT is administered.
- Reporting Adverse Events: Facilities must report any complications that serve as a check on the therapy’s safety.
Certifications And Guidelines: Standards Of Practice
Certifications are vital signals of adherence to best practices in ECT administration. They guarantee that clinicians and facilities meet rigorous standards. Guidelines, on the other hand, serve as the roadmap for high-quality care. These guidelines often encompass:
- Training Requirements: Staff involved in ECT delivery must have specialized training.
- Treatment Frequency and Dosage: Guidelines specify limits to prevent overuse and under-treatment.
- Quality Control Measures: Regular audits ensure persistent alignment with evolving standards.
These governance frameworks collaborate in maintaining the integrity and efficacy of ECT treatments while recognizing the complex ethical landscape they occupy.
The Road To Recovery: Life After Ect
Embarking on the road to recovery after completing electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) opens a new chapter filled with hope and wellness. Following ECT—a treatment often used to provide relief from severe mental health conditions like major depression and bipolar disorder—individuals encounter adjustments and transformations as they move forward in their lives. The path to maintaining the positive results of ECT lies in a strong recovery plan.
Follow-up Care: Sustaining Mental Health
Post-ECT follow-up care is vital in nurturing and preserving the benefits gained from the treatment. To ensure a smooth transition, healthcare providers typically propose a customized follow-up care plan tailored to each individual’s needs. This may include:
- Medication Management: Adjusting or maintaining mental health medications to maximize ECT benefits.
- Continuation ECT: Scheduling additional ECT sessions at decreasing frequency to prevent relapse.
- Therapy Sessions: Engaging in psychotherapy or counseling to provide emotional support and coping strategies.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Recommending healthy lifestyle changes such as proper sleep, nutrition, and exercise.
Support Systems: Role Of Family And Therapy
The support from family and therapy emerges as a cornerstone in the journey of healing. Family members often play a significant supportive role by offering encouragement, understanding, and a helping hand through the process. They may also work with mental health professionals to better comprehend the effects of ECT and how to foster a supportive environment at home. Here’s how a support system contributes:
| Support Type | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Emotional Support | Listening, empathizing, and providing a shoulder to lean on. | Aids in emotional stability and reassurance. |
| Practical Support | Help with daily tasks and appointments. | Reduces stress and promotes focus on recovery. |
| Therapeutic Support | Professional counseling and therapy sessions. | Offers strategies for coping and long-term mental health. |
Engaging in regular therapy sessions, be it group therapy, individual counseling or family therapy, also plays an integral part. Therapists can facilitate discussions that address persistent symptoms, provide emotional guidance, and teach coping mechanisms.
Debunking The ‘Brain Damage’ Myth
Many people believe electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) causes brain damage, but this is a myth.
Let’s set the record straight with hard evidence.
Scientific Evidence: Brain Health Post-ect
Research shows that ECT is safe for our brains.
Advanced imaging techniques have given scientists a close look inside the brain after ECT. These scans show no harm to brain structure. In some cases, they even suggest improved brain functioning.
- EEG monitors indicate normal brain activity patterns post-treatment.
- Neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to change and adapt, can increase with ECT.
- Data reveals no loss in memory formation ability, debunking another common myth.
Long-term Studies: No Link To Brain Damage
Long-term studies reinforce the positive consequence of ECT on the brain.
Extensive research over decades has found no evidence supporting the claim of ECT-related brain damage. In fact:
- Many participants report enhanced cognitive abilities after ECT courses.
- Follow-up examinations years later show persistent normal brain function.
- Large-scale analysis reveals that ECT is a brain-healthy option compared to other treatments.
ECT stands strong as a safe and effective treatment, wrongly accused of damaging the brain.
Electroconvulsive Therapy And Informed Consent
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can help certain mental health conditions. It uses electric currents for treatment. A doctor should always explain ECT carefully to patients. This is called informed consent. Patients have the right to understand their treatment options. They must know the risks and benefits. This ensures patients make the best decisions for their health.
Rights And Responsibilities: Understanding The Consent Process
The consent process is a critical step before starting ECT. Here are the key points each patient should know:
- The purpose of the ECT procedure is explained.
- Risks and benefits are discussed in detail.
- Alternatives to the procedure are presented.
- Information on the likely outcomes is given.
