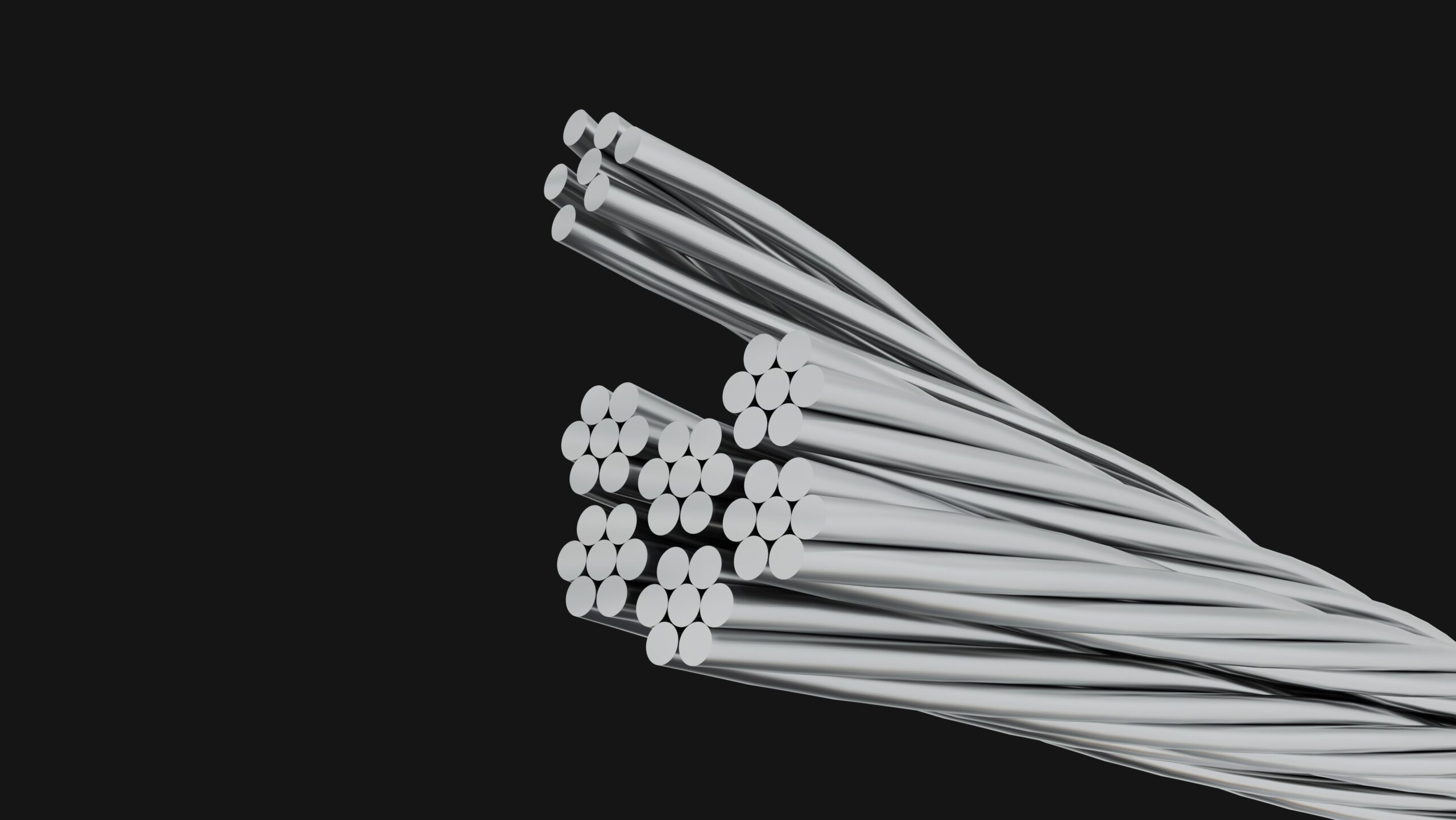
Wires consist of a single conductor, while cables have multiple conductors wrapped together. Cables are typically insulated for safety.
Wires and cables are essential components in electrical systems, but they serve different purposes. Wires are single conductors, often made of copper or aluminum. They are usually used for connecting electrical devices. Cables, on the other hand, contain multiple conductors bundled together and are generally insulated to prevent electrical hazards.
