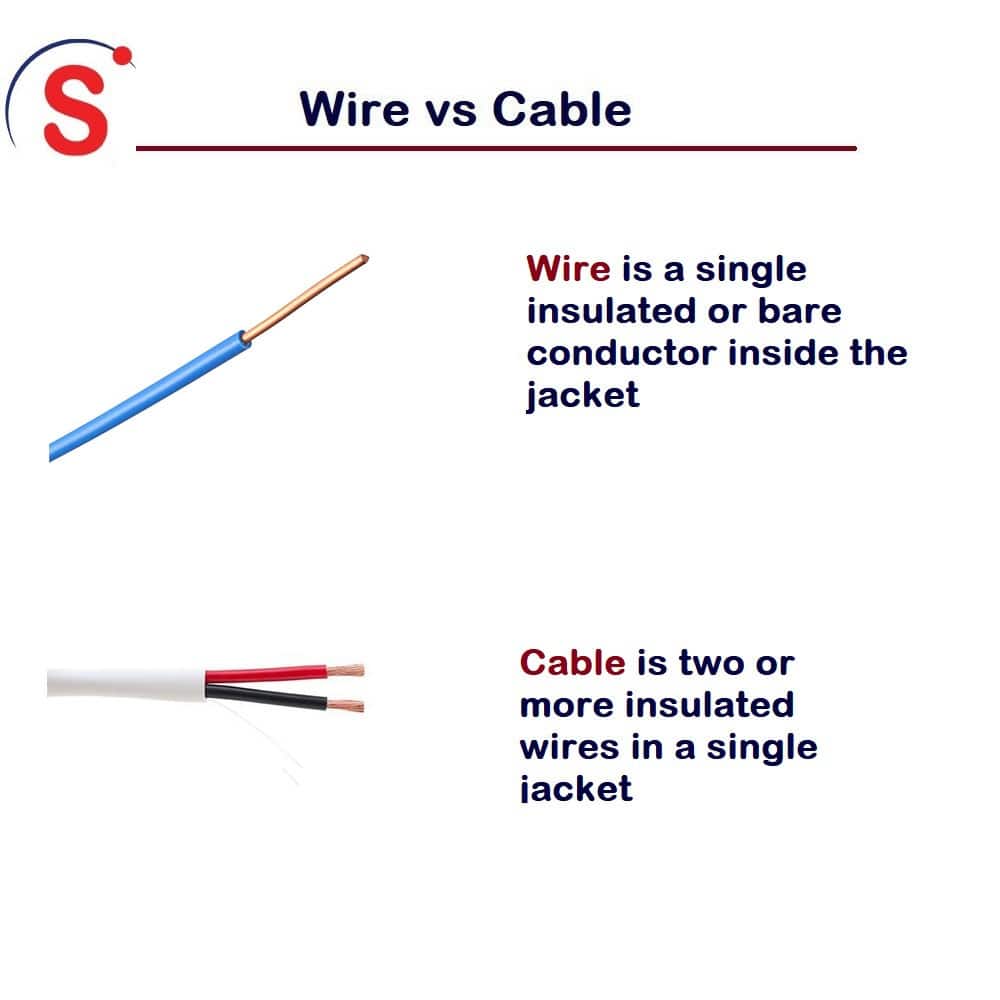
Cable consists of multiple wires, while wire is a single strand of conductive material. Both have distinct uses and properties.
Cables and wires are fundamental components in electrical and electronic systems. A wire is a single conductor, usually made of copper or aluminum, used for transmitting electricity or signals. Cables, on the other hand, consist of multiple wires bundled together, often insulated, to protect and organize them.
Wires are typically used for simpler, straightforward connections, while cables are suitable for more complex applications requiring multiple connections. Understanding the differences between cables and wires can help in selecting the right component for specific electrical tasks. This knowledge ensures safety, efficiency, and optimal performance in various electrical projects.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Differences In Composition
Understanding the differences in composition between cables and wires is vital. These differences affect their performance, applications, and durability. In this section, we will explore the key differences in the composition of cables and wires.
Material Composition
Wires are made from a single metal conductor, typically copper or aluminum. They offer excellent electrical conductivity. Copper wires are more common due to their superior conductivity and flexibility. Aluminum wires are lighter and used in specific applications.
Cables consist of multiple wires bundled together. These wires can be made from copper, aluminum, or a combination of both. The bundled wires are often twisted or braided. This design provides higher strength and better conductivity.
Insulation Differences
Wires usually have a single layer of insulation. The insulation material can be plastic, rubber, or other polymers. This layer protects against electrical shocks and environmental damage.
Cables have multiple layers of insulation. These layers include an inner insulating layer, a shielding layer, and an outer protective layer. The inner layer covers each wire, while the shielding layer protects against electromagnetic interference. The outer layer provides additional protection from physical damage and environmental factors.
| Feature | Wires | Cables |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Copper or Aluminum | Multiple Wires (Copper/Aluminum) |
| Insulation | Single Layer | Multiple Layers |
The differences in composition between cables and wires highlight their distinct uses. These differences can help you choose the right type for your specific needs.
Conductivity And Resistance
When discussing cables and wires, conductivity and resistance are crucial. Conductivity refers to how well a material can carry an electric current. Resistance measures how much a material opposes the current. Both factors are vital in deciding between cables and wires for various applications.
Conductivity Of Cable
Cables are often designed to carry more current. They have multiple strands of conductors. This increases their surface area. Higher surface area means better conductivity. More current can flow with less resistance.