- The choice to accept or refuse treatment is up to the patient.
Doctors must make sure patients understand this information fully. Patients should ask questions until they are clear about everything.
Ethical Considerations: Autonomy In Mental Health Treatment
Autonomy is a patient’s freedom to make health choices. It is a key part of mental health care. Here’s why it matters in ECT:
- Patients must have control over their treatment choices.
- Their decisions should be respected and honored.
- This builds trust between the patient and the doctor.
In ECT, respecting autonomy means patients know all about their treatment. They choose what is best for them after understanding all the details.
Age And Ect: Pediatric To Geriatric Use
‘Age and ECT: Pediatric to Geriatric Use’ explores how Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) adapts to meet the needs of different ages. From children facing severe psychiatric conditions to older adults battling chronic depression, the use range exemplifies ECT’s versatility. This section delves into the peculiarities encountered at the extremities of the age spectrum.
Ect In Children: Rare Cases And Outcomes
Children receiving ECT represent a tiny group. ECT treats severe mental health issues. Doctors consider it when other treatments do not work. It can be life-changing.
What can ECT help with? ECT may address major depression, bipolar disorder, or schizophrenia in children. It is not the first choice but can be a pivotal one.
- Safety: It’s generally safe with proper monitoring.
- Effectiveness: Many children see symptom improvement.
- Consideration: A child’s developing brain requires careful assessment before ECT.
Outcomes are mostly positive, recognizing the sensitivity of using such a powerful tool in young individuals.
Geriatric Ect: Elderly Patients And Special Considerations
ECT among the elderly comes with special considerations. The therapy is often well-tolerated and can improve the quality of life significantly for those battling with severe depression, especially when other treatments have failed.
Notable benefits include Rapid symptom relief and cognitive preservation.
- Risk Assessment: Doctors pay extra attention to heart and brain health.
- Medication: Elderly patients may have complex medication regimes to be considered.
- Support: Post-treatment care is crucial for geriatric patients.
Individualized treatment plans ensure that elderly patients receive the full advantages of ECT with as few risks as possible.
Alternative Treatments: Options Beyond Ect
Exploring alternatives to Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) opens new pathways toward mental health treatment. An array of options provides hope and solutions for those seeking different methods. These include pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy, among other integrated approaches. Understanding the range of available treatments empowers patients to make informed decisions best suited to their individual needs.
Pharmacotherapy: Medication Regimens
Pharmacotherapy involves treating psychiatric disorders with medication. Doctors often customize it to fit one’s unique condition. Patients find relief through various prescribed drugs, each with specific functions to address mental health needs.
- Antidepressants – alter brain chemicals that influence mood and stress.
- Antipsychotics – help manage symptoms like delusions or hallucinations.
- Mood stabilizers – used to treat mood swings in conditions like bipolar disorder.
- Anxiolytics – relieve anxiety and reduce tension.
Regular follow-ups ensure medications are working as intended and minimize side effects.
Psychotherapy And Integrated Approaches
Psychotherapy is talk therapy, a powerful tool in mental health treatment. It involves discussions with therapists to unearth underlying issues. Different styles cater to diverse needs:
| Type of Therapy | What It Helps With |
|---|---|
| Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) | Alters negative thought patterns. |
| Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) | Improves emotional regulation. |
| Interpersonal Therapy (IPT) | Enhances communication skills. |
Combining medication with psychotherapy often leads to superior outcomes. Each patient’s journey is distinct and may involve a mix of therapies. Always consult a medical professional before starting any new treatment regimen.
Ect Among Special Populations
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) Among Special Populations delves into the effectiveness and safety of ECT in groups with specific needs. These populations may react differently to treatments common in general cases. Exploring this aspect of ECT reveals insights into the versatility and adaptability of the therapy. Unique considerations ensure all patients receive the best possible care tailored to their circumstances.
Treatment Resistant Conditions
Conditions that do not improve with standard treatments pose a challenge. ECT shows promise as an alternative.
- Depression that resists medication often responds to ECT.
- Schizophrenia with persistent symptoms may benefit from ECT.
- Bipolar disorder patients with rapid cycling find relief in ECT sessions.
Each scenario demands unique ECT protocols considering factors like severity and patient history.