This insulation makes cables safer and more suitable for complex installations. Understanding the differences between wires and cables can help in selecting the right components for electrical projects. Both play critical roles in ensuring efficient and safe transmission of electricity in various applications.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Composition
The composition of wires and cables differs in several ways. Knowing these differences is crucial for choosing the right one for your needs. Below, we explore the unique elements that make up wires and cables.
Wires Composition
Wires are simple in structure. They consist of a single conductor. This conductor is usually made of copper or aluminum. Copper is popular due to its high conductivity. Aluminum is used for its lightweight properties.
Wires can be insulated or bare. Insulated wires have a protective coating. This coating can be made of plastic, rubber, or other materials. Bare wires lack this protective layer.
Here is a brief overview of wire components:
- Conductor: Typically copper or aluminum
- Insulation: Plastic, rubber, or other materials (in insulated wires)
Cables Composition
Cables are more complex. They consist of multiple wires bundled together. These wires are known as conductors. Each conductor in a cable is insulated.
Cables also have additional layers. These layers include shielding and jackets. Shielding protects against electromagnetic interference. Jackets provide an outer protective layer.
Below is a table highlighting the components of cables:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Conductors | Multiple insulated wires bundled together |
| Insulation | Protective layer for each conductor |
| Shielding | Guards against electromagnetic interference |
| Jacket | Outer protective layer |
Cables are versatile. They are used for power transmission, data transfer, and telecommunications. The additional layers make cables more durable and reliable than single wires.
Functionality
Understanding the functionality of wires and cables is crucial. Wires and cables serve different purposes. Each has unique features that cater to specific needs. Let’s explore these functions in detail.
Wires Function
Wires are single conductors. They are often made of copper or aluminum. Their primary job is to carry electrical current. Wires can be bare or insulated.
Here are some key functions of wires:
- Electrical transmission: Wires carry electricity from one point to another.
- Signal transmission: Wires can transmit signals in communication systems.
- Grounding: Wires are used to ground electrical systems, ensuring safety.
Cables Function
Cables consist of multiple wires bundled together. They are designed for more complex tasks. Cables can also be insulated for added protection.
Key functions of cables include:
- Power distribution: Cables distribute electrical power over longer distances.
- Data transmission: Cables are used in networking to transmit data efficiently.
- Enhanced safety: Cables have insulation and shielding to prevent interference and damage.
| Criteria | Wires | Cables |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Single conductor | Multiple bundled wires |
| Primary Use | Electric current transmission | Power and data distribution |
| Insulation | Sometimes | Always |
Types
Understanding the different types of wires and cables is essential for any electrical project. Each type has specific uses and characteristics. This section covers the main types of wires and cables used in various applications.
Types Of Wires
Wires are essential for conducting electricity. They come in various forms, each suited to different tasks. Here are the main types:
- Solid Wire: Made of a single piece of metal. It’s durable and used in fixed positions.
- Stranded Wire: Consists of many thin strands twisted together. It’s flexible and ideal for moving parts.
- Tinned Wire: Coated with tin to resist corrosion. Commonly used in marine applications.
- High-Temperature Wire: Designed to withstand high heat. Used in ovens and engines.
Types Of Cables
Cables consist of multiple wires bundled together. They serve different purposes and come in various designs. Let’s explore the main types:
| Type of Cable | Description |
|---|---|
| Coaxial Cable | Used for TV and internet connections. It has a central conductor, insulating layer, and metal shield. |
| Twisted Pair Cable | Contains pairs of wires twisted together. Common in telephone and network connections. |
| Fiber Optic Cable | Uses light to transmit data. Ideal for high-speed internet and long distances. |
| Shielded Cable | Has a protective shield to reduce interference. Used in sensitive electronic equipment. |

Credit: m.youtube.com
Applications
Understanding the applications of wires and cables is crucial. Each type has unique uses in various industries. This section will discuss where wires and cables are commonly used.
Wires Applications
Wires are essential in many electrical and electronic systems. They are used for:
- Household Wiring: Wires connect electrical appliances and outlets. They ensure smooth power distribution.
- Telecommunications: Wires help in transmitting signals over short distances.