Consider a power cable used for heavy machinery. It needs to carry a large current. The cable’s multiple strands help achieve this. Copper and aluminum are common materials for high conductivity in cables.
Here’s a simple comparison of materials:
| Material | Conductivity |
|---|---|
| Copper | High |
| Aluminum | Moderate |
Resistance Of Wire
Wires are usually single strands. This makes them simpler and cheaper. However, a single strand means higher resistance. Higher resistance means less current can flow. Wires are better for low-power applications.
For example, a wire used in a light bulb circuit does not need to carry a lot of current. Copper wires are common because they offer good conductivity with manageable resistance.
Factors affecting wire resistance include:
- Material: Copper or aluminum
- Length: Longer wires have more resistance
- Diameter: Thicker wires have less resistance
Application And Usage
Cables and wires are essential in modern life. They serve distinct purposes based on their design and construction. Understanding their applications helps in selecting the right one for specific needs. Below are the key applications in both industrial and domestic settings.
Industrial Applications
In industrial settings, cables and wires play critical roles. Heavy-duty cables are often used for power transmission. They handle high voltage and ensure safe electricity flow. Wires, on the other hand, are used for short-distance connections. They are integral in machinery and equipment.
Control cables are used in automation systems. They transmit signals to control machines. Instrumentation cables are essential in monitoring systems. They carry low-voltage signals for accurate readings.
| Application | Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Power Transmission | Heavy-duty Cables | High voltage electricity |
| Machinery Connections | Wires | Short-distance electricity flow |
| Automation Systems | Control Cables | Signal transmission |
| Monitoring Systems | Instrumentation Cables | Low-voltage signal transmission |
Domestic Usage
In homes, cables and wires are everywhere. Electrical cables connect homes to the power grid. These cables ensure consistent electricity for daily activities. Wires are used inside walls and ceilings. They distribute electricity to lights, outlets, and appliances.
Coaxial cables are common for TV connections. They provide clear signal transmission. Ethernet cables are necessary for internet connectivity. They connect computers, routers, and other devices. The use of speaker wires enhances home entertainment systems. They ensure quality sound for music and movies.
- Electrical Cables: Connect homes to power grid
- Wires: Distribute electricity inside walls
- Coaxial Cables: TV connections
- Ethernet Cables: Internet connectivity
- Speaker Wires: Home entertainment systems
Flexibility And Durability
Flexibility and durability are crucial factors in choosing between cables and wires. Each has its own unique properties. Knowing these can help you make the best choice for your needs.
Flexibility Of Wire
Wires are often more flexible than cables. This is because wires consist of a single strand or a group of strands. This makes them easier to bend and shape.
When you need a material that can bend into tight spaces, wires are a good option. Wires are great for internal electronics and small appliances.
Durability Of Cable
Cables are known for their durability. They are made of multiple wires bundled together. This provides extra strength and protection.
Cables are ideal for outdoor use and heavy-duty applications. They can withstand more wear and tear compared to single wires.
| Feature | Wires | Cables |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High | Moderate |
| Durability | Moderate | High |
| Best Use | Indoor, small appliances | Outdoor, heavy-duty |
Cost And Installation
When considering cable vs wire, the cost and installation aspects are crucial. This section delves into the financial implications and installation challenges of both options.
Cost Comparison
The cost of cables and wires varies significantly. Cables tend to be more expensive than wires due to their complex structure and extra features. Wires are simpler and cheaper, making them a cost-effective choice for basic installations.
| Type | Approximate Cost per Meter |
|---|---|
| Single Wire | $0.10 – $0.50 |
| Multi-core Cable | $0.50 – $2.00 |
Choosing between cables and wires depends on the project requirements. If the budget is tight, wires might be the better option. For more advanced needs, cables offer greater reliability and features.
Installation Challenges
Installing cables and wires poses different challenges. Cables are bulkier and require more space for routing. They may need specialized connectors and tools for proper installation.
- Space Requirements: Cables need more room due to their size.
- Tools: Special tools may be required for connecting cables.
On the other hand, wires are easier to install. Their simple structure means fewer complications during installation. But, wires may need additional insulation for safety.
- Ease of Installation: Wires are simpler and faster to install.
- Safety Concerns: Additional insulation might be necessary for wires.
In summary, while cables are costlier and harder to install, they offer more features. Wires are cheaper and simpler but may require extra safety measures.
Credit: satmaximum.com

Credit: www.jiukaigroup.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Difference Between A Wire And Cable?
A wire is a single conductor, while a cable is a group of insulated wires bundled together. Wires are ideal for simple connections. Cables are used for complex setups. Both transmit electrical signals but serve different purposes.
What Is The Difference Between Copper Wire And Cable?
Copper wire is a single electrical conductor. Cable consists of multiple wires grouped together. Copper wire suits simple circuits. Cable handles complex setups and higher power needs.
Why Is A Cable Called A Cable?
A cable is called a cable because it originates from the Latin word “capulum,” meaning a rope or tie. It historically referred to thick ropes used on ships. Over time, it evolved to describe insulated wires used for transmitting electricity or signals.
What Are The Three Types Of Cable?
The three types of cable are coaxial, twisted pair, and fiber optic. Coaxial is used for TV signals. Twisted pair is common in telephone networks and LANs. Fiber optic offers high-speed data transmission over long distances.
Conclusion
Choosing between cable and wire depends on your specific needs and applications. Both offer unique advantages. Cables are ideal for complex setups requiring durability. Wires are suitable for simpler, flexible installations. Evaluate your project requirements carefully to make an informed decision.
Both options can meet your electrical needs effectively.