Pregnant Women And Ect: Safety And Efficacy
ECT for pregnant women requires careful consideration. Risks exist, yet ECT remains a safe option for expectant mothers with severe mental health issues when medications pose a greater threat.
| Aspect | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Anesthesia | Types safe for fetal development |
| Monitoring | Fetus heart rate during ECT |
| Frequency | Minimum effective sessions |
Positive outcomes for both mother and child highlight ECT’s suitability when medications are not an option.
The Cost Of Ect: Financial Factors
Understanding the cost of Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) is crucial for patients seeking this treatment. Financial considerations can have a significant impact on accessing ECT. This segment explores the financial aspects, including insurance coverage and out-of-pocket expenses.
Insurance Coverage: Navigating The Financial Aspects Of Ect
Many insurance plans provide some level of coverage for ECT. The extent of coverage varies depending on:
- The type of insurance plan
- Whether the provider is in-network
- The specific medical indications for treatment
To navigate insurance coverage, patients should:
- Review their policy documents carefully.
- Speak with their insurance provider to understand what is covered.
- Confirm with the treatment facility about any additional costs.
Out-of-pocket Costs: When Insurance Falls Short
If insurance does not fully cover ECT, patients might face out-of-pocket costs. These can include:
| Cost Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Deductibles | The amount paid before insurance kicks in |
| Co-payments | Fixed fees for each treatment session |
| Co-insurance | A percentage of the total cost |
| Medication | Costs for any associated prescriptions |
Patients must plan financially for these potential costs. Assistance programs may be available to help cover these expenses. Researching and applying for such programs is advisable.
Ect In Different Cultures And Countries
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) is a medical procedure. It treats severe mental health conditions. Different cultures and countries view ECT in unique ways. This section explores these views and the treatment’s prevalence globally.
Global Perspectives: Acceptance And Prevalence
ECT’s acceptance varies around the world. Some countries embrace it, others use it less. Below are key points on its global use:
- United States: Widely accepted, often used for severe depression.
- Europe: Mixed acceptance, with regulations differing by country.
- India: Increasing use, especially in urban areas.
- Latin America: Less common, but growing in medical communities.
| Region | Prevalence |
|---|---|
| North America | High |
| Europe | Variable |
| Asia | Moderate to High |
| South America | Low to Moderate |
Cultural Stigma: Barriers To Access
Cultural beliefs can create barriers. Stigma often prevents people from seeking ECT. Here’s how different cultures view ECT:
- Middle East: Religious and social beliefs may limit usage.
- Africa: Varying opinions, often influenced by traditional medicine.
- East Asia: Fear of social judgment may deter treatment.
In many places, mental health stigma presents challenges. Knowledge and education can break down these barriers. Efforts to increase understanding and acceptance are crucial.
Training And Education For Ect Practitioners
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) requires precise knowledge and skills. Psychiatrists and medical teams must receive specialized training to deliver this treatment safely and effectively. The education for ECT practitioners is rigorous, reflecting the serious nature of this psychiatric intervention. Let’s explore what it takes to become an ECT expert.
Specialized Training: What It Takes To Administer Ect
Becoming a qualified ECT provider involves a series of critical steps:
- Formal Medical Education: A medical degree with a specialization in psychiatry
- ECT Certification: Specific courses that cover the technical and ethical aspects of ECT
- Hands-on Clinical Training: Supervised practice under an experienced ECT clinician
- Understanding Contradictions: Recognizing conditions where ECT should not be used
- Safety Protocols Mastery: Learning how to minimize risks and manage potential side effects
These essential steps ensure that every ECT treatment meets the highest standards of care.
Continuing Education: Keeping Up With Advances
Medical advancements occur rapidly, and ECT is no exception. Providers must remain informed.
- Annual Conferences: These gatherings showcase the latest research and clinical best practices.
- Journal Subscriptions: Reading current literature keeps providers aware of new findings and techniques.
- Online Courses and Webinars: These platforms offer convenient ways to learn about emerging aspects of ECT.
- Peer Networks: Engaging with fellow professionals allows for the exchange of knowledge and experience.
Active engagement in continuing education keeps ECT practitioners at the forefront of psychiatric care.
The Future Of Ect: Trends And Innovations
As science advances, so does the way we approach mental health treatments. Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) has been a well-known treatment for severe depression and other mental conditions. Looking into the future, ECT is evolving. New technologies promise greater effectiveness and fewer side effects. Here’s a glimpse into the trends and innovations shaping the future of ECT.