- Automobiles: Wires connect various components in cars. They ensure proper functioning of lights, horns, and other systems.
- Electronics: Wires are used in circuit boards. They connect different components like resistors and capacitors.
Cables Applications
Cables are used in more complex and heavy-duty applications compared to wires:
- Power Transmission: Cables carry electricity over long distances. They connect power plants to homes and businesses.
- Data Transmission: Cables like fiber optics transmit data at high speeds. They are used in internet and telephone networks.
- Industrial Machinery: Heavy-duty cables power large machines. They are vital in manufacturing plants and factories.
- Marine and Aerospace: Specialized cables withstand harsh conditions. They are used in ships, submarines, and aircraft.
Both wires and cables are indispensable in modern life. Their specific applications ensure efficient and safe electrical and data transmissions.
Installation
When it comes to wiring and cabling in any electrical setup, the installation process is crucial. Proper installation ensures safety, efficiency, and longevity. Let’s explore the differences between wires installation and cables installation.
Wires Installation
Wires are single conductors, usually made of copper or aluminum. They come in various sizes and types. The installation of wires involves several steps:
- Planning the layout: Determine the route for the wires.
- Measuring lengths: Cut the wire to the required length.
- Stripping insulation: Remove the insulation from the ends.
- Connecting: Use connectors or terminals to join wires.
- Securing: Fasten the wires using clips or conduits.
Properly installed wires are essential for safe electrical systems. Incorrect installation can lead to short circuits or fires.
Cables Installation
Cables consist of multiple conductors bundled together. They provide a more organized solution for complex electrical systems. The installation process for cables includes:
- Planning the route: Identify the best path for the cable.
- Measuring: Measure the required length and cut the cable.
- Stripping the outer sheath: Carefully remove the outer covering.
- Exposing inner wires: Strip the individual wires inside the cable.
- Termination: Use proper connectors to terminate the cable ends.
- Securing: Secure the cable using cable ties, clamps, or conduits.
Cables offer better protection and organization. They are ideal for complex installations where multiple conductors are needed.
The table below highlights the key differences:
| Aspect | Wires | Cables |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Single conductor | Multiple conductors |
| Flexibility | More flexible | Less flexible |
| Protection | Less protected | More protected |
| Installation complexity | Simple | Complex |
Understanding the differences between wires and cables can help in choosing the right option for your electrical projects.
Factors To Consider
Understanding the difference between wires and cables helps in making informed choices. Each has unique properties and uses. Knowing these factors can save time, money, and ensure safety.
Considerations For Wires
Wires are single conductors, usually made of copper or aluminum. Here are some key points to consider:
- Material: Copper is more conductive, while aluminum is lighter and cheaper.
- Gauge: The thickness of the wire affects its capacity. Thicker wires handle more current.
- Insulation: The type of insulation impacts durability and safety. Common insulations include PVC and Teflon.
- Flexibility: Stranded wires are more flexible than solid wires.
Considerations For Cables
Cables consist of multiple wires bundled together. Here are some key points to consider:
- Type: There are various types like coaxial, twisted pair, and fiber optic. Each serves different purposes.
- Shielding: Shielded cables reduce electromagnetic interference. Unshielded cables are less expensive.
- Length: Longer cables can suffer from signal loss. Choose the right length for your needs.
- Jacket Material: The outer layer protects the wires inside. Common materials include PVC and rubber.

Frequently Asked Questions
How Do You Identify Wires And Cables?
Identify wires and cables by checking color codes, labels, and markings. Use a multimeter to test connections and continuity.
What Is Wire And Cable Used For?
Wire and cable transmit electrical power, signals, and data. They connect devices, provide lighting, and ensure communication. Widely used in homes, industries, and telecommunications.
What Are The Three Types Of Wires?
The three types of wires are live (hot), neutral, and ground. Live wires carry current, neutral wires complete circuits, and ground wires prevent electric shock.
What Are The 4 Wires In A Cable?
The four wires in a cable are typically: live (hot), neutral, ground, and a second live (for 240V circuits).
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between wires and cables is crucial. Wires are single conductors, while cables are multiple conductors. This knowledge helps in making informed electrical decisions. Always choose the right type for safety and efficiency. Stay informed to ensure your electrical projects are both safe and effective.