Next-generation Techniques: Ultrasound And Magnetic Seizure Therapy
Recent advancements aim to make ECT safer and more comfortable. Two groundbreaking techniques are leading the charge: ultrasound and magnetic seizure therapy (MST). These methods target very specific brain areas. This precision reduces overall side effects.
- Ultrasound is non-invasive. It uses sound waves to stimulate the brain.
- MST uses magnetic fields to produce seizures. These are much like traditional ECT but more focused.
Both these advanced technologies could revolutionize how patients received treatment, making ECT an option for even more people.
Research Frontiers: New Insights Into Ect
In the realm of research, fresh insights into ECT are unfolding. Scientists are exploring how ECT works in the brain. This research helps to refine the therapy.
| Research Area | Insight | Impact on ECT |
|---|---|---|
| Neural pathways | Understanding which neural pathways ECT affects. | Enhances precision in treatment, and minimizes side effects. |
| Genetic factors | Identifying which genetic factors respond best to ECT. | Customizes therapy to individual patient needs. |
| Biological markers | It is finding biological signs that predict ECT response. | Improves patient selection for better outcomes. |
Every discovery offers hope. These insights could lead to highly personalized and effective treatment plans. Research propels ECT towards a future where it is not only effective but also suits each patient’s condition perfectly.
Making An Informed Choice: Navigating Ect Decisions
Electroconvulsive therapy, or ECT, often comes into the picture during challenging times. It’s essential for mental health recovery. Understanding ECT fully is key before deciding to proceed.
Knowing The Right Questions To Ask
Embarking on the ECT journey demands clarity. Well-informed questions lead to confident choices.
- What is ECT? An overview of how it works.
- Why ECT? Reasons for this treatment recommendation.
- What are the benefits? Positive outcomes and success rates.
- Are there risks? Potential side effects and how to manage them.
- How is ECT performed? The procedure steps are explained simply.
- What to expect after ECT? Post-treatment care and lifestyle considerations.
Embracing Ect: When All Roads Lead Here
Sometimes, ECT is the clearest path to wellness. It’s a decision that comes after trying other treatments.
| Treatment | Response |
|---|---|
| Medication | Not effective or tolerable |
| Therapy | Limited improvement |
| ECT | Potentially life-changing |
For some, ECT is a beacon of hope. Open conversations with healthcare providers are crucial. Together, you’ll ensure this choice is the right step toward healing.

Credit: www.auroraarizona.com
Frequently Asked Questions For Ect? Electroconvulsive Therapy
What Is Electroconvulsive Therapy (ect)?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a medical treatment involving electrically induced seizures to treat severe mental illnesses.
How Does Ect Work For Depression?
ECT works by altering brain chemistry to quickly relieve symptoms of severe depression, often when other treatments have failed.
Is Ect A Safe Procedure?
ECT is considered safe when performed by a qualified medical team, with risks similar to those from general anesthesia.
Can Ect Improve Bipolar Disorder?
Yes, ECT can provide rapid relief from severe episodes of both mania and depression in bipolar disorder.
What Are The Side Effects Of Ect?
Common side effects include temporary memory loss, confusion, and physical side effects similar to those from minor surgery.
How Long Does An Ect Session Last?
An ECT session typically lasts around 5-10 minutes, with additional time for preparation and recovery.
How Many Ect Treatments Will I Need?
The number of ECT treatments varies but generally ranges from 6-12 sessions, depending on the individual’s response.
Does Insurance Cover Ect Treatments?
Many insurance plans cover ECT treatments, but coverage can vary, so it’s important to check with your provider.
Can Ect Be Used For Anxiety Disorders?
ECT is occasionally used for severe, treatment-resistant anxiety disorders, but it is not a frontline treatment.
Is Hospitalization Required For Ect?
Hospitalization may not be required, as ECT can be done on an outpatient basis, depending on the case’s severity and health status.
Conclusion
Ect? Electroconvulsive therapy, often referred to as ECT, has proven its value as an effective medical treatment. With a track record of helping countless patients, its benefits can’t be ignored. Always consult a healthcare professional before making any decision. Remember, ECT could be a beacon of hope on your journey to wellness.